Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Background: Discoid Lupus Erythematosus (DLE) is disfiguring autoimmune skin disorder, associated with defects in the adaptive immune system. The innate immune system is likely involved as seen in the presence of interface dermatitis, observed in viral exanthem, and improvement of DLE using inhibitors to membrane-bound Pattern Recognition Receptors (PRR).
Hypothesis: Genes associated with defects in the innate immune system would be upregulated in DLE skin compared to normal controls.
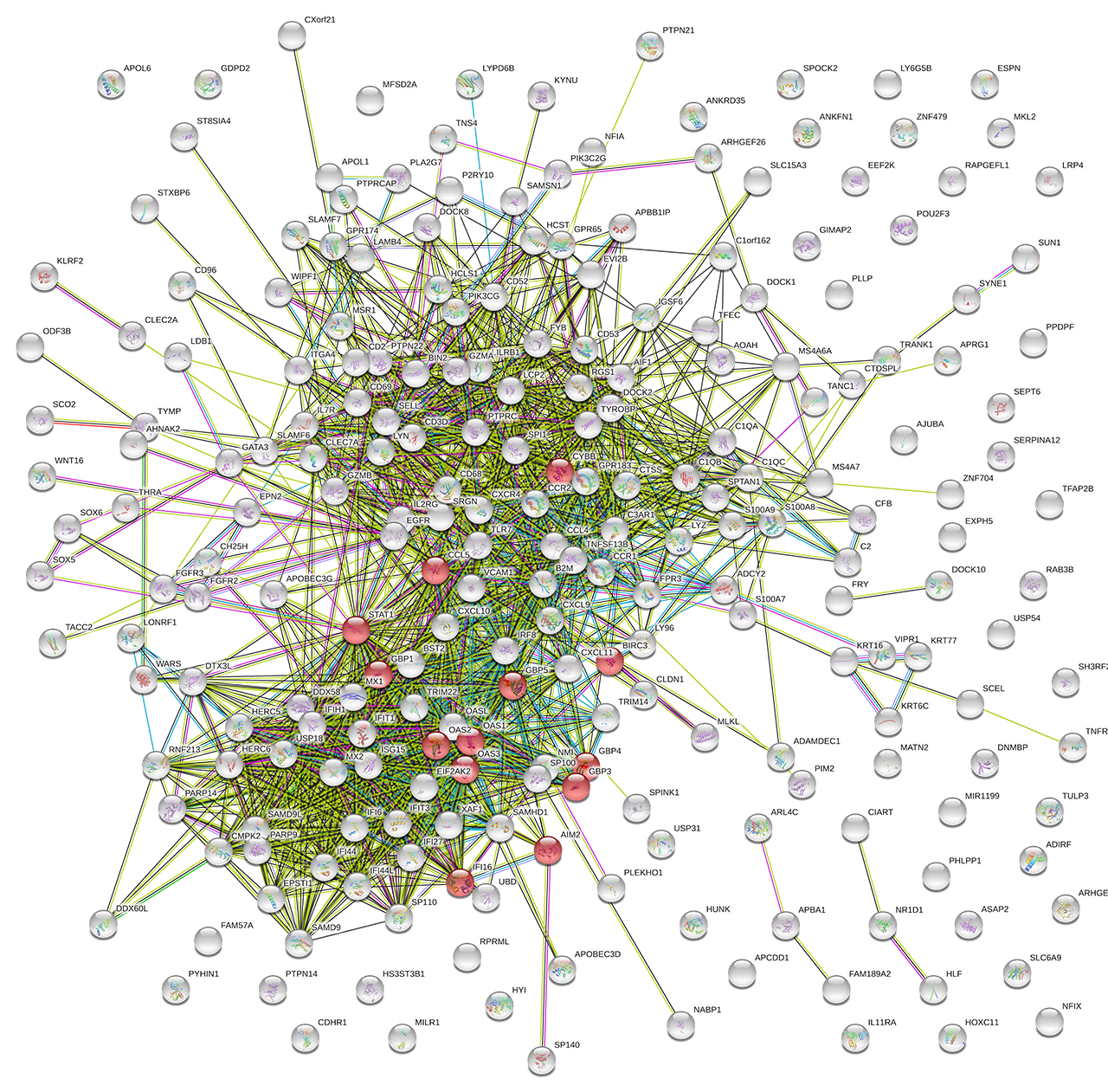
Methods: Methods: Datasets selected from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO), GSE109248, GSE81071, GSE52417, GSE95474, and GSE72535 were analyzed using GEO2R to compare the gene expressions between DLE and normal controls. Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Genes/Proteins (STRING) database, Gene Card, and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) Pathway analysis were used to identify the interaction and function of specific genes.
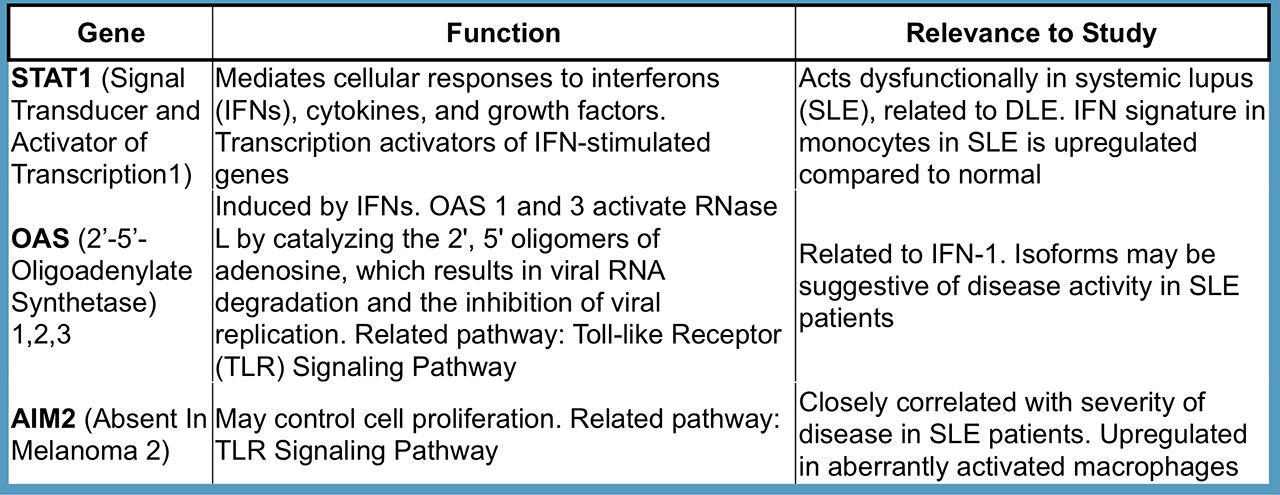
Results: Results: There were a total of 54 DLE skin samples and 37 normal controls. Genes associated with the Nucleotide Oligomerization Domain-Like Receptor (NLR) signaling pathway were consistently differentially expressed in DLE skin samples in all datasets (p-value < 8.74e-05). Five genes associated with the NLR signaling pathway, STAT1, OAS1, OAS2, OAS3, and AIM2, were found to be upregulated in skin samples of DLE patients compared to normal controls in all datasets. These five genes are associated with transcription activation, regulation of viral infection, and interferon response.
Conclusion: Conclusion: Genes associated with the NLR signaling pathway are differentially expressed in the skin of DLE patients compared to normal controls, supporting the role of the innate immune system in DLE. Further validation studies using experimental methods are needed.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Calderon I, Lee I, Mina R. Genes Associated with Nucleotide Oligomerization Domain-Like Receptor Signaling Pathway Are Upregulated in Discoid Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/genes-associated-with-nucleotide-oligomerization-domain-like-receptor-signaling-pathway-are-upregulated-in-discoid-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/genes-associated-with-nucleotide-oligomerization-domain-like-receptor-signaling-pathway-are-upregulated-in-discoid-lupus-erythematosus/