Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1434–1466) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Secukinumab has demonstrated long-lasting efficacy and a favorable safety profile across multiple clinical trials and domains of psoriatic disease. Real-world data provides additional valuable information on the long-term outcomes of secukinumab in routine clinical practice. Secukinumab has shown high retention rates and sustained effectiveness in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (r-axSPA) during 5 years of follow-up in the SERENA study. This post hoc analysis assesses minimal disease activity (MDA) components and retention rates in biologic-naïve and biologic-experienced patients during the study period.
Methods: SERENA (CAIN457A3403) was a non-interventional, prospective real-world study conducted across 19 countries in patients with moderate to severe chronic plaque-type psoriasis, active PsA, or r-axSpA, who had received secukinumab for ≥16 weeks before enrollment. The different components within the MDA assessment were evaluated for patients achieving the following criteria: tender joint count (TJC ≤1), swollen joint count (SJC ≤1), Psoriasis Area and Surface Index (PASI ≤1) or body surface area (BSA ≤3), patient pain visual analogue scale (VAS ≤15 mm), Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ-DI ≤0.5), and tender entheseal points (TEP ≤1) from years 1 to 5. Secukinumab retention rate was derived from Kaplan-Meier estimates for the proportion of patients who had been treated with secukinumab from years 1 to 5.
Results: Overall, 522 patients with PsA were included in the analysis. The mean age at inclusion was 52.5 years, 44.8% male. The mean ± SD BMI was 28.7 ± 5.5 kg/m2 and mean time since diagnosis was 8.6 ± 7.4 years (Table 1). Before inclusion in the study, the patients had been receiving secukinumab treatment for a mean duration of 1 year, and 68.6% had previous biologic exposure. Secukinumab retention rates were numerically higher in the biologic-naïve subgroup compared with the biologic-experienced subgroup, from years 2.5 onwards (Figure 1). The percentage of patients reaching the threshold of the different components within the MDA assessment are shown in Figure 2. Since the patient’s global assessment (≤20) was not collected, it was not possible to report the overall MDA. There were no new safety signals in this subanalysis of patients with PsA.
Conclusion: In this real-world data analysis, secukinumab demonstrated sustained clinical effectiveness and a favorable safety profile in patients with PsA over 5 years of observation. Retention rates remained high throughout the observation time, with no statistically significant differences observed in biologic naïve or pre-treated patients. Importantly, secukinumab demonstrated sustained long-term remission across all six collected components of the MDA criteria. These results reinforce the long-term value of secukinumab in managing multiple PsA domains in routine clinical practice.
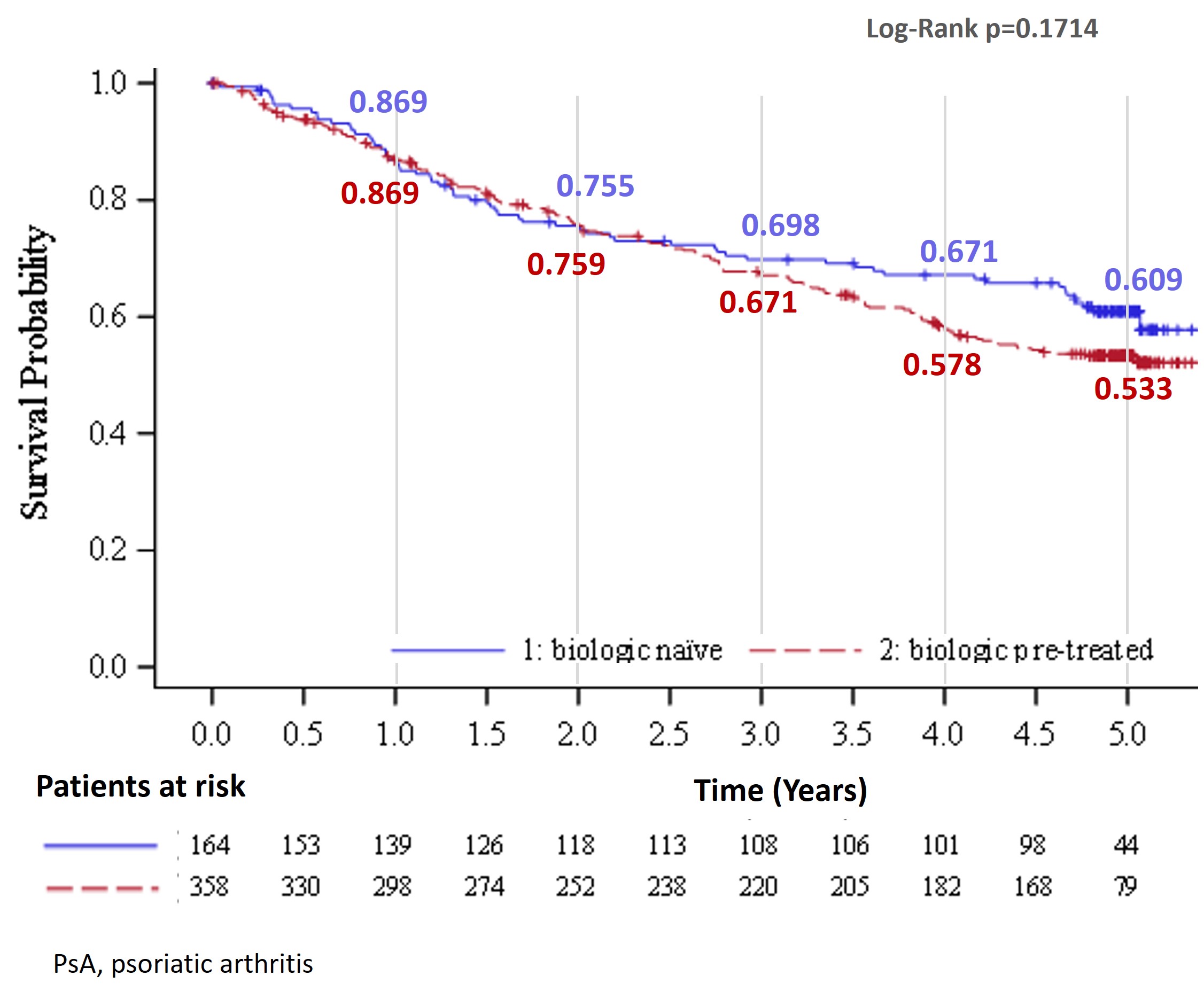 Table 1: Demographics and baseline characteristics
Table 1: Demographics and baseline characteristics
.jpg) Figure 1. Kaplan-Meier estimates of the retention rate of secukinumab by biologic-experienced vs biologic-naïve in PsA cohort
Figure 1. Kaplan-Meier estimates of the retention rate of secukinumab by biologic-experienced vs biologic-naïve in PsA cohort
.jpg) Figure 2. MDA response (components of MDA criteria)
Figure 2. MDA response (components of MDA criteria)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kiltz U, Sfikakis P, Bounas A, Gullick N, LESPESSAILLES E, Brandt-Juergens J, Rashkov R, Vizcaya C, Clemens A, Hoyt K, Bao W, Gaffney K. Five-Year Results of Secukinumab on Minimal Disease Activity (MDA) Components and the Impact of Biologic Treatment Status on Effectiveness and Safety in Patients With Psoriatic Arthritis: Real-World Data From the SERENA Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/five-year-results-of-secukinumab-on-minimal-disease-activity-mda-components-and-the-impact-of-biologic-treatment-status-on-effectiveness-and-safety-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-real-world-d/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/five-year-results-of-secukinumab-on-minimal-disease-activity-mda-components-and-the-impact-of-biologic-treatment-status-on-effectiveness-and-safety-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-real-world-d/
