Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Clinical Aspects Poster I: Treatment Patterns and Response
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Baricitinib (BARI), an oral inhibitor of Janus kinase (JAK)1 and JAK2, is being developed for the treatment of RA. RA-BEGIN (NCT01711359) was a phase 3, double-blind, three-arm, multicenter study of BARI administered as monotherapy or in combination with methotrexate (MTX) to patients with early active RA who had no or limited treatment with MTX; MTX monotherapy was the active comparator. This analysis was conducted to identify factors associated with risk of radiographic progression in an early RA population after 52 weeks of treatment with BARI 4mg monotherapy, MTX monotherapy, or a combination of the two drugs.
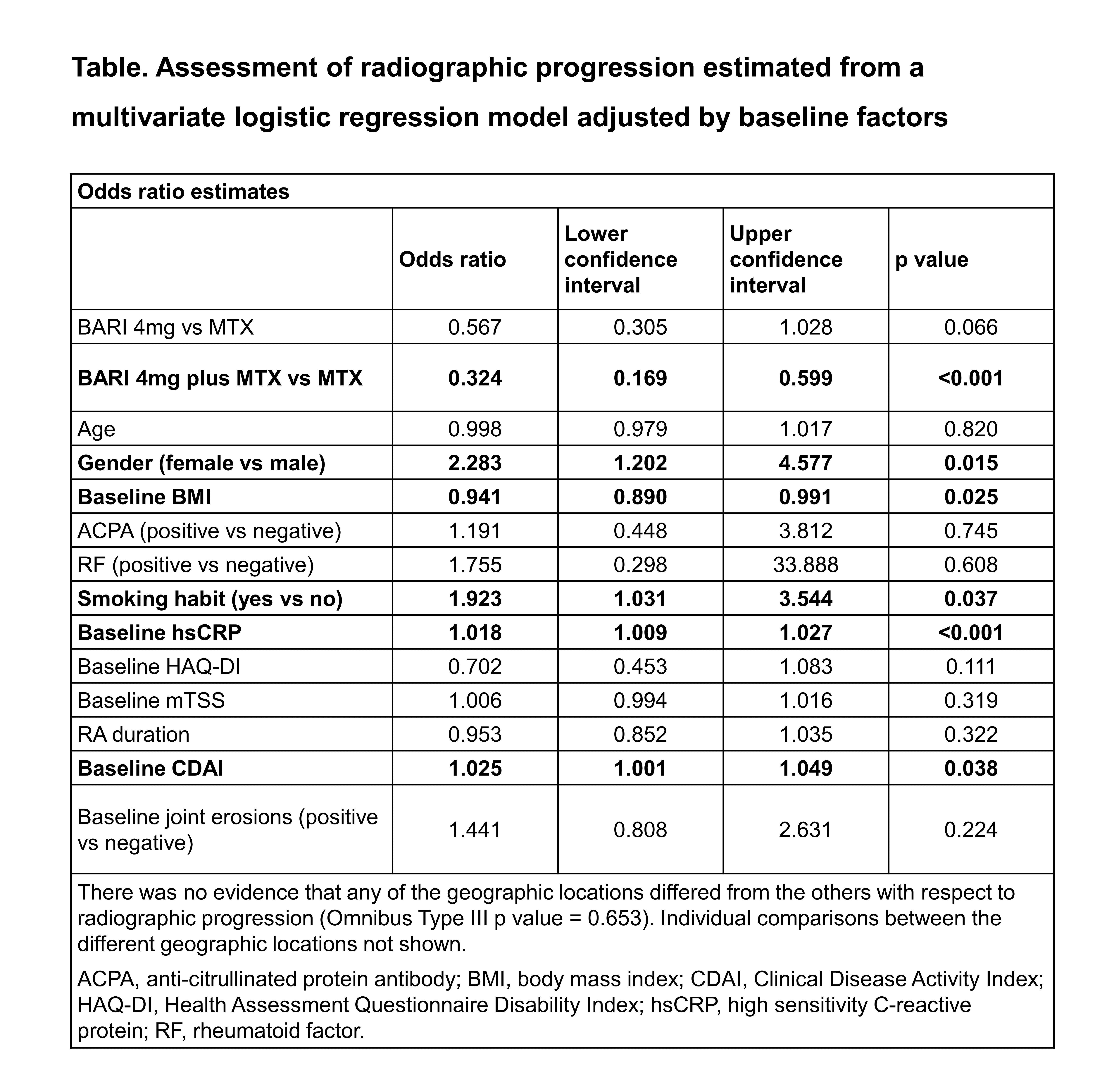
Methods: Radiographic progression was defined as change from baseline (CFB) greater than the smallest detectable change (SDC) in van der Heijde-modified total Sharp score (mTSS) at week 52. The SDC in mTSS in the RA-BEGIN modified intent-to-treat population at week 52 was 1.4. Missing mTSS data at week 52 were imputed using linear extrapolation based on baseline data and the most recent radiographic data before the missed radiograph. Data for 39/584 patients with completely missing radiographic data were omitted from the analysis. The association of different baseline factors with radiographic progression was assessed using a multivariate logistic regression model including: treatment, age, gender, BMI, ACPA (≤10U/ml negative; >10U/ml positive), RF (≤14IU/ml negative; >14IU/ml positive), presence of joint erosions (yes/no), smoking habit (yes/no), hsCRP, HAQ-DI, mTSS, RA duration, CDAI, and geographic location.
Results: Radiographic progression at week 52 was seen in 21.9% (MTX), 14.9% (BARI 4mg) and 10.1% (BARI 4mg plus MTX) of patients. Female gender, smoking habit, higher hsCRP at baseline (Fig), higher CDAI at baseline (Fig) and lower BMI at baseline were significantly associated with an increased risk of radiographic progression (Tab).
Conclusion: In patients with early RA and no or limited previous use of MTX who were treated with MTX, Bari 4 mg, or Bari 4mg plus MTX, risk factors for radiographic progression can be identified. After multivariate adjustment, female gender, smoking, baseline hsCRP, CDAI and BMI showed a statistically significant association with radiographic progression.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
van der Heijde D, Durez P, Schett G, Naredo E, Østergaard M, Meszaros G, Lopez-Romero P, de Leonardis F, Fleischmann R. Exploratory Analysis to Identify Factors Associated with Risk of Structural Progression, Defined As Change from Baseline [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/exploratory-analysis-to-identify-factors-associated-with-risk-of-structural-progression-defined-as-change-from-baseline/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/exploratory-analysis-to-identify-factors-associated-with-risk-of-structural-progression-defined-as-change-from-baseline/