Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Gender has been lately suggested as influential in the response to treatment with biological drugs in spondyloarthritis. However, data about the association between gender and treatment response in axial PsA (axPsA) or peripheral PsA (pPsA) are scarce.
Objective: to analyze the association between gender and clinical response to biological therapy in patients with axPsA and pPsA.
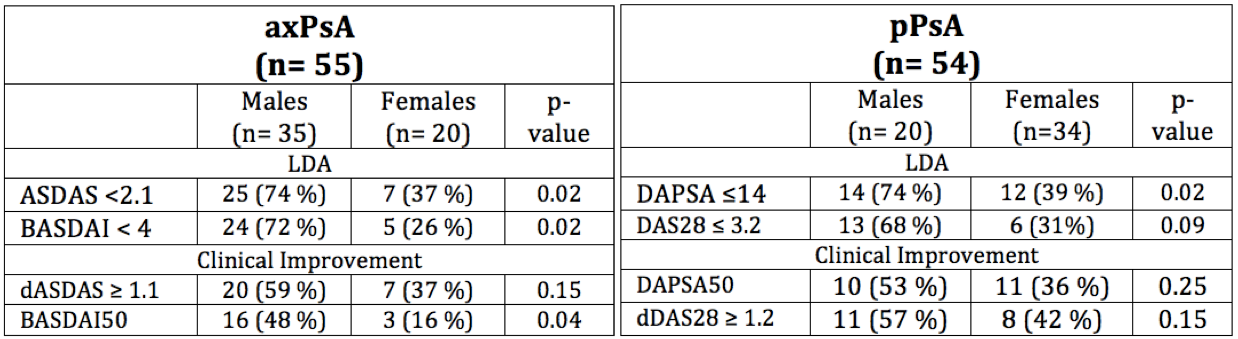
Methods: An observational cohort study was conducted, prospectively collecting data from 108 patients treated with biological therapy (93% TNFi and 7% IL-17i) from 2002-2018. Patients were divided into two groups according to their clinical predominant manifestation: axPsA or pPsA. Disease activity indexes (ASDAS and BASDAI for axPsA and DAPSA and DAS28 for PsA) were collected before starting drug and 6 months later (baseline and 6m visit, respectively). Low disease activity (LDA) was defined as ASDAS < 2.1 or BASDAI < 4 (axPsA) and DAPSA ≤14 or DAS28 ≤ 3.2 (pPsA). Clinical improvement was defined as an improvement ≥ 1.1 points in ASDAS (dASDAS) or 50% in BASDAI (BASDAI50) for axPsA, and an improvement of 50 % in DAPSA (DAPSA50) or dDAS28 ≥ 1.2.
First, the frequency of male- and females – patients achieving LDA and clinical improvement at 6m were compared using Fisher test, separately for axPsA and pPsA. Second, the association between gender and each of the clinical outcomes was analyzed using logistic regression models adjusted for confounders (age, disease duration, previous biologics, smoking habit, body mass index (BMI), baseline DMARDs and baseline disease activity).
Results:
Out of 108 included patients, 55 (51%) had predominant axPsA and 54 (49%) pPsA.
In the group of axPsA, 35 (64%) were males, 33 (60%) were nonsmokers, 33 (60%) had a BMI ≥25, with mean (SD) baseline disease activity of ASDAS: 3.3 (1.0) and BASDAI: 5.4 (2.0). The frequency of patients achieving clinical response was higher in males than females (Table 1). After adjusting for confounders, male gender was significantly associated with higher probability of achieving LDA (ASDAS OR=4.4; p=0.03 and BASDAI OR=6.0; p=0.01), and clinical improvement (dASDAS: OR=4.8; p=0.04 and BASDAI50: OR=5.19; p=0.03).
In the group of pPsA, 20 (37%) were males, 37 (68%) were nonsmokers, 34 (63%) had a BMI ≥25, with mean (SD) baseline disease activity indexes of DAPSA: 26 (14.9) and DAS 28: 4.8 (1.2). The frequency of patients achieving LDA was higher in males than females (74% vs 39%; p=0.02, respectively). After adjusting for cofounders, male gender was independently associated with higher probability of achieving LDA by DAPSA (OR=4.0; p=0.03) and DAS28 (OR= 2.1; p=0.3). Finally, an association between male gender and clinical improvement was also observed but this was statistically significant only when using dDAS28 as the outcome: OR=2.9; p=0.1 for DAPSA50 and OR=5.8; p=0.02 dDAS28.
Conclusion:
Male gender is associated with a higher rate of response to biological treatment (TNFi and IL-17i) in axPsA and pPsA. This association is robust despite using the new recommended disease activity indices and cut-off points for clinical practice. Further investigations of these gender-related differences are important for a better management of PsA and for the development of new therapies.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Benavent D, Plasencia C, Navarro-Compán V, Peiteado D, Villalba A, Nuño L, Fernández E, Balsa A. Gender Influence on Treatment Effectiveness in Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/gender-influence-on-treatment-effectiveness-in-psoriatic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/gender-influence-on-treatment-effectiveness-in-psoriatic-arthritis/