Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Belimumab, an inhibitor of B lymphocyte stimulator, is approved for the treatment of adult patients with active, autoantibody-positive systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) receiving standard of care. The recommended dosing regimen for intravenous belimumab is 10 mg/kg at 2-week intervals for the first 3 doses (loading dose period) and at 4-week intervals thereafter (maintenance period), for a total of 15 doses in the first year of therapy. However, in routine clinical practice, many patients may not be receiving the recommended number of loading or maintenance doses. This study evaluated the frequency of infusions in patients with SLE under routine care settings, using data from a US administrative claims database.
Methods: A retrospective analysis (study 206345) was conducted using the Truven Health MarketScan® Commercial Claims and Encounters database (Sept 01, 2010 to Dec 31, 2015). The analysis cohort comprised patients 18–64 years of age with a SLE diagnosis (ICD-9: 710.0 or ICD-10: M32) and ≥1 belimumab infusion. The index date was defined as the date patients received their first belimumab infusion. Continuous enrollment was required for 6 months pre-index and ≥3 months post-index date. The loading dose period was defined as the 34-day period post-index date; patients were divided into subgroups according to the number of infusions received in this time (1–2 or ≥3). Here we present data for those patients with 12 months of follow-up data.
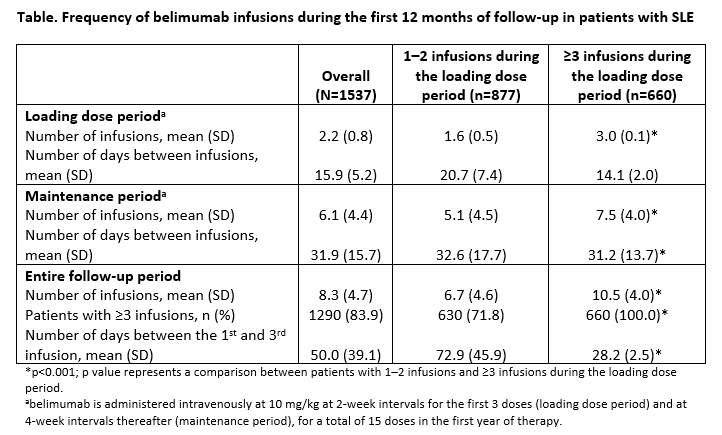
Results: Overall, there were 2067 patients; the majority were female (94.7%) and had a mean (standard deviation [SD]) age of 43.9 (11.1) years. From this population, 1537 patients had 12 months of follow-up data; 877 (57.1%) received 1–2 infusions during the loading dose period and 660 (42.9%) received ≥3 infusions. The mean number of infusions and time between infusions are summarized (Table).
Conclusion: In this sample of US patients with SLE in a routine care setting, a high proportion did not receive the recommended number of belimumab loading doses. Furthermore, compared with those who completed the recommended loading dose period, patients who did not complete the loading dose period received significantly fewer belimumab infusions during the maintenance period. This study provides valuable information on belimumab treatment patterns in a real-world setting using a US claims database. These data suggest that belimumab is not always administered as recommended; the effects of this on treatment outcomes remain to be determined.
Study funded/conducted by GSK. Editorial assistance provided by Jennie McLean, PhD, of Fishawack Indicia Ltd, UK, funded by GSK.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bell CF, Priest J, Stott-Miller M, Kan H, Amelio J, Song X, Limone B, Noxon V, Costenbader KH. Frequency of Infusions Among Patients Diagnosed with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Initiating Treatment with Intravenous Belimumab [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/frequency-of-infusions-among-patients-diagnosed-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-initiating-treatment-with-intravenous-belimumab/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/frequency-of-infusions-among-patients-diagnosed-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-initiating-treatment-with-intravenous-belimumab/