Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: SpA Including PsA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Diagnostic delay (DD) in spondyloarthritis (SpA) is well documented, but most of the available data are reported in patients with axial SpA (axSpA). In this ancillary analysis from the international ASAS-PerSpA study, we aimed to estimate the DD across all SpA entities, considering the inaugural disease manifestation, and evaluate the factors associated with DD.
Methods: This is an ancillary analysis of the ASAS-PerSpA study, based on 4,339 patients diagnosed by their rheumatologists with any SpA entity (axSpA, peripheral SpA (pSpA), inflammatory bowel diseases associated SpA (IBD-SpA), reactive arthritis (ReA), Juvenile SpA (Juv) also including psoriatic arthritis (PsA). The first disease manifestation was identified across SpA entities and classified as axial, peripheral (arthritis, enthesitis, or dactylitis), and extra-musculoskeletal (EMM). In addition, the time lag between EMM and musculoskeletal manifestation (MM) was calculated. The DD was estimated using two definitions (definition 1, including the EMM as an accepted inaugural manifestation, and definition 2, considering the first MM as the onset of the rheumatic disease). DD was compared across disease entities using the Kruskal-Wallis test. Factors associated with DD, using definition 2, were evaluated using 4 multivariable linear regression models (axSpA, PsA, pSpA, and IBD-SpA, respectively).
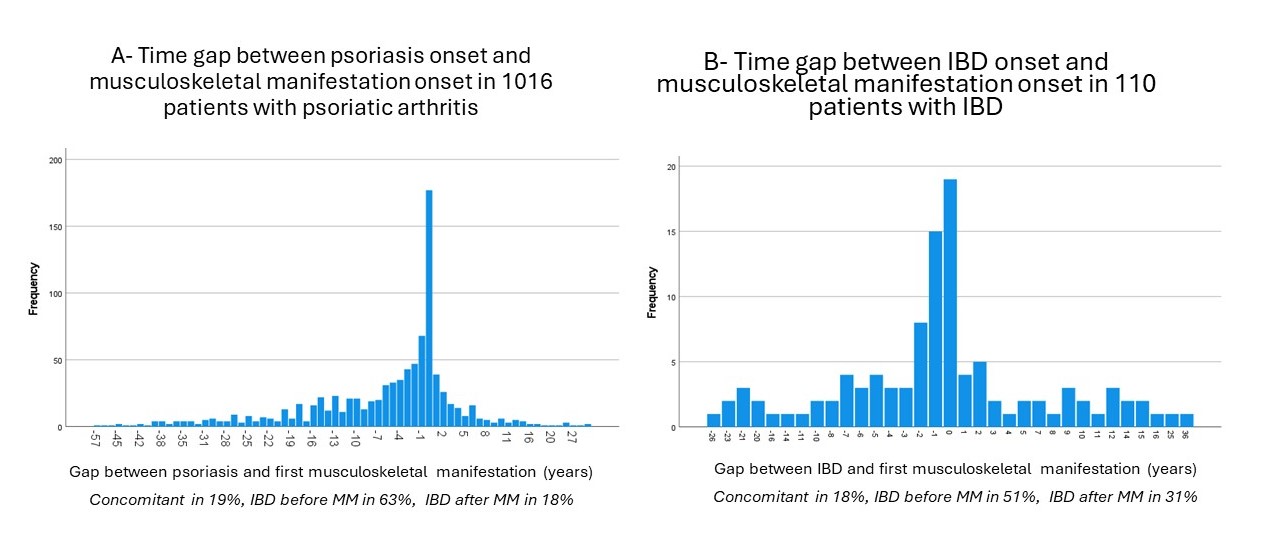
Results: The analysis included 2622 patients with axSpA, 1016 with PsA, 424 with pSpA, 110 with IBD-SpA, and 167 others, mean age 44.4 years (±13.9), 60.9% females. The first disease manifestation was the axial MM in axSpA (83%), peripheral MM in pSpA (63%) and others (70%), EMM in PsA (psoriasis 72% followed by peripheral MM 31%) and IBD-SpA (IBD 63%, followed by axial MM 32%). The average time lag between psoriasis and PsA was -6.0 years (± 11.2), and IBD and IBD-SpA -0.8 years (± 9.4)) (Figure 1).
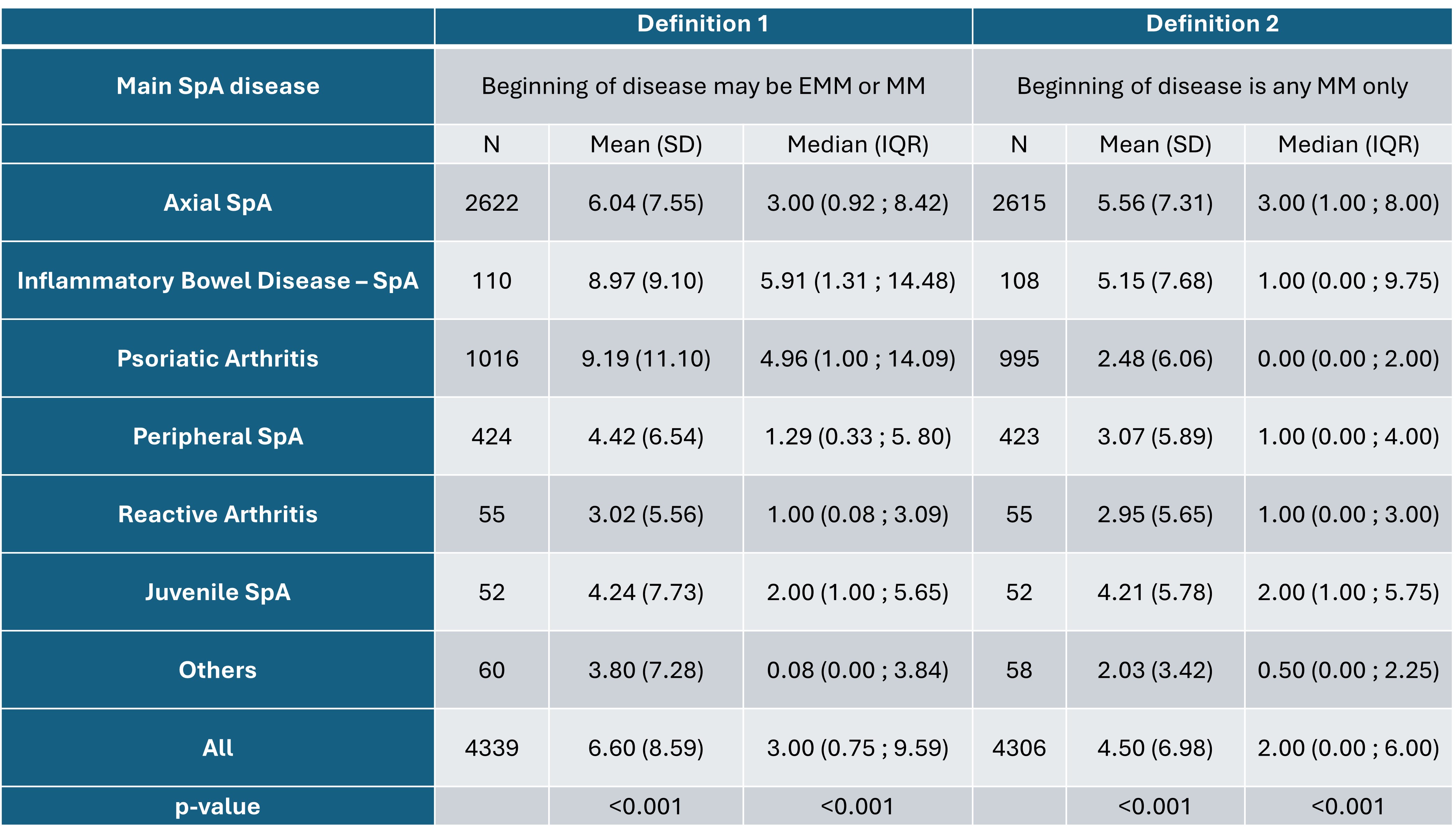
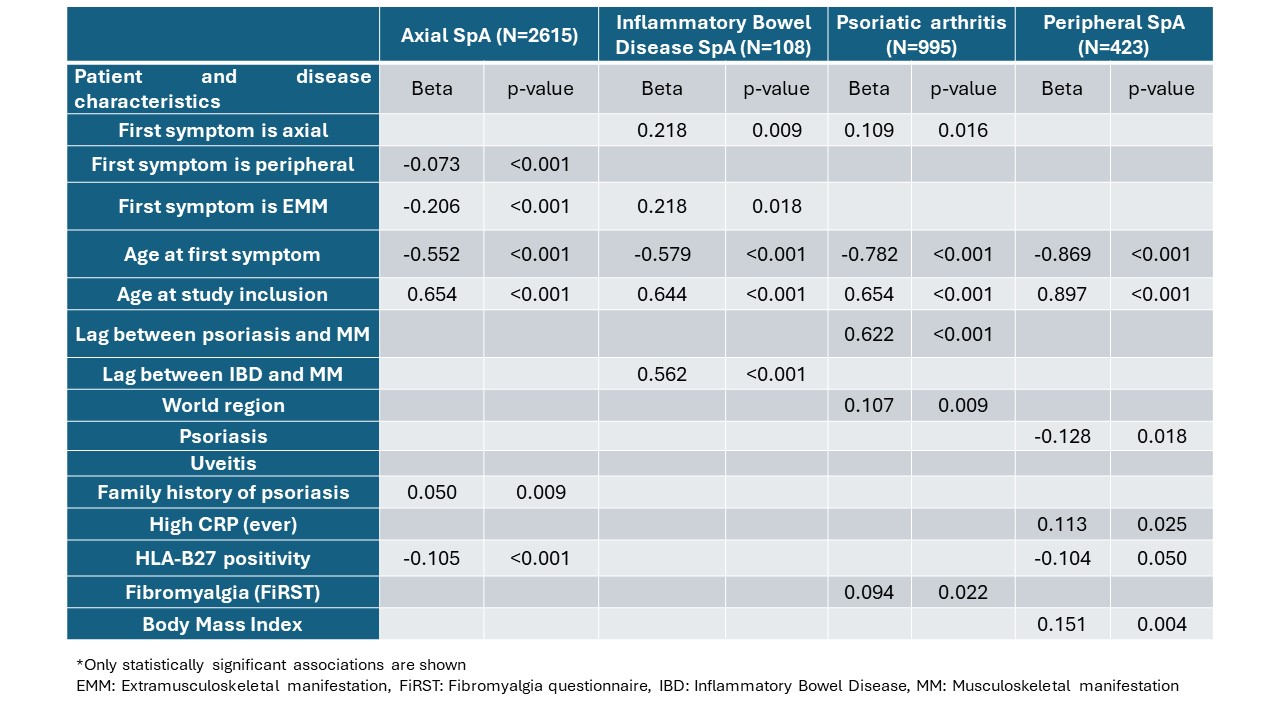
The mean global DD was longer (6.6 years ± 8.6) while using definition 1 compared to definition 2 (4.5 years ±7.0) (Figure 2). Based on definition 2, the DD was significantly longer for axSpA and IBD-SpA -where the first MM was axial, compared to PsA, pSpA, and other forms -where the first MM was peripheral. Factors associated with DD varied across the SpA entities, with the type of first manifestation (i.e., longer with axial, shorter with peripheral MM), age at first symptom (younger), age at study inclusion (older) being associated with all 4 main SpA entities (Figure 3).
Conclusion: DD was significantly longer in axSpA and IBD-SpA compared to PsA, pSpA, and other forms of SpA and was associated with the phenotype of the inaugural symptom. Factors associated with DD varied across SpA entities, thus indicating the necessity of considering both the main SpA entity and the initial disease manifestation when evaluating and reporting DD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ziade N, Gamal S, Aoun M, Hmamouchi I, López Medina C, Dougados M, Elzorkany B. Global Distribution and Determinants of Diagnostic Delay Across Diverse Spondyloarthritis Entities: Data from the International ASAS-Perspa Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/global-distribution-and-determinants-of-diagnostic-delay-across-diverse-spondyloarthritis-entities-data-from-the-international-asas-perspa-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/global-distribution-and-determinants-of-diagnostic-delay-across-diverse-spondyloarthritis-entities-data-from-the-international-asas-perspa-study/