Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2015
Title: Vasculitis Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Giant
Cell Arteritis and Risk of Cerebrovascular Accident: A
Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Background/Purpose: Several chronic inflammatory
disorders, such as systemic lupus erythematosus and psoriatic
arthritis, have been linked to an increased risk of cerebrovascular
accident (CVA). However, the data on giant cell arteritis (GCA), one of
the most common systemic vasculitides in older adults, are
unclear as epidemiologic studies yielded inconsistent results. Thus, to
further investigate this association, we conducted a systematic review and
meta-analysis of observational studies that compared the risk of
CVA in patients with GCA versus participants without it.
Methods: Two investigators independently searched
published studies indexed in MEDLINE, EMBASE and the Cochrane database from
inception to April 2015 using the terms “giant cell arteritis” and “temporal
arteritis” combined with the terms for cerebrovascular accident. A
manual search of references of selected articles was also performed. The
inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) cohort or case-control study evaluating
the association between GCA and CVA (2) odds ratio (OR),
relative risk (RR) or hazard ratio (HR) or standardized incidence ratio (SIR)
with 95% confidence interval (CI) were provided. Study
eligibility was independently determined by the two investigators.
Newcastle-Ottawa scale was used to assess the quality of the included studies.
Point estimates and standard errors were extracted from
individual studies and were combined by the generic inverse variance method of
DerSimonian and Laird. In light of the high likelihood of between study
variance, we used a random-effect model rather than a fixed-effect model.
Statistical heterogeneity was assessed using the Cochran’s Q test. This
statistical analysis was performed using RevMan 5.3 software.
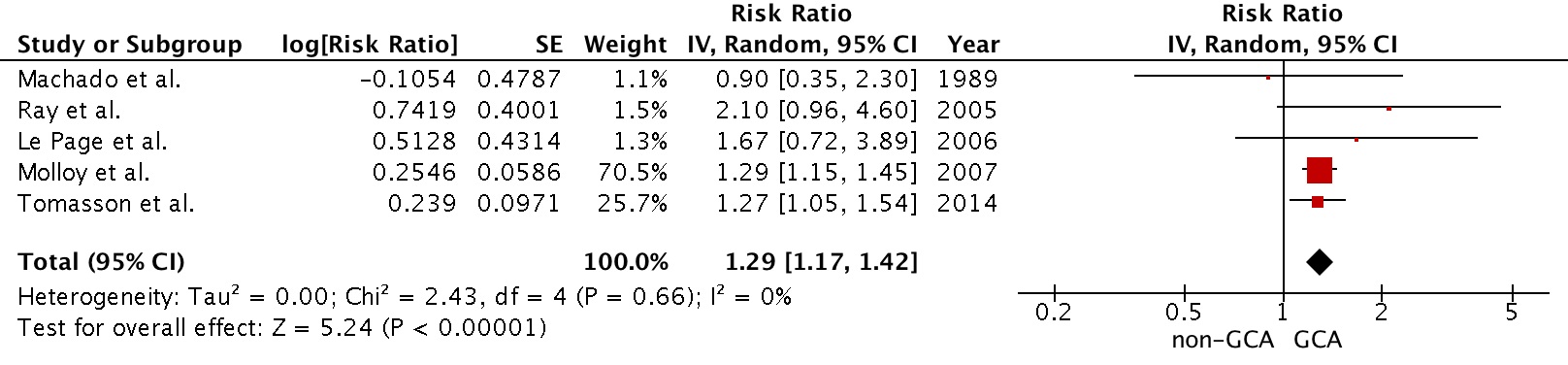
Results: Out of 713 potentially relevant articles,
five studies (three retrospective cohort studies, one prospective study and one
case-control study) were identified and included in our data analysis.
The pooled risk ratio of CVA in patients with GCA was 1.29 (95% CI, 1.17
to 1.42). The statistical heterogeneity of this meta-analysis was insignificant
with an I2 of 0%.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrated a significantly increased
CVA risk among patients with GCA with 29% excess risk
compared with general population.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ungprasert P, Srivali N, Kittanamongkolchai W. Giant Cell Arteritis and Risk of Cerebrovascular Accident: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/giant-cell-arteritis-and-risk-of-cerebrovascular-accident-a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/giant-cell-arteritis-and-risk-of-cerebrovascular-accident-a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis/