Session Information
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-4:00PM
Background/Purpose: Aberrantly activated T- and B-lymphocytes play a major pathophysiological role in SLE. Cenerimod, a potent, selective sphingosine-1-phosphate 1 receptor modulator, blocks the egress of lymphocytes from lymphoid organs, thereby reducing their availability, thus providing rationale for development. The study investigated the effect of cenerimod on circulating lymphocytes, disease activity, safety and pharmacokinetics in SLE patients.
Methods: This study was conducted in two parts, separated by a safety review. Patients with SLEDAI-2K score ≥2 points for mucocutaneous or musculoskeletal manifestations and positive serum test for ANA or anti-dsDNA antibodies were randomised evenly in Part A to cenerimod 0.5, 1, or 2 mg or placebo once daily (QD) and 3:1 in Part B to cenerimod 4 mg or placebo QD and treated for 12 weeks. Predefined Day 1 safety assessments included heart rate (HR) monitoring and hourly 12-lead ECG monitoring (pre dose, to 6 hours post-dose). Endpoints included treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs), changes in total lymphocyte count, SLEDAI-2K score (modified [mSLEDAI] to exclude leucopoenia), biomarker anti-dsDNA antibody and pharmacokinetic assessments. All 67 patients (A: 49; B: 18) met at least 4 ACR criteria in the past, 70% had 4 to 11 ACR criteria ongoing at screening. Mean (SD) mSLEDAI-2K was 7.7 (±3.1) at baseline.
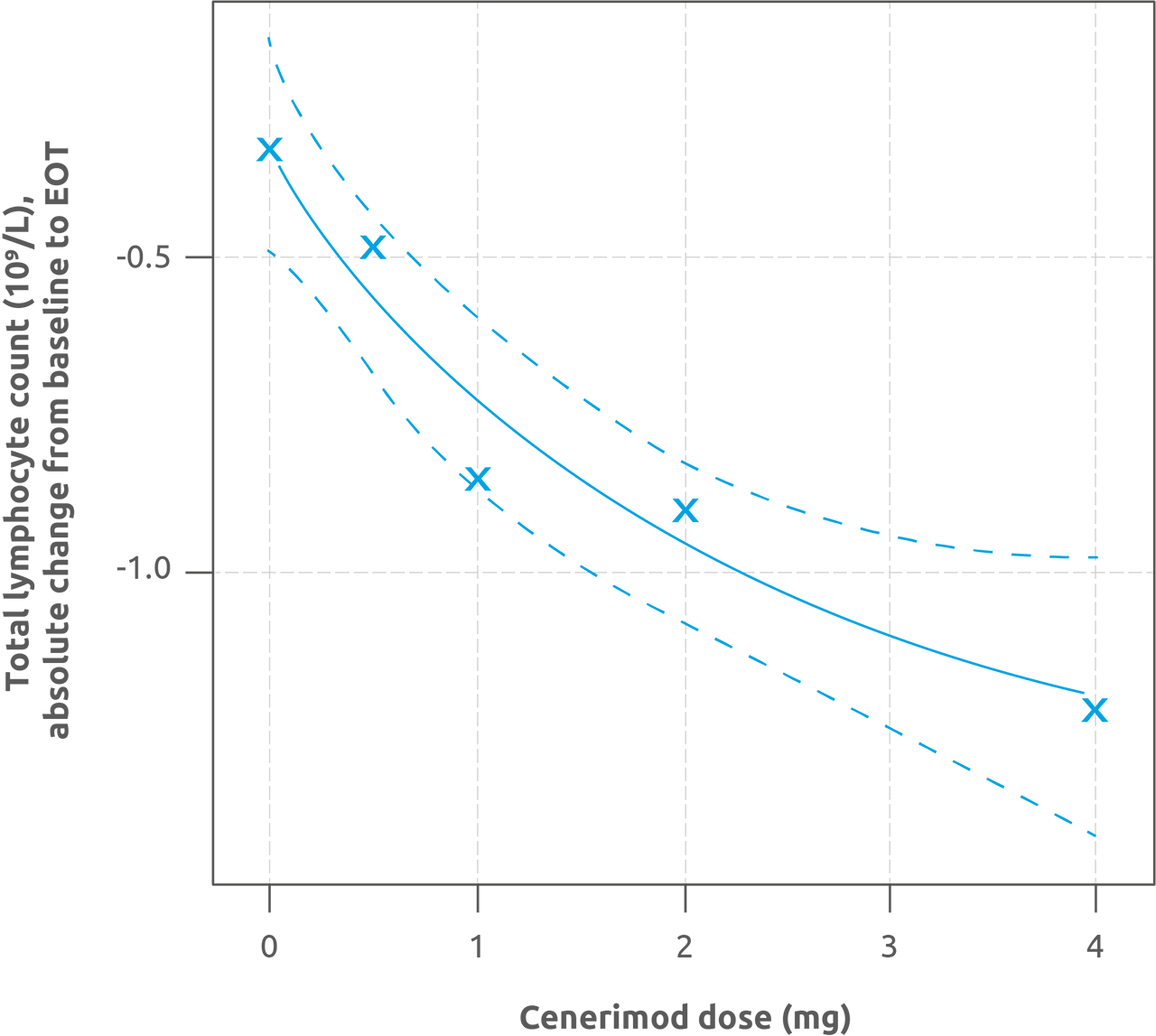
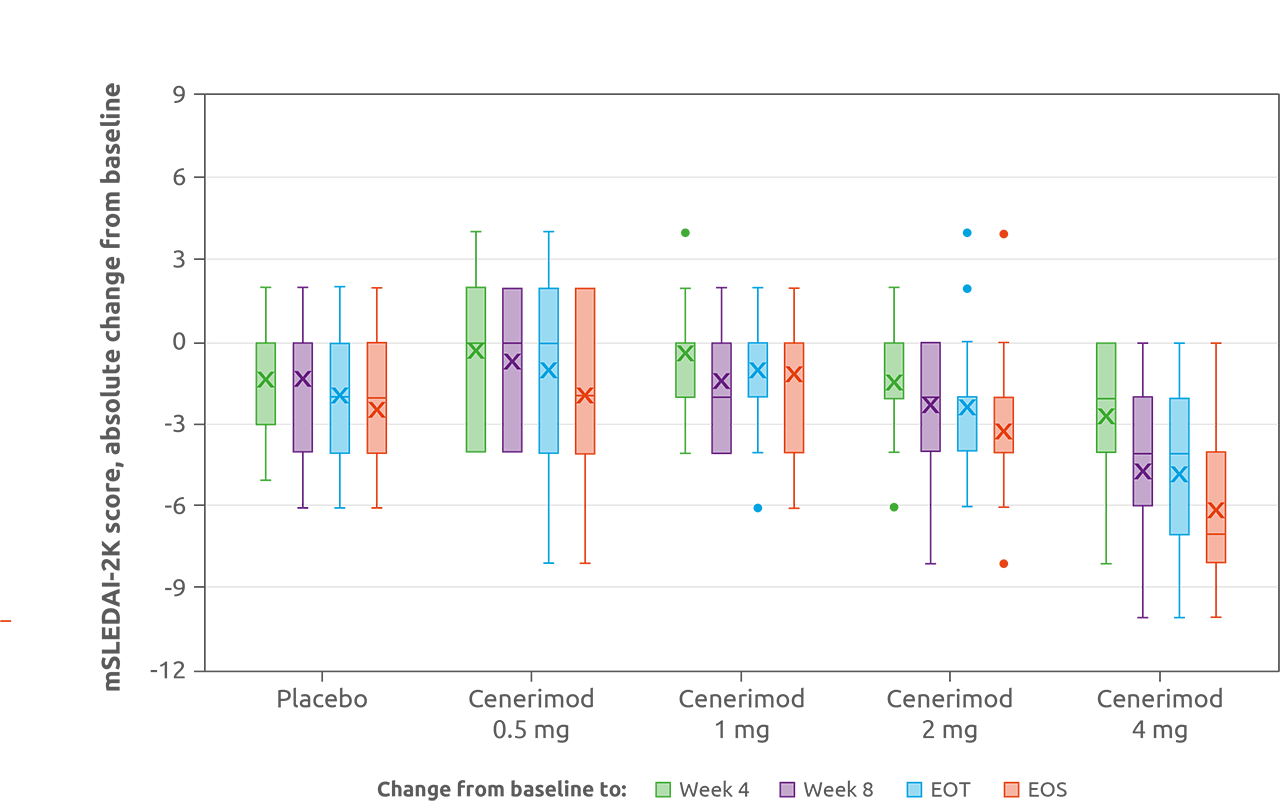
Results: Part A included 49 patients (12:12:13:12 receiving cenerimod 0.5, 1, 2 mg or placebo); Part B included 18 (13 cenerimod 4 mg; 5 placebo). Cenerimod dose-dependently reduced total lymphocyte count from baseline to end of treatment (EOT; p< 0.001; Figure 1). In pairwise comparisons, cenerimod 1, 2, and 4 mg significantly decreased lymphocytes versus placebo (all p< 0.001). Exploratory analyses indicated clinical and biological improvement with cenerimod 4 mg with an estimated mean treatment effect on change from baseline to EOT in mSLEDAI-2K score of −2.420 (p=0.0306; Figure 2), and a decrease in anti-dsDNA of −28.80 U/mL (p=0.0146) compared with placebo. All treatment groups reported similar and non-dose-related rates of TEAEs (cenerimod 0.5: 41.7%; 1: 41.7%; 2: 46.2%; 4 mg: 38.5%; and placebo: 58.8%). After the first dose, cenerimod induced minimal, transient and dose-dependent decreases in HR; no patient had an HR < 40 bpm at any time post baseline. Small decreases in pulmonary function, not dose-related, were observed in cenerimod-treated patients at EOT. Cenerimod did not increase blood pressure or show any effects on laboratory variables. Trough plasma concentrations revealed steady-state conditions were reached after 4–8 weeks of QD dosing and dose-proportionality was observed.
Conclusion: Cenerimod has the potential to be a new therapeutic approach for patients with SLE and has shown to date an acceptable efficacy and safety profile with minimal, non-clinically relevant cardiovascular effects. These results warrant further evaluation in a larger study over a longer treatment duration. A Phase IIb, randomised dose-finding study was initiated in December 2018 to evaluate efficacy and safety of cenerimod in addition to background therapy in moderate-to-severe SLE (NCT03742037).
Medical writing support provided by Zoe Kelly (InterComm) funded by Idorsia.
The MCP-Mod approach was performed for each of the five considered dose-response models. Plot shows the maximum effect -Emax- curve, with 95% CI -dashed lines-, related to the model with the highest t-statistic. CI, confidence intervals; EOT, end of treatment; MCP-Mod, Multiple Comparison Procedure and Modelling.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hermann V, Batalov A, Smakotina S, Cornelisse P. First Use of Cenerimod, a Selective sphingosine-1-phosphate 1 (S1P1) Receptor Modulator, for the Treatment of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Double-Blind, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled, Phase II, Proof-of-Concept Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/first-use-of-cenerimod-a-selective-sphingosine-1-phosphate-1-s1p1-receptor-modulator-for-the-treatment-of-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-a-double-blind-randomised-placebo-controlled-phase-ii-pr/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/first-use-of-cenerimod-a-selective-sphingosine-1-phosphate-1-s1p1-receptor-modulator-for-the-treatment-of-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-a-double-blind-randomised-placebo-controlled-phase-ii-pr/