Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Neuropilin-1 (NRP-1) is a transmembrane glycoprotein that acts as a receptor of class III/IV semaphorins which role in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases. The NRP-1 has been studied for its immunomodulatory activity in malignancy, but there have been limited studies on the role of autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic disease, including systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). This study was aimed to investigate the expression and the clinical implication of NRP-1 in lupus mouse models and patients with SLE.
Methods: The expression of NRP-1 was measured in T cells in spleen and renal tissue and monocyte-induced dendritic cells from control mouse and TLR-7 agonist-induced lupus mouse by flow cytometry, PCR, and immunofluorescence. CD4+ T cells from human peripheral blood were isolated to investigate the expression of NRP-1 in healthy control and the patients with SLE (n=40). In vitro analysis, the activation of the JAK-STAT pathway was examined in monocyte-induced dendritic cells treated with TLR-7 agonists with or without NRP-1 receptor antagonists.
Results: The frequency of NRP-1 positivity in CD4+ T cells in spleen was significantly higher in lupus mouse group compared to vehicle mouse group. The quantitative analysis of NRP-1 fluorescence intensity in the kidney, and monocyte-derived dendritic cells isolated from bone marrow revealed an increased level in the lupus group compared to the control group.
The CD4+ T cells from peripheral blood mononuclear cells in the patients with lupus also showed significantly higher frequency of NRP-1 positive CD4+ T cells than those from healthy controls. Comparing the correlation of the expression of NRP-1 and disease activity with SLEDAI, C3, C4, and anti-DNA antibodies, the significant correlation between NRP-1 and disease activity markers were confirmed.
In vitro analysis of monocyte-derived dendritic cells, the phosphorylation of STAT and expression of NRP-1 were enhanced by treatment of TLR7 agonist and these expressions were decreased by co-treatment of EG00229, which is an NRP-1 receptor antagonist.
Conclusion: Our results show that NRP-1 is involved in the phosphorylation of STATs activated by TLR-7 agonists, and the expression of NRP-1 significantly correlates with the disease activity of patients with SLE.
These results indicate the significant contribution of NRP-1 in the pathogenesis of SLE and the potential of targeting NRP-1 for the treatment of SLE.
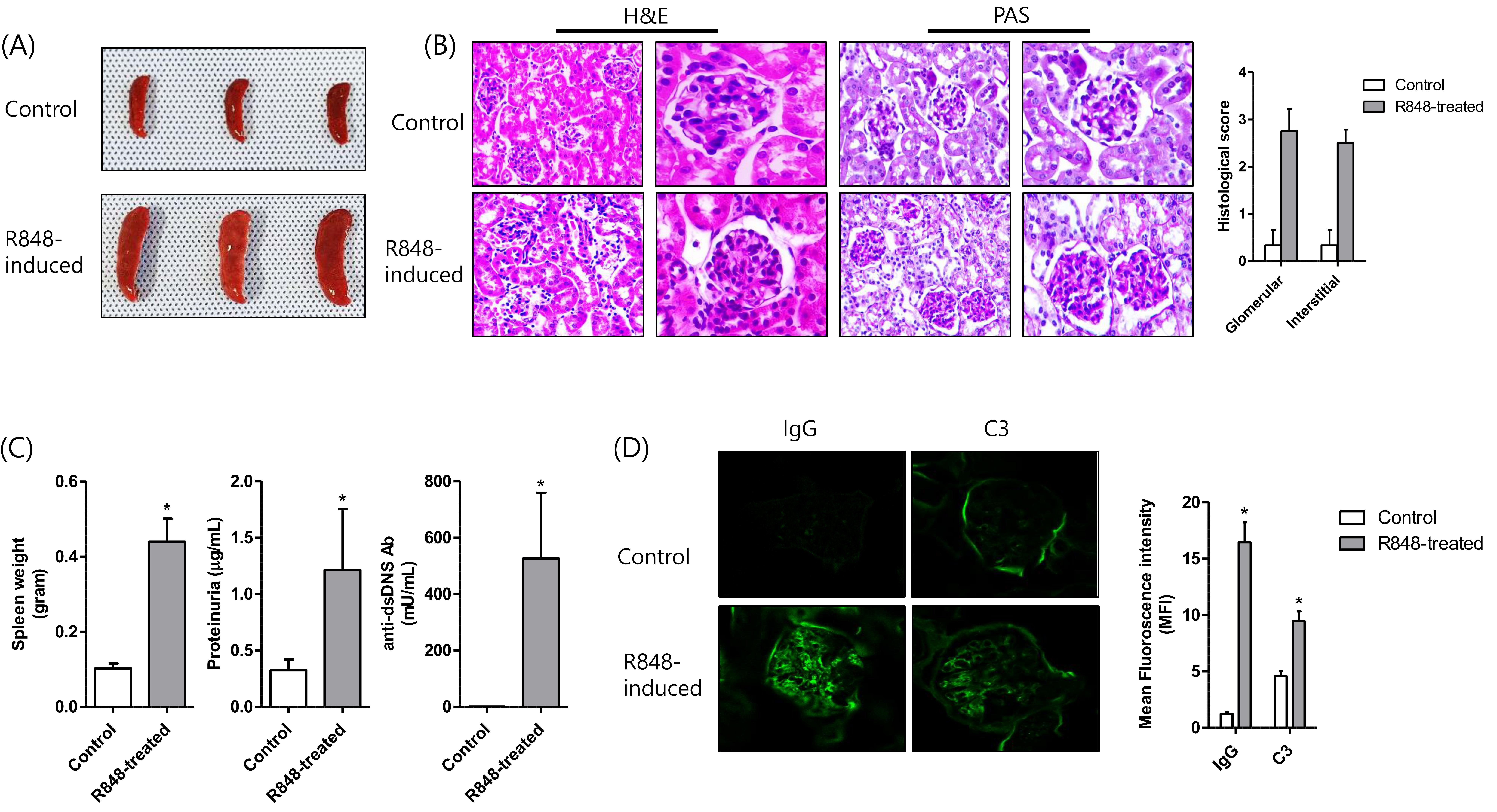 Toll-Like Receptor 7 agonist-induced lupus model
Toll-Like Receptor 7 agonist-induced lupus model
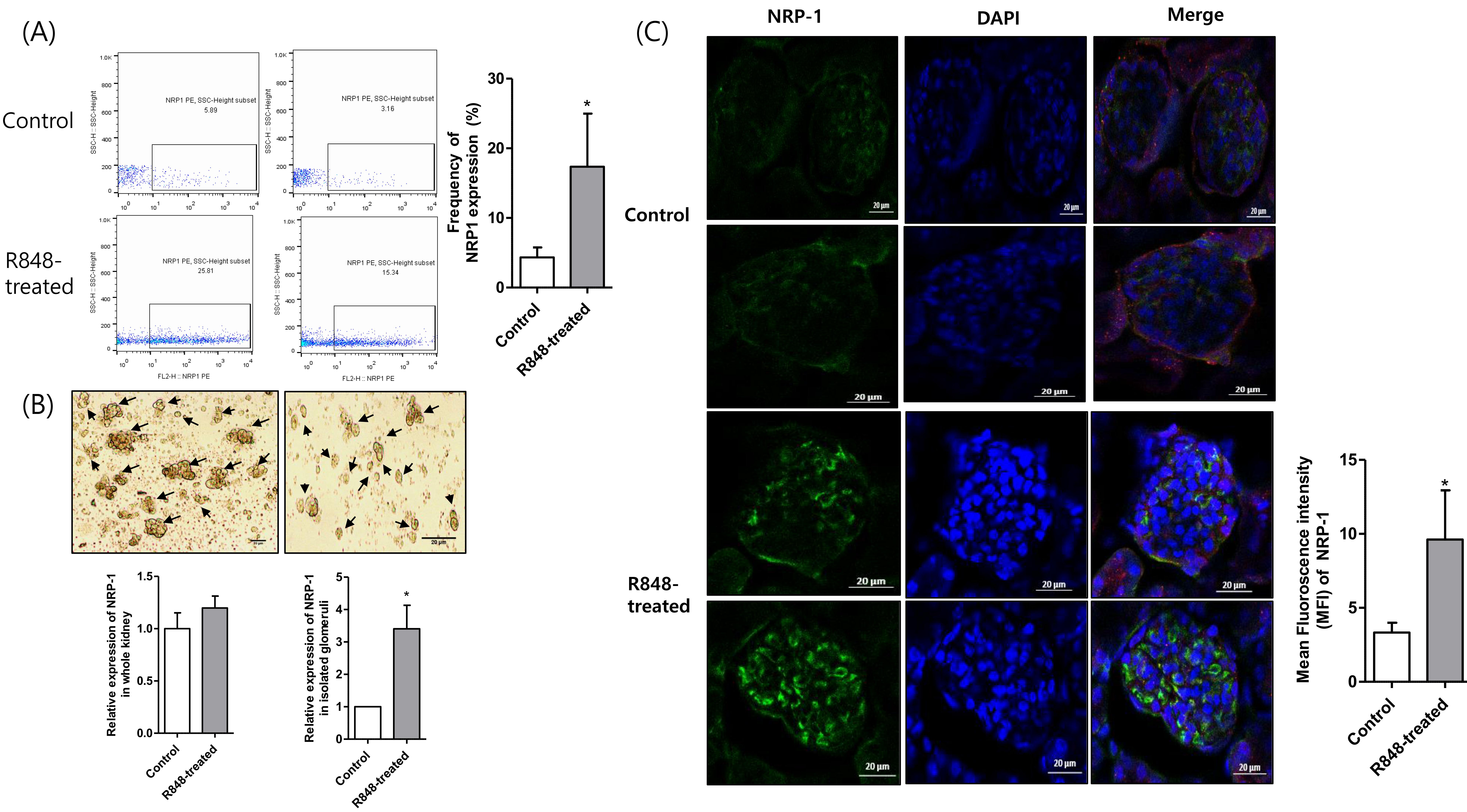 Upregulated expression of NRP_1 in spleen and kidney of lupus murine model
Upregulated expression of NRP_1 in spleen and kidney of lupus murine model
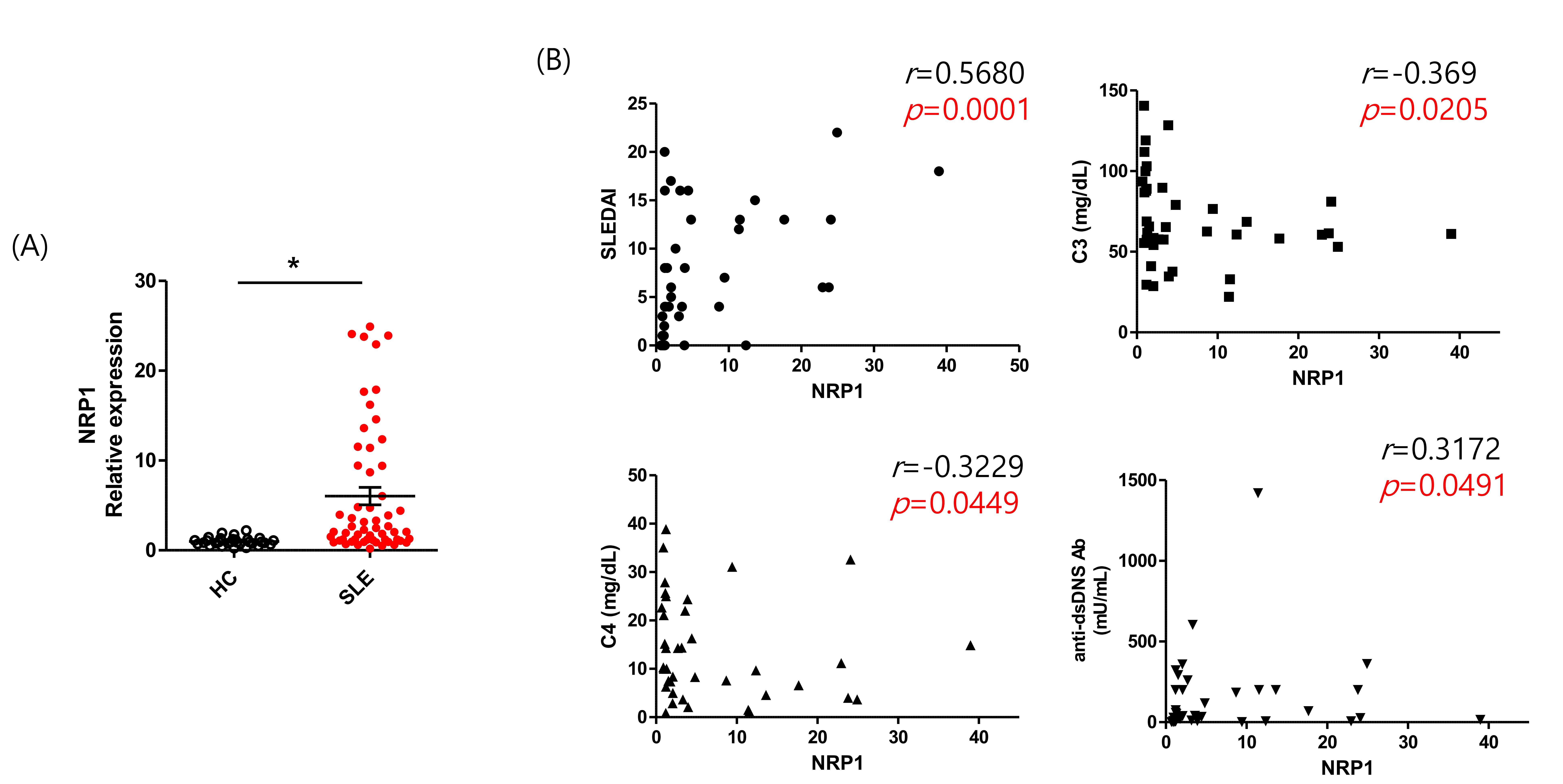 The correlation of NRP_1 expression and disease activity in the patients with SLE
The correlation of NRP_1 expression and disease activity in the patients with SLE
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Choi Y, Lee E, Lee Y, Lee M, Lee C, Chung C, yoo W. Expression of Neuropilin-1 Is Significantly Increased in Dendritic Cells and CD4 + T Cells and It Correlates Disease Activity in the Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/expression-of-neuropilin-1-is-significantly-increased-in-dendritic-cells-and-cd4-t-cells-and-it-correlates-disease-activity-in-the-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/expression-of-neuropilin-1-is-significantly-increased-in-dendritic-cells-and-cd4-t-cells-and-it-correlates-disease-activity-in-the-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/
