Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: F759 mice with single amino-acid substitution in IL-6 receptor gp130 (Y759F) develops features of autoimmune disorders like arthritis, multiple sclerosis due to IL-17A and IL-6 mediated synergistic activation of positive-feedback loop of STAT3 and NF-kB signaling (inflammation amplifier) in non-immune cells like fibroblasts1. IL17A activates epiregulin/ErbB1 axis, which in turn triggers activation of multiple growth factors like Placental Growth Factor (PLGF), amphiregulin. These growth factors contribute to this amplification loop in Rheumatoid Arthritis patients2 and blocking them abrogates inflammation in animal models3. In this study, we explored the possiblity whether this inflammation amplifier loop is playing a role in synovitis of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Enthesitis Related Arthritis (JIA-ERA) by estimating PLGF in sera and synovial fluid(SF) of patients.
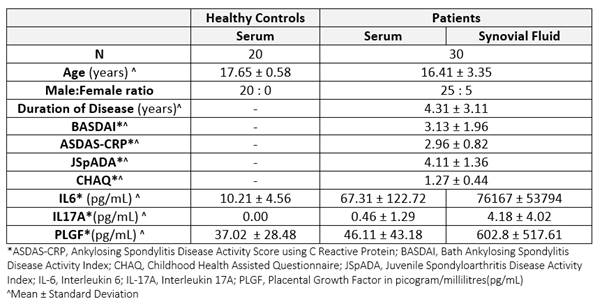
Methods: Sera and Synovial Fluid(SF) of 30 adolescents of JIA-ERA, diagnosed as per ILAR classification, with effusion undergoing therapeutic aspiration were collected and stored between October 2016-April 2018. Disease activity were measured. Levels of IL6, IL17A and PLGF were measured by ELISA. IL6, IL17A and PLGF Kits were procured from BD Biosciences (IL6) and Biolegend Inc.(IL17A and PLGF), San Diego, CA. Sensitivity of the assays were 4.7 picogram(pg)/millilitres(mL), 2 pg/mL and 6.3 pg/mL respectively.
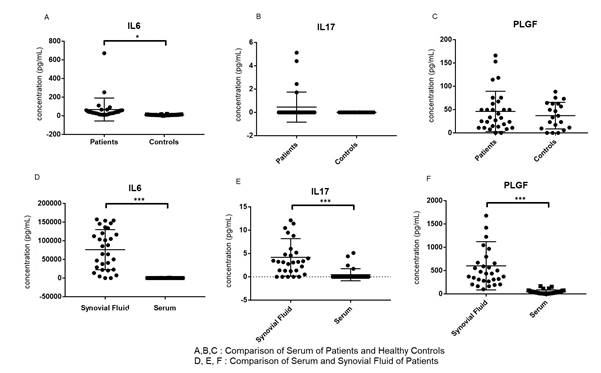
Results: The mean age of patients and controls were 16.41 ± 3.35 years and 17.65 ± 0.58 years respectively (p= 0.11). Mean duration of disease was 4.31 years. Two third of the patients were on NSAIDS and few were on Disease Modifying Drugs. JSpADA and ASDAS CRP of the patients were 4.11 ± 1.36, 2.96 ± 0.82 suggesting active disease with moderate disease activity. IL6, IL17A and PLGF were significantly higher in SF as compared to serum (p<0.0001 for each). However, only IL6 was significantly higher in serum of patients as compared to healthy controls (IL6, p<0.001; IL17A, p = 0.092; PLGF, p=0.655). Serum IL6 correlates with SF PLGF (r=0.460, p=0.01) and Serum IL17A(r=0.443, p=0.01). However, no correlation of ILs/Growth Factors in SF with disease activity scores were found.
Conclusion: The increased SF levels of IL6, IL17A and PLGF suggest activation of IL6 and IL17A mediated amplification loop in synovial compartment of patients with JIA-ERA. Further study of other growth factors like epiregulin, amphiregulin, norepinephrine is warranted.
1. Ogura, H. et al. Immunity 29, 628–36 (2008)
2. Harada, M. et al. J. Immunol. 194, 1039–46 (2015)
3. Murakami, M. et al. Cell Rep. 3, 946–59 (2013)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mistry R, Kumar S, Majumder S, Kansurkar S, Aggarwal A, Misra R. Evidence of Inflammation Amplification By Interleukin-6 and Interleukin-17A in Synovial Compartment of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis – Enthesitis Related Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evidence-of-inflammation-amplification-by-interleukin-6-and-interleukin-17a-in-synovial-compartment-of-juvenile-idiopathic-arthritis-enthesitis-related-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evidence-of-inflammation-amplification-by-interleukin-6-and-interleukin-17a-in-synovial-compartment-of-juvenile-idiopathic-arthritis-enthesitis-related-arthritis/