Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Title: SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster III: Outcomes (1257–1303)
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune disease that can affect multiple organ systems and can vary in its manifestations between individuals. SLE can range in severity, resulting in some patients being unable to continue working while others can remain employed.
The purpose of this study is to analyze and compare factors including SLE disease activity between work disabled and employed patients with SLE to elucidate variables associated with unemployment.
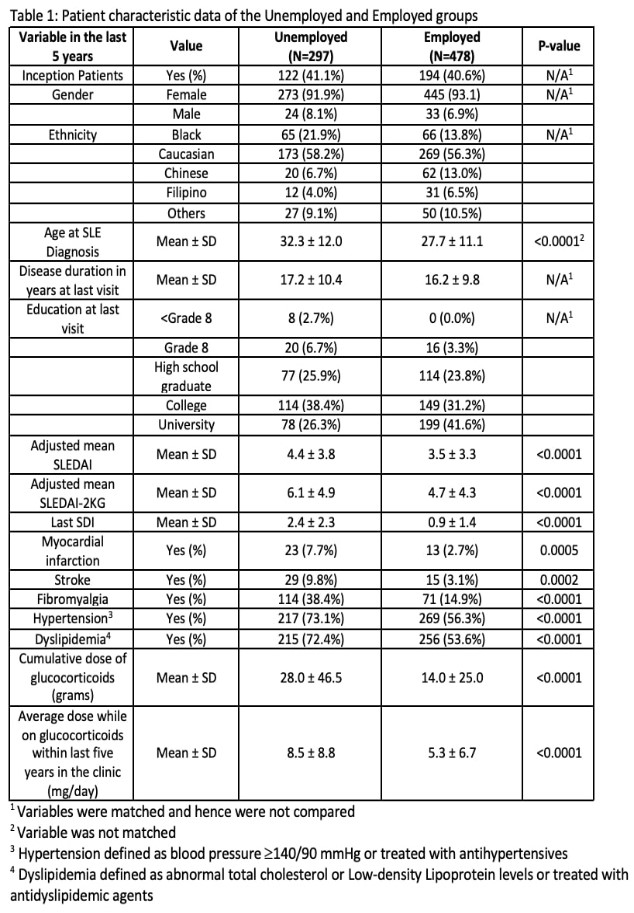
Methods: This is a cross-sectional study focused on the status of last employment reported in the data on 1110 adult SLE patients followed at a single centre where 746 patients were categorized as “Employed” and 364 as “Unemployed” (work disability or Sick Leave). In the employed group, 478 patients were matched to 297 patients in the unemployed group by 2:1 matching. Patients were matched on gender, inception status (whether patient was first seen at clinic within 12 months of SLE diagnosis), disease duration at last visit (+/- 3 years), ethnicity (Caucasian or non-Caucasian) and highest education level obtained. Associations between variables and employment status were assessed using univariate and multivariate conditional logistic regressions in a nested case-control study. Greedy matching algorithm was used to assemble the cases and controls. Patients’ characteristics were compared by paired t-test and McNemar’s test in matched cohorts, and a conditional logistic regression was performed to examine patients’ demographics, last five years’ disease activity, organ damage, disease burdens and treatment to the last employment status. Step-down variable selection method was adopted in the multivariable model building with Akaike Information Criterion (AIC) used as the model fitting statistics.
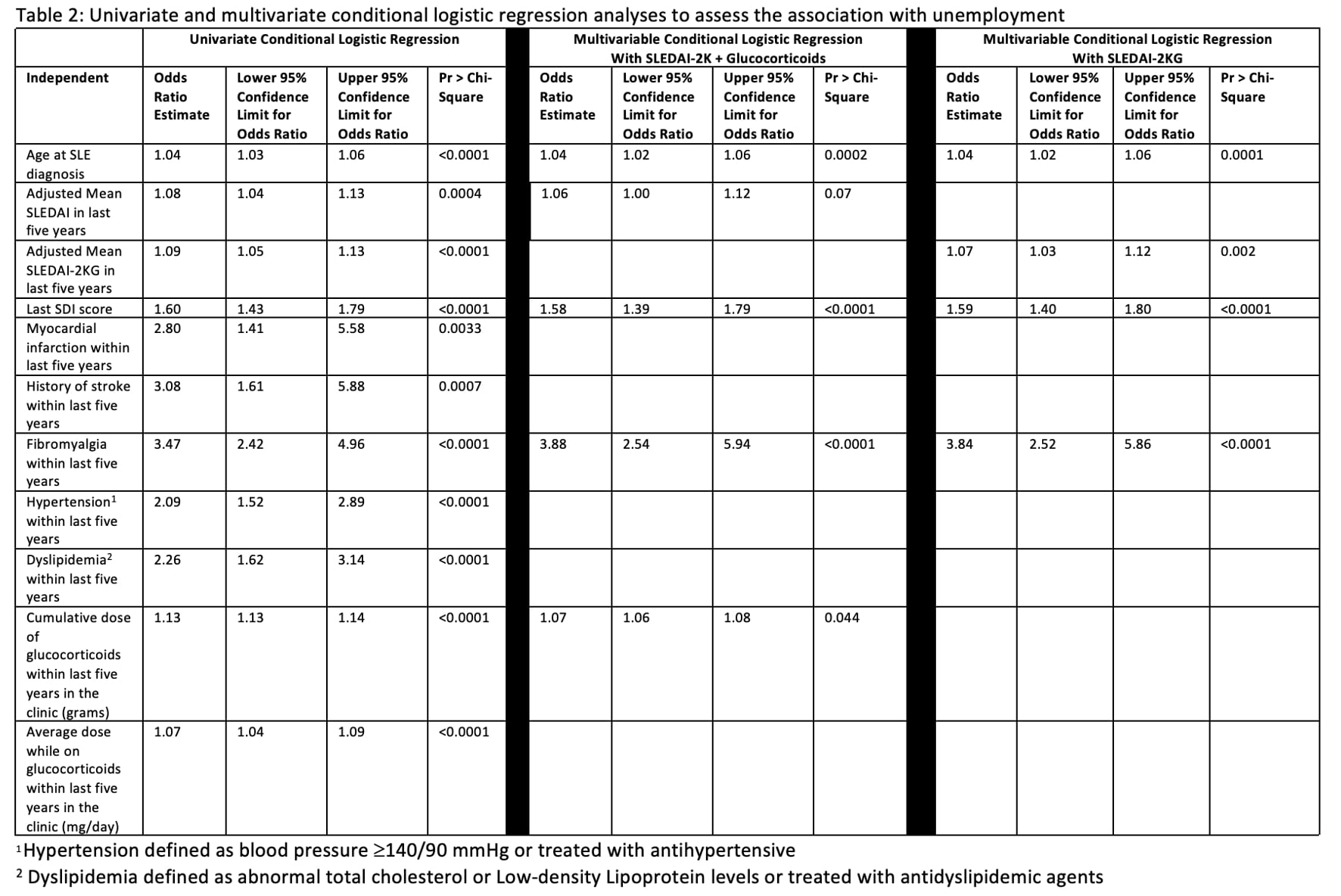
Results: The demographics of 775 patients were represented in Table 1. Patients in the unemployed group showed significantly greater disease activity (higher adjusted mean SLEDAI-2K and SLEDAI-K Glucocorticoid index (SLEDAI-2KG) in the past five years and greater damage by SDI). Patients were also found to have a significantly higher prevalence of myocardial infarction, stroke, fibromyalgia, hypertension, and higher daily and cumulative glucocorticoid use. In the multivariable analysis (Table 2), age at SLE diagnosis (OR, 95% CI: 1.04,1.02-1.06), adjusted mean SLEDAI-2KG in past five years (OR, 95% CI: 1.07, 1.03-1.12), SDI (OR, 95% CI: 1.59, 1.40-1.80) and prevalence of fibromyalgia (OR, 95% CI: 3.84, 2.52, 5.86) were associated with the increased risk of unemployment. We conducted additional modeling where adjusted mean SLEDAI-2KG was substituted by adjusted mean SLEDAI-2K and cumulative glucocorticoid dose in the past five years, and the results were similar to the previous model.
Conclusion: High disease activity, damage and use of glucocorticoids were associated with an increased likelihood of patients being unemployed. Similarly, fibromyalgia was strongly associated with a patient being unemployed. Employment status may be improved by better control of SLE disease activity and management of fibromyalgia and other risk factors.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Maddock C, Nowrouzi-Kia B, Su J, Touma Z. Factors Associated with Employment and Work Disability in Patients with SLE: A Nested Case-control Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/factors-associated-with-employment-and-work-disability-in-patients-with-sle-a-nested-case-control-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/factors-associated-with-employment-and-work-disability-in-patients-with-sle-a-nested-case-control-study/