Session Information
Date: Monday, October 22, 2018
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Hallux valgus (HV) is a common foot disorder that is highly heritable. A genome-wide association study (GWAS) conducted in 4,409 Caucasians from the Framingham Heart Study (FHS), the Genetics of Generalized Osteoarthritis (GOGO) Study, and the Johnston County Osteoarthritis (JoCoOA) Project did not find genome-wide significant (GWS) associations with HV in both gender-specific and sex-combined GWAS meta-analyses. In this analysis, we expand the sample by including data from Caucasians enrolled in the Osteoarthritis Initiative (OAI), and impute genotypes to the most current Haplotype Reference Consortium (HRC) reference panel. Our objective was to identify novel genetic variants associated with HV in this expanded sample of Caucasian adults with deeper imputation.
Methods: We included 5,925 participants of European Ancestry (EA) from four cohorts: FHS, GOGO, JoCoOA and OAI. HV was considered present if determined by trained examiners using validated protocol (FHS, GOGO, JoCoOA), or the participant reported a bunionectomy or Manchester grade (MG) was 3 or 4 in one or both feet (OAI). Controls included those without surgery and MG of one in both feet and those who did not meet examiner’s criterion. Genotyping was performed using commercially available arrays with imputation to the HRC reference panel. In OAI and JoCoOA, GWAS was performed using logistic regression models with additive genetic effects to examine association between SNPs and HV. For FHS and GOGO, GEE models were used to account for the within-family correlations. All models were adjusted for age, gender, body mass index and study specific covariates. After harmonization and quality control of GWAS results, fixed-effect inverse-variance weighted meta-analysis was conducted for the total sample and for men and women, separately. The genome-wide significance (GWS) level was set at p<5×10–8.
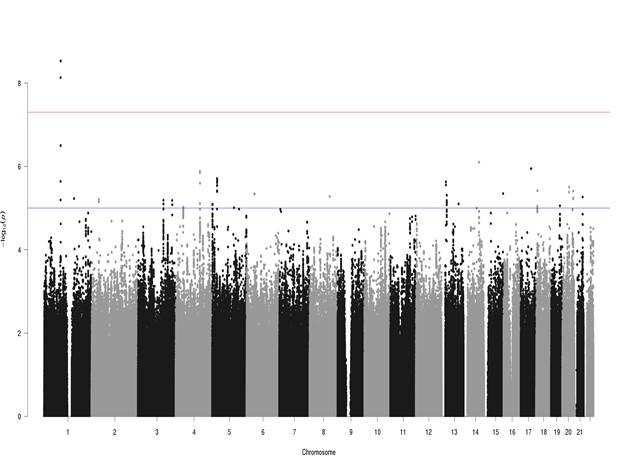
Results: Two intronic variants in the gene CLCA2 on chromosome 1 were GWS for HV: rs55807512 (OR=0.48, p=2.96E-09, MAF=0.04) and rs12124247 (OR=2.20, p=7.38E-09, MAF=0.03). The SNPs were in weak LD (r2=0.46). No other loci reached GWS although four variants of suggestive significance were located near the MIR2054 gene on chromosome 4. The association signals diminished in gender-specific analyses.
Conclusion: We identified two novel variants in the gene CLCA2 associated with HV. This gene encodes a member of the calcium-activated chloride channel regulator family of proteins. CLCA2 plays a role in modulating chloride current across the plasma membrane in a calcium-dependent manner, and cell adhesion. These findings require replication.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Arbeeva L, Mitchell B, Jackson RD, Yau MS, Ryan K, Golightly YM, Hannan MT, Nelson A, Jordan JM, Hochberg MC. Genome-Wide Meta-Analysis Identified Two Novel Variants Associated with Hallux Valgus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/genome-wide-meta-analysis-identified-two-novel-variants-associated-with-hallux-valgus/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/genome-wide-meta-analysis-identified-two-novel-variants-associated-with-hallux-valgus/