Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1088–1122) Immunological Complications of Medical Therapy Poster
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) retinopathy is a progressive, vision-threatening retinal disease. While HCQ is typically discontinued after toxicity is detected, some patients undergo tapering due to disease control needs. This study investigates whether ellipsoid zone (EZ) loss progresses more rapidly in patients who taper HCQ compared to those who discontinue it, using longitudinal optical coherence tomography (OCT) data from a Taiwanese cohort.
Methods: In the NTUH‑HCQ cohort, we retrospectively included patients who were diagnosed with HCQ retinopathy by a retinologist following the onset of visual symptoms, seen at National Taiwan University Hospital between March 2017 and August 2024. The inclusion criteria required that each eye had at least 6 months of serial OCT follow-up after HCQ tapering or complete discontinuation, while patients with concurrent retinal diseases or other ocular conditions affecting the macula were excluded. Tapering was defined as the continuation of HCQ at less than 75% of the patient’s long-term maintenance dose. EZ width was defined as the average distance between nasal–temporal and superior–inferior ellipsoid zone termini on OCT scans. The primary outcome was the individual rate of EZ loss (µm per year). We compared the average EZ loss rates between individuals and assessed differences across treatment and pattern subgroups.
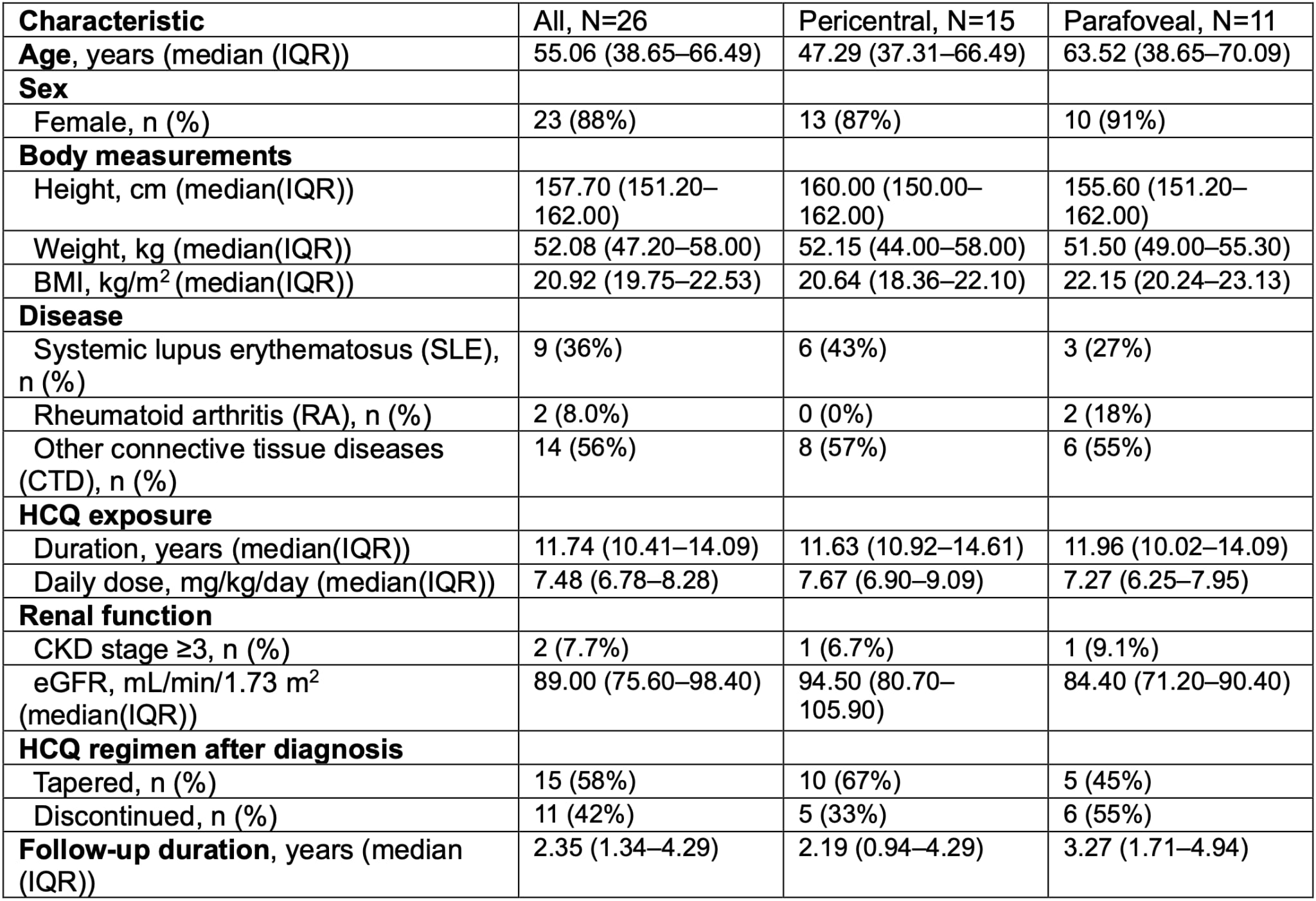
Results: A total of 51 eyes from 26 patients were included in the analysis. Among them, 88% (23/26) were female. The median age was 55.06 years (interquartile range [IQR], 38.65–66.49), and the median duration of HCQ exposure was 11.74 years (IQR, 10.41–14.09). The median follow-up duration after HCQ retinopathy diagnosis was 2.35 years (IQR, 1.34–4.29). Pericentral-type HCQ retinopathy was observed in 15 patients (57.7%), while 12 patients (42.3%) had the parafoveal type. Following diagnosis, 15 patients (57.7%) continued HCQ on a tapered regimen, and 11 patients (42.3%) discontinued the drug entirely. Full patient characteristics are summarized in Table 1.Figure 1 shows that the most rapid EZ loss occurred in patients with pericentral-type HCQ retinopathy who remained on a tapered regimen, averaging ‑600 ± 407 µm per year. In contrast, those who discontinued HCQ in the same subgroup declined significantly more slowly, at ‑149 ± 139 µm per year (p < 0.001). In the parafoveal subgroup, the corresponding rates were ‑162 ± 116 µm per year with taper and ‑124 ± 81 µm per year after discontinuation, with no significant difference between groups (p = 0.394).
Conclusion: Our findings show that EZ loss progresses more rapidly in pericentral-type HCQ retinopathy patients who continued HCQ at a reduced dose than in those who discontinue it entirely, indicating heightened susceptibility of the perifoveal region to continued low-dose toxicity. These results underscore the limitations of tapering alone and support complete drug cessation once retinopathy is detected. EZ width may serve as a sensitive marker to guide management and monitor progression in clinical practice.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Li K, Chang T, Lai T, Kao J, LAN T, Lee T, lai p, Pai S, Shen C, Hsieh S. Faster Ellipsoid Zone Loss in Hydroxychloroquine Retinopathy with Tapering versus Discontinuation: A Longitudinal Optical Coherence Tomography Study from a Single Center in Taiwan [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/faster-ellipsoid-zone-loss-in-hydroxychloroquine-retinopathy-with-tapering-versus-discontinuation-a-longitudinal-optical-coherence-tomography-study-from-a-single-center-in-taiwan/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/faster-ellipsoid-zone-loss-in-hydroxychloroquine-retinopathy-with-tapering-versus-discontinuation-a-longitudinal-optical-coherence-tomography-study-from-a-single-center-in-taiwan/

.jpg)