Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is known to be associated with an increased risk of serious infection. It has been discussed about the risk of the surgical site infection in the RA patients. However there are few reports about the postoperative deep infection in those patients. The aims of the study were to investigate the postoperative deep infection in RA patients treated in our institution and to clarify the frequency of the postoperative deep infection.
Methods: We reviewed a total of 696 orthopaedic surgeries for RA patients underwent between January 2004 and December 2013. We investigated the cases of deep infection after surgery, the sites of infection, and surgical techniques. We researched the postoperative deep infection free rate for the RA patients.
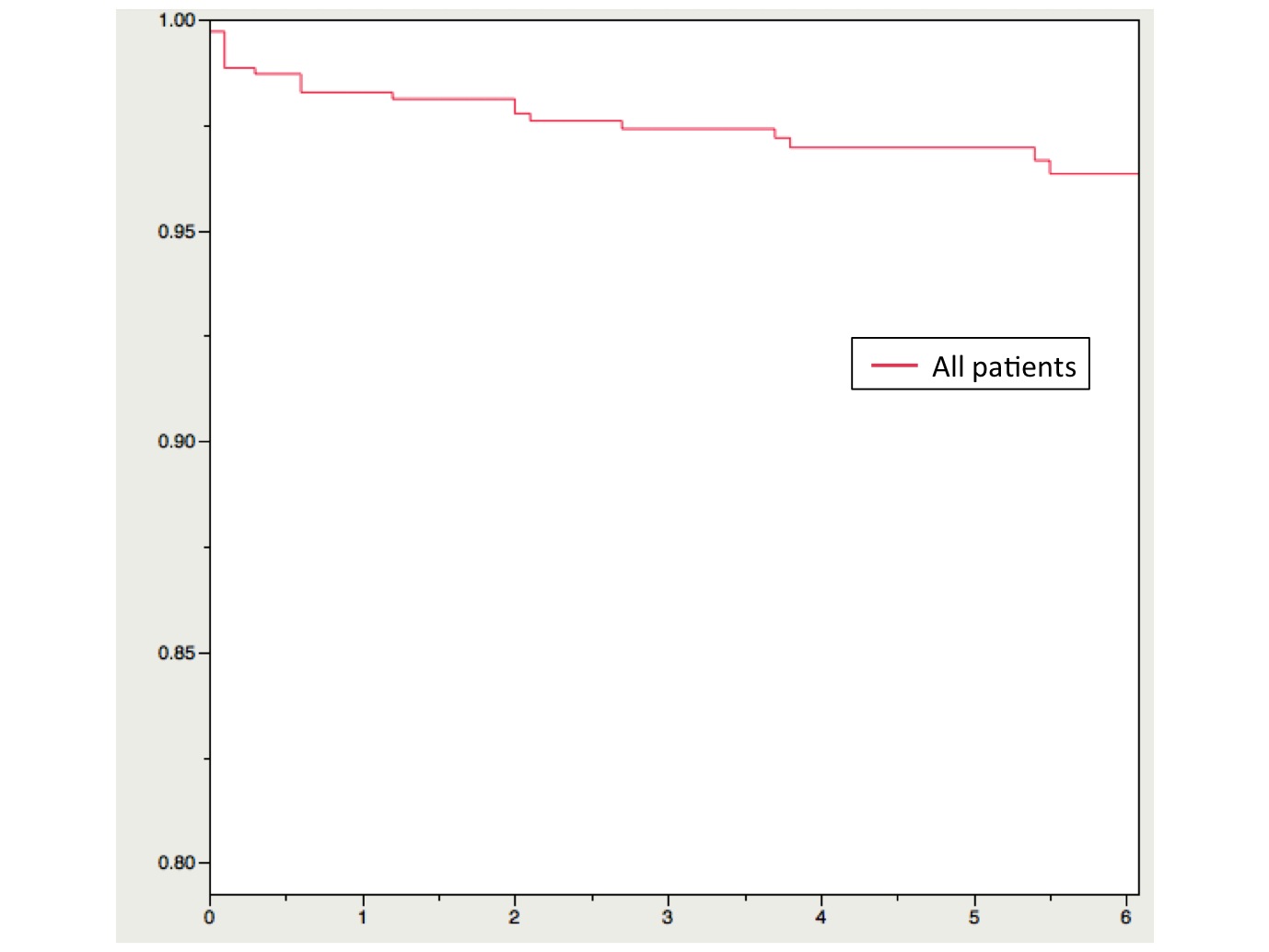
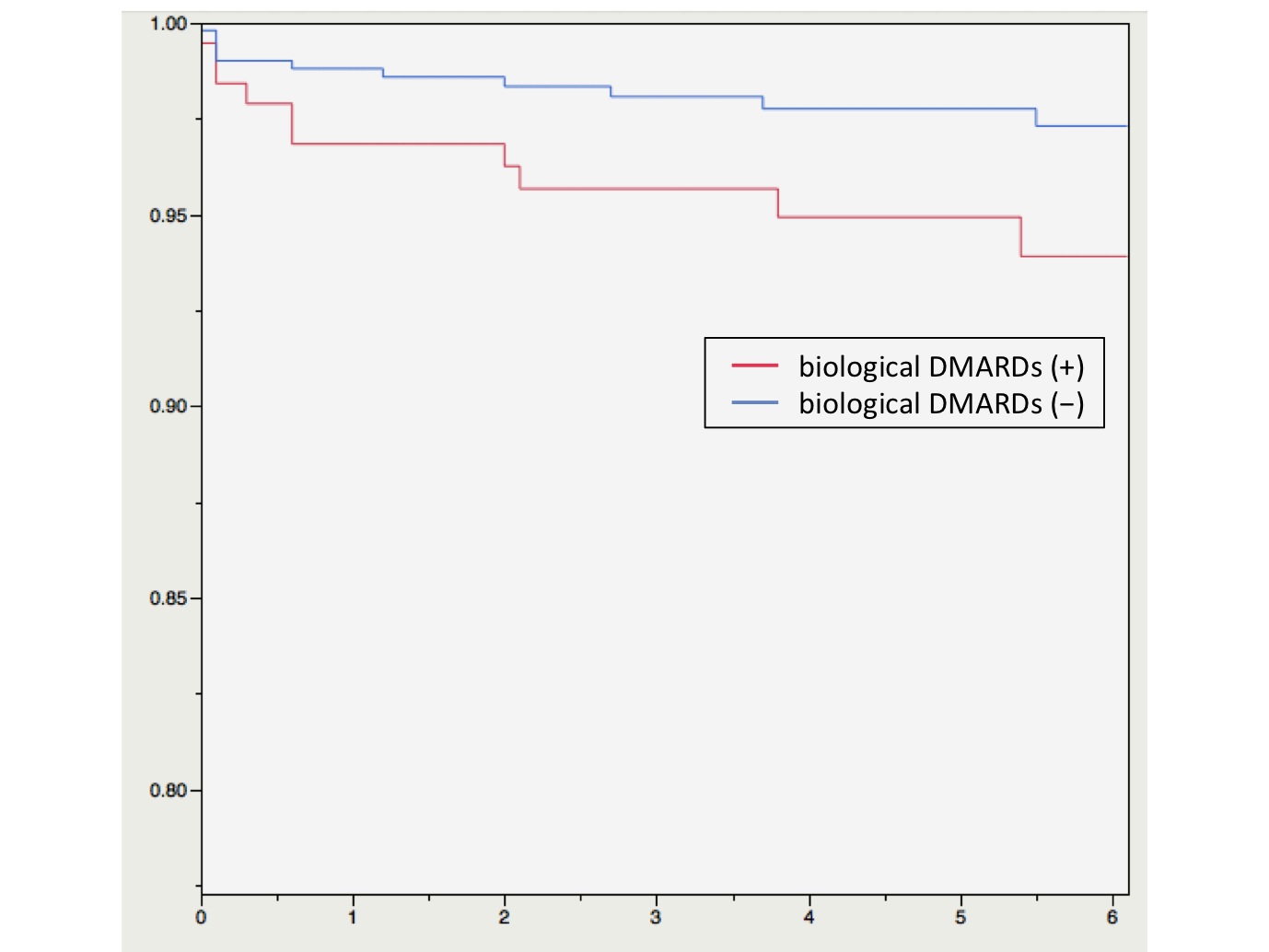
Results: The mean follow-up period was 4.7 years. 27.3% of all RA patients used Biological DMARDs. Twenty-five cases (3.6%) were suffered from the postoperative deep infection. Infection sites (surgical procedures) are 5 hips (bipolar hemiarthroplasty and total hip arthroplasty), 6 knees (total knee arthroplasty), 6 elbows (total elbow arthroplasty), one shoulder (total shoulder arthroplasty), 2 hands (metacarpophalangeal joint arthroplasty and proximal interpharangeal joint arthroplasty), one ankle (ankle arthrodesis) and 4 spines (Magerl technique, cervical posterior fixation, transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion). According to the Kaplan-Meier survival analysis, the cumulative deep infection free rate of all patients in 3 months, in 2 years and in 5 years was 98.7%, 97.8%, and 97.0%, respectively. That of the patient treated with biologic DMARDs was significantly lower than that of without biologic DMARDs. (Log-rank Test: p = 0.0068)
Conclusion: These results suggest that the postoperative deep infection is likely to occur within the first 3 months after surgery in the RA patients, and that the use of biological DMARDs is a risk factor for postoperative deep infection. We should pay more attention to the postoperative deep infection within 3 months of a procedure.
Disclosure:
M. Azukizawa,
None;
H. Ito,
None.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/frequency-of-postoperative-deep-infection-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/