Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
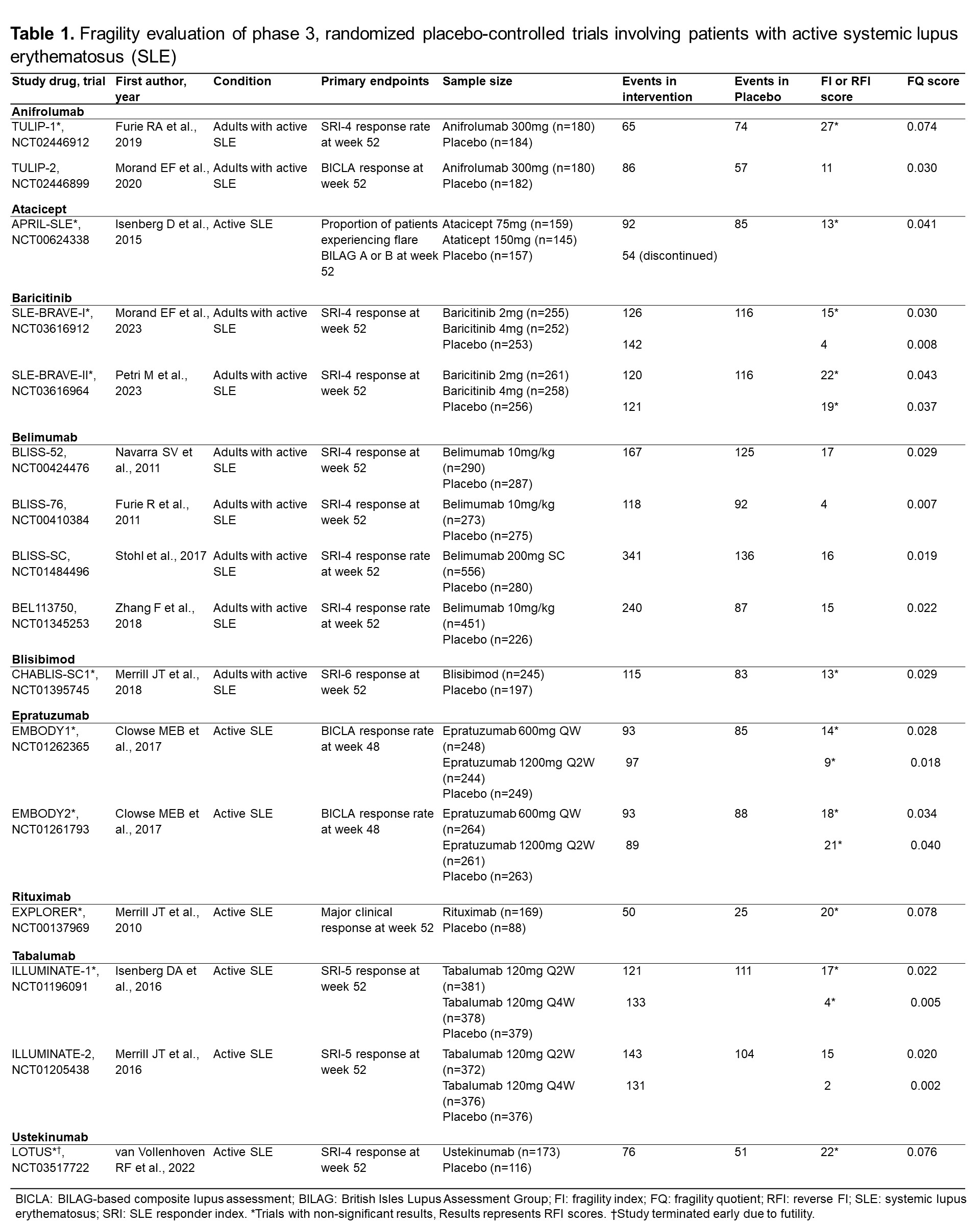
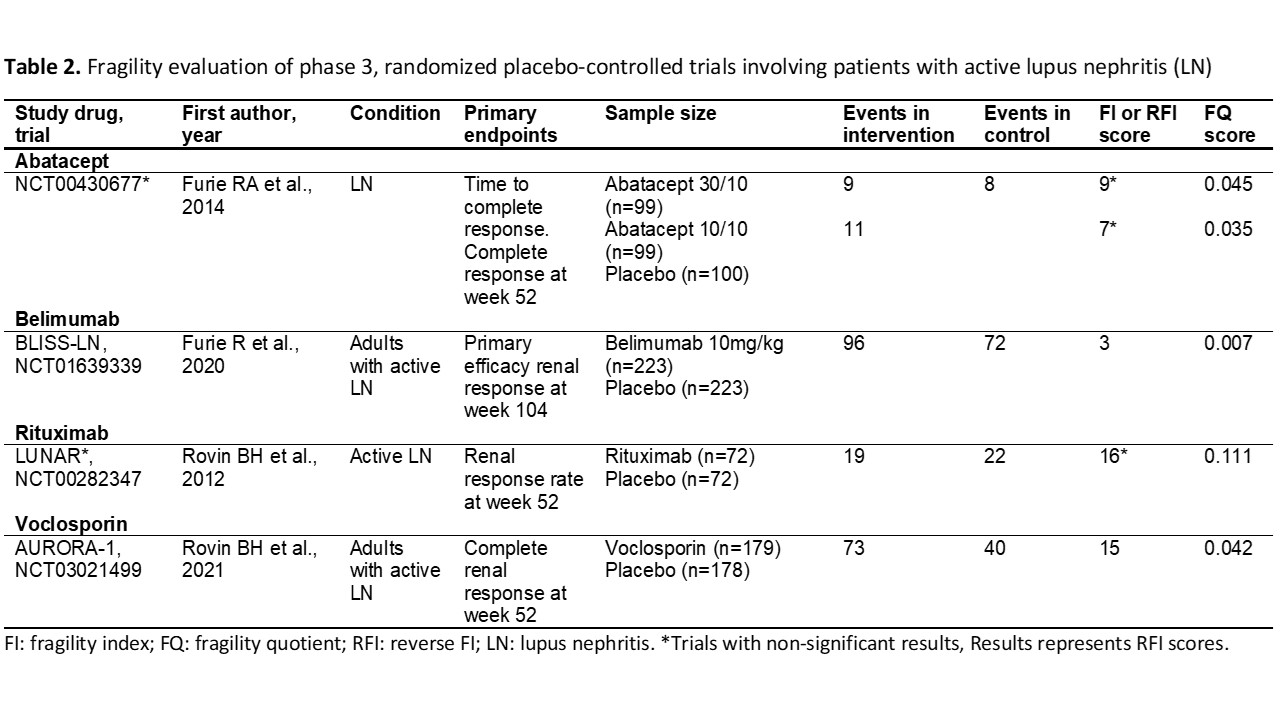
Background/Purpose: Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) for novel therapeutics have frequently failed to meet criteria for regulatory approval. Even among drugs that were recently approved, trials been mixed in their conclusions or have had small effect sizes for outcomes that matter. The Fragility Index (FI) is a recently described method for assessing the robustness of RCTs findings, which calculates the minimum number of patients whose status would be required to change from an event to a non-event to make the study lose statistical significance (p< 0.05). We aimed to assess the robustness of pivotal phase 3 RCTs for SLE and LN treatments using the FI, the reverse FI (RFI), and the fragility quotient (FQ) scores to aid the interpretation of these RCTs.
Methods: To identify all RCTs, we searched on ClinicalTrials.gov for all phase 3, placebo-controlled RCTs, including patients with active SLE or LN. Trials were excluded if they were unpublished, phase 2 or 4 RCTs, or terminated due to reasons other than futility. Data on pre-specified primary endpoints, total participants, participants within each trial arm, and the number of events in the intervention and placebo groups were obtained from the full publications. FI score was calculated using an online calculator (available at https://clincalc.com/Stats/FragilityIndex.aspx), the RFI was calculated for RCTs with non-statistically significant results by modifying the number of events in the intervention arm until a p-value < 0.05 is reached while keeping the total number of participants constant. The FQ score was calculated by dividing the FI (or RFI) score by the total sample size of the trial. We used descriptive statistics to present the results.
Results: We evaluated 20 RCTs (16 in SLE, 4 in LN). The mean FI/RFI score of the 20 studies was 13.6±6.6. There were 9 studies with statistically significant results (7 in SLE, 2 in LN), and the mean FI score was 10.2±6.2. Twelve studies showed non-statistically significant results (9 in SLE, 2 in LN) with a mean RFI score of 15.6±6.1. The lowest FI was for the ILLUMINATE-2 trial (score: 2, Tabalumab), and the highest FI was found in the BLISS-52 trial (score: 17, Belimumab). The lowest RFI (non-significant trials) was for the ILLUMINATE-1 trial (score: 4, Tabalumab), and the highest RFI was for the TULIP-1 trial (score: 27, Anifrolumab). The RCT that granted FDA approval to anifrolumab was the TULIP-2 trial, with a FI score of 11. Voclosporin trial (AURORA-1) had an FI score of 15. Regarding the belimumab studies, BLISS-52 had an FI score of 17, BLISS-76 had an FI score of 4, BLISS-SC had an FI score of 16, and BLISS-LN had a FI score of 3. The lowest FQ scores were found in the ILLUMINATE trials and the highest in the Rituximab trials (LUNAR & EXPLORER) and the early terminated LOTUS trial.
Conclusion: The evidence supporting the recent approval of therapies for patients with SLE and LN is derived mostly from fragile RCTs, both among trials that met thresholds for statistical significance and among those that did not.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Figueroa-Parra G, Putman M, Duarte-Garcia A. Fragility of Randomized Clinical Trials of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Lupus Nephritis Therapies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/fragility-of-randomized-clinical-trials-of-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-and-lupus-nephritis-therapies/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/fragility-of-randomized-clinical-trials-of-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-and-lupus-nephritis-therapies/