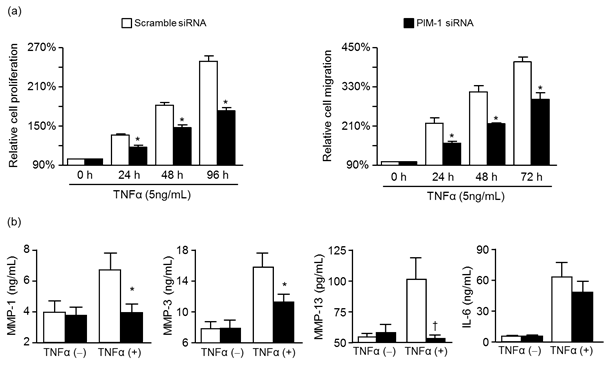Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2015
Title: Cytokines, Mediators, Cell-cell Adhesion, Cell Trafficking and Angiogenesis Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The Proviral
Integration site of Moloney murine leukemia virus (PIM) kinases are important
mediators of cell survival and considered as attractive targets in cancer chemotherapy.
Their implication has not been studied in the function of rheumatoid arthritis
(RA)-fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS).
Methods: Immunoblot or
quantitative real-time RT-PCR was performed to investigate the expression of 3
isoforms of PIM kinases (PIM-1, PIM-2, and PIM-3) in of RA- and osteoarthritis
(OA)-FLS. The presence of PIM-1 was confirmed using immunostaining on synovial
tissue from RA and OA patients. After knockdown of PIM-1 using siRNA, proliferation
and migration assay were carried out. Additionally, matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs)
and interleukin (IL)-6 secretion was measured using ELISA from RA-FLS
transfected with control or PIM-1 siRNA.
Results: Among PIM kinases,
PIM-1 was most strongly induced by IL-6 stimulations in RA-FLS. The expression
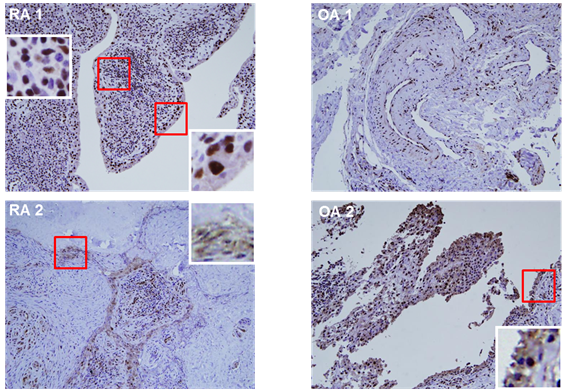
of PIM-1 protein was higher in RA-FLS than in OA-FLS. In the synovial tissues
from RA patients, PIM-1 was immunostained in the synovial lining layer and
mononuclear cells (Fig. 1). When RA-FLS with PIM-1 knockdown were stimulated
with TNF-a, RA-FLS proliferation or migration was
significantly decreased (Fig. 2). Moreover, the production of MMP-1, MMP-3, and
MMP-13 was significantly suppressed in RA-FLSs with PIM-1 knockdown (Fig. 2).
IL-6 production from PIM-1 knockdown RA-FLS was also reduced, but statistically
insignificant.
Conclusion: These results suggest
that PIM-1 is involved in the survival, migration, and matrix-degradation of
RA-FLS and PIM-1 could be a potential target for RA treatment.
Fig. 1. The immunohistochemical
staining of PIM-1 kinase in the synovial tissue from 2 RA and 2 OA patients.
Fig. 2. The effect of PIM-1
on RA-FLS. (a) Under the stimulation with TNF-a,
proliferation and migration was significantly inhibited in PIM-1
siRNA-transfected RA-FLS. (b) PIM-1 knockdown also significantly suppressed the
secretion of MMP-1, MMP-3, and MMP-13 from RA-FLS stimulated with TNF-a in serum-free media.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Choi YS, Ha YJ, Hur J, Kang EH, Song YW, Lee YJ. Expression and Function of Proviral Integration Site for Moloney Murine Leukemia Virus 1 (PIM-1) Kinase in Rheumatoid Arthritis Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/expression-and-function-of-proviral-integration-site-for-moloney-murine-leukemia-virus-1-pim-1-kinase-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-fibroblast-like-synoviocytes/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/expression-and-function-of-proviral-integration-site-for-moloney-murine-leukemia-virus-1-pim-1-kinase-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-fibroblast-like-synoviocytes/