Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 12, 2022
Title: Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated and Related Disorders Poster I: Giant Cell Arteritis
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: The detection of temporal arterial abnormalities (TA) is one of the ACR 1990 criteria to define the diagnosis of cranial Giant Cell Arteritis (GCA). However, there is a lack of data concernig clinical examination and the subsequent temporal artery biopsy (TAB) results of the same biopsied vessel.
Evaluate the predictive value of the physical temporal artery examination on the TAB result in patients with suspected GCA.
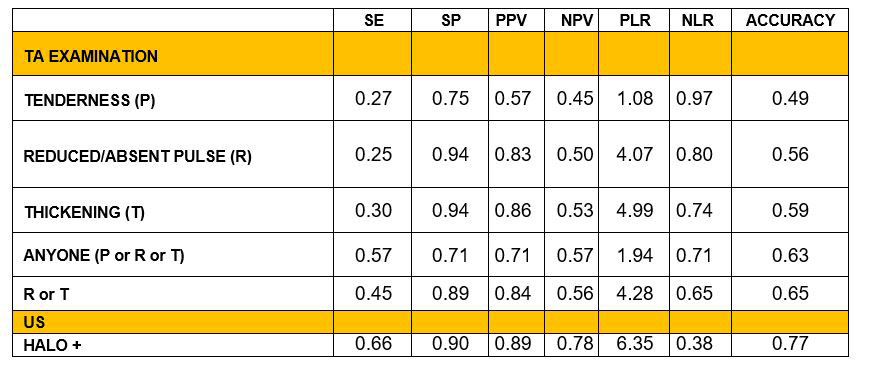
Methods: All consecutive patients with suspected diagnosis of cranial GCA seen at our center between 01.01.2018 and 31.12.2021 entered the study. All patients underwent a complete clinical examination, laboratory investigations (including determination of ESR and CRP), physical examination of the superficial temporal arteries (PTA), concerning presence of pain (P), reduced or absent pulse (R) and thickening (T). All patients underwent arterial ultrasound (US) followed by a TAB of the most US involved frontal branches. The presence of inflammatory infiltrate of the vessel wall or the inflammation of the adventitial blood vessel were considered positive for the presence of arteritis. The clinical features of the biopsied vessel were compared with the histological results by chi square test and the correspondent OR with 95% CI. Sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values (PPV and NPV), negative and positive LR (PLR and NLR) and Accuracy, were calculated for each single clinical abnormalities detected by PTA.
Results: 108 patients entered the study [F 64 (59%)], mean age 73 + 9, positive TAB 59 (55%). At physical examination of the biopsied vessel P was reported in 16 cases (27%) of TAB positive vs 12 (25%) in TAB negative group (p = 0.804, OR 1.12; 95% CI 0.47-2.66). R in 15 TAB positive (25.4%) vs 3 (6.3%) (p = 0.009, OR 5.11; 95% CI 1.38-18.9) and T in 18 TAB positive (30.5%) vs 2 (4.2%) (p < 0.001, OR 10.00; 95% CI 2.21-48.18). Anyone (T or P or R) in 34 TAB positive (56.7%) vs 14 (29.2%), (p = 0.004, OR 3.18; 95% CI 1.42-7.10). Presence of T or R in 27 TAB positive (45%) vs 5 (10.4%) (p < 0.001, OR 7.04; 95% CI 2.44-20.24). Sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV, PLR, NLR and Accuracy of any singular PTA data and US examination, are shown in table 1.
Conclusion: Clinical examination of the temporal arteries in patients with suspected GCA (in particular reduced pulse and arterial thickening) is predictive of histological positivity of the TAB.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Germanò G, macchioni P, Klinowski G, Cavazza A, Boiardi L, Salvarani C. Giant Cell Arteritis: Physical Examination of the Superficial Temporal Arteries Can Predict Temporal Artery Biopsy Result [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/giant-cell-arteritis-physical-examination-of-the-superficial-temporal-arteries-can-predict-temporal-artery-biopsy-result/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/giant-cell-arteritis-physical-examination-of-the-superficial-temporal-arteries-can-predict-temporal-artery-biopsy-result/