Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2015
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis - Human Etiology and Pathogenesis Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Trans-ethnic analyses have found similarities and differences in
genetic influences on RA susceptibility among Caucasians and Asians, making
both validation and novel gene association studies important in the less well studied African-American (AA) population.
Methods:
535 ACPA-positive AA RA cases and 1,506 AA controls were genotyped using
Illumina Omni 1M and 1S arrays. Associated and suggestive loci were defined as
variants within 100kB on either side of lead SNPs identified by Okada et al
[Nature 506:376 (2014)] with a p-value of <10-8, or < 10-5,
respectively. In addition to
traditional association analyses, we used the novel technique, Probabilistic
Identification of Causal SNPs (PICS) [Farh et al.
Nature 518:337 (2015)], to identify candidate causal SNPs. We used a binomial test to assess
whether SNPs with association p-values (using two thresholds: p<0.01 and p<0.001) in AA RA were
enriched for PICS identified in 21 autoimmune diseases as provided by Farh et al.
Results:
The association of HLA-DRB1 and PRKCQ was confirmed through the chip data, as
was the absence of association of PTPN22, with RA in AA. We found a peak of
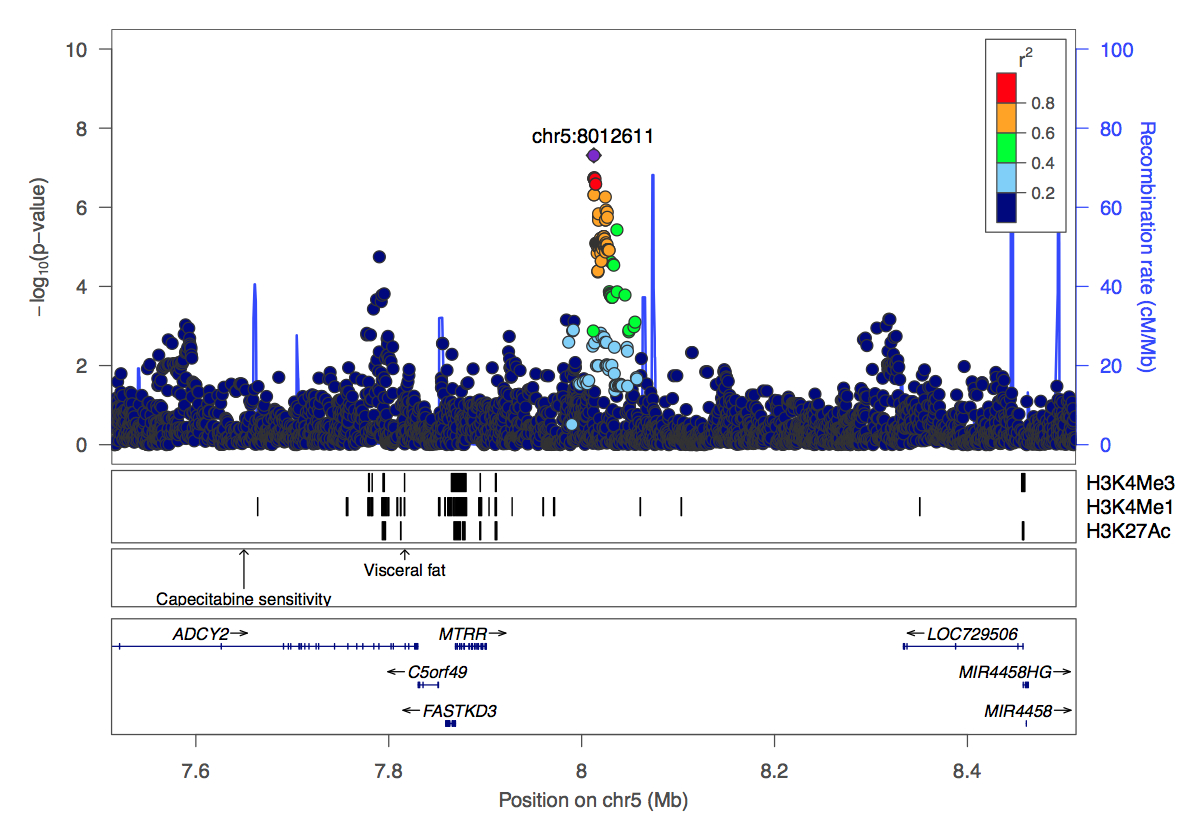
association at 5p15.31 with the most strongly associated SNP being rs13169313 (p
= 4.87*10-8, OR=1.44, nearest gene, MTRR). Initial analysis of this
locus seems to implicate ancestral African haplotypes, not Caucasian
haplotypes. Figure 1 shows a LocusZoom plot of this
region. There was significant enrichment of association of autoimmune disease
PICS SNPs among SNPs associated with RA at p-value < 0.01 (p=1.55*10-11)
and at p-value < 0.001 (p=5.9*10-5, binomial test).
Conclusion: This analysis confirms gene and variant-level associations of
HLA-DRB1 and PRKCQ with RA in AA and shows association with 5p15.31. The marked enrichment of PICS
SNPs with low association p-values in our cohort suggests pleiotropy between autoimmune diseases and susceptibility
to RA in AA.
Figure 1 –
LocusZoom plot of this region. Here, colored dots refer to linkage to the
lead SNP assuming West African LD patterns. The correlation between association
p-values and LD to the lead SNP is substantially weaker if European LD is
assumed.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Laufer VA, Reynolds RJ, Danila MI, Tiwari HK, Patki A, Langefeld CD, Absher D, Arnett DK, Bridges SL Jr.. Genetic Influences of Susceptibility to Rheumatoid Arthritis in African Americans [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/genetic-influences-of-susceptibility-to-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-african-americans/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/genetic-influences-of-susceptibility-to-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-african-americans/