Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 9:00AM-9:15AM
Background/Purpose: Since the Phase 3 clinical studies of all three COVID-19 vaccines excluded patients on immunosuppressants or immune-modifying drugs within 6 months of enrollment, data on SLE is virtually absent. Given the potential of disease flares following immunization, there has been hesitancy for vaccination in patients with rheumatic diseases, including those with SLE. Accordingly, this study was initiated to evaluate seroreactivity and disease flares after COVID-19 vaccination in a multi-ethnic/racial cohort of patients with SLE.
Methods: 90 patients from the NYU Lupus cohort and 20 healthy controls who received a complete COVID-19 vaccine schedule were included. IgG seroreactivity to the SARS-CoV-2 Spike receptor-binding domain (RBD) measured by ELISA and SARS-CoV-2 microneutralization assay were used to evaluate B cell responses, and IFN-γ production to assess T cell responses as measured by ELISpot. Disease activity was measured by the hybrid SLE disease activity index (SLEDAI) and flares assigned by the SELENA/SLEDAI flare index.
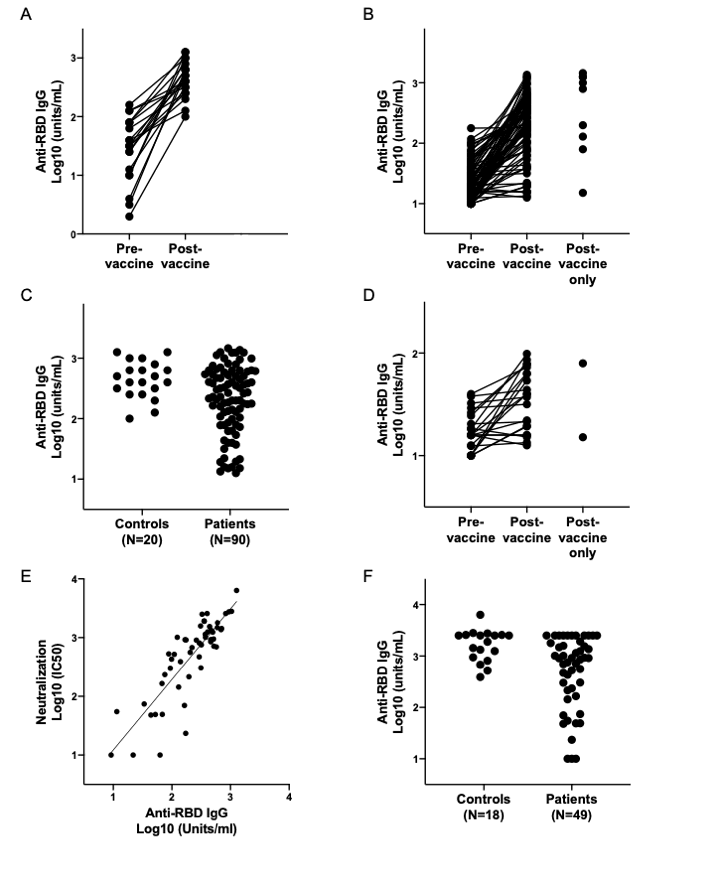
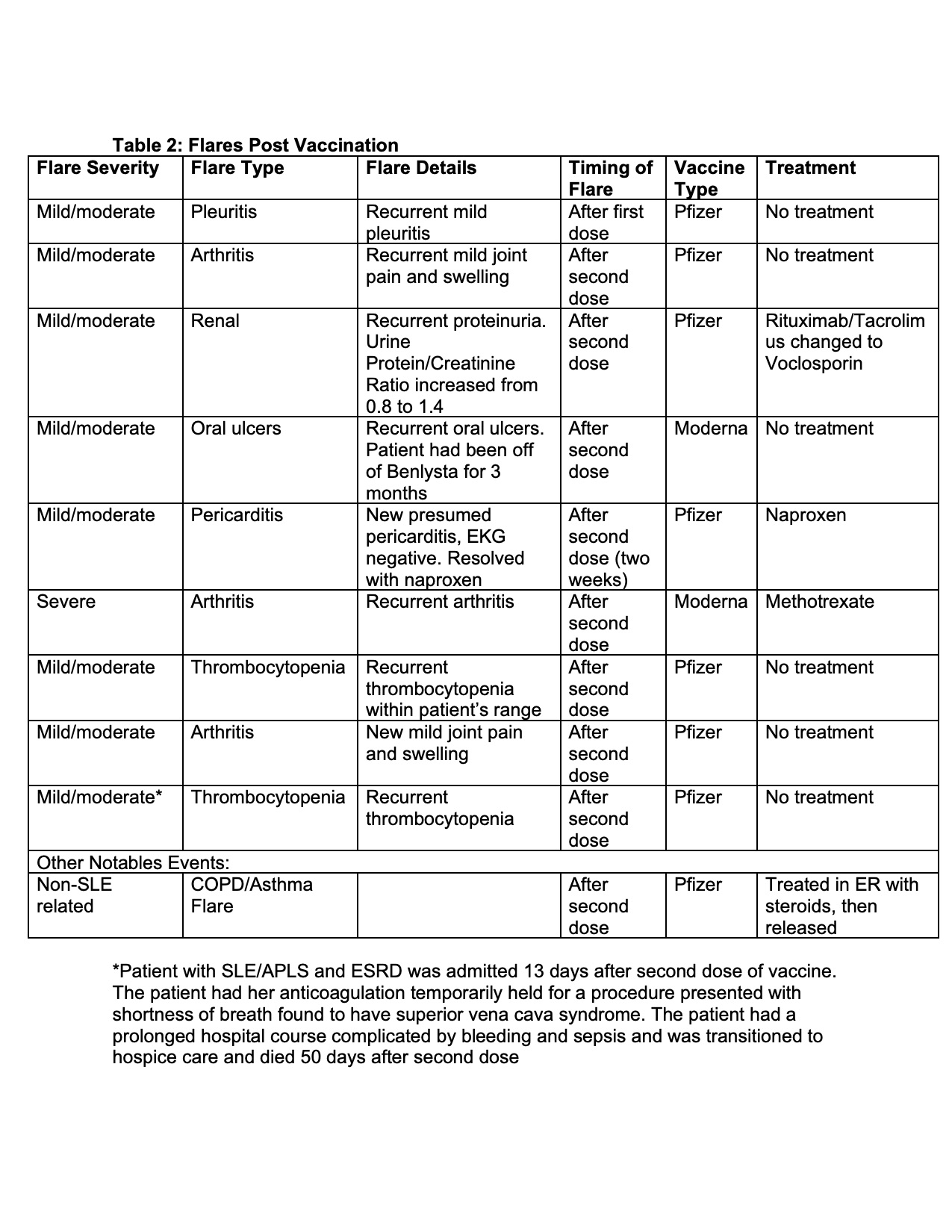
Results: Overall, the mean titers of post-vaccine antibody levels were lower in SLE patients compared to controls (Figure 1). Specifically, 26 (29%) patients generated IgG antibody responses to the SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD that fell below that of the lowest response obtained for the controls (≤100) (Table 1). Factors in the SLE patients which significantly associated with poor responses in bivariate analysis included prednisone use in combination with at least 1 immunosuppressant (p=0.049), a combination of two immunosuppressants (p=0.01), prednisone use (p=0.021), mycophenolate mofetil or mycophenolic acid use (p=0.001), receiving the Jansen/Johnson & Johnson vaccine (p=0.04) and a normal anti-dsDNA level prior to vaccination (p=0.03); only antimalarial use associated with a positive response (p< 0.0001). A logistic regression model of predictors of ELISA response >100 among SLE patients showed that taking antimalarials or no medications [OR 11.8 (95%CI 2.9, 48.5, p=0.0006)], and elevated anti-dsDNA prior to vaccination [OR 7.8 (95%CI 2.9, 48.5, p=0.0047)] are independent predictors of vaccine response. IgG seroreactivity to the SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD strongly correlated with the SARS-CoV-2 microneutralization assay (R=0.81; p< 0.0001, Figure 1) and correlated with the ELISpot (R=0.57; p=0.0135). In a subset of patients with poor antibody responses, IFN-γ production was likewise diminished. In aggregate, there was no change in post-vaccination SLEDAI scores compared to those measured pre-vaccination. Only 11% of patients were considered to have post vaccination disease flares; 1% severe (further details in Table 2).
Conclusion: In a multi-ethnic/racial study of SLE patients nearly 30% had a low response to the COVID-19 vaccine. Having a normal anti-dsDNA and taking any medications other than antimalarials independently associated with a decreased vaccine response. Reassuringly, disease flares were rare. While minimal protective levels remain unknown, these data suggest protocol development to assess efficacy of booster vaccination.
 MTX=Methotrexate, MMF=mycophenolate mofetil, HCQ=hydroxychloroquine, RTX=Rituximab
MTX=Methotrexate, MMF=mycophenolate mofetil, HCQ=hydroxychloroquine, RTX=Rituximab
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Izmirly P, Kim M, Samanovic-Golden M, Fernandez Ruiz R, Ohana S, Engel A, Deonaraine K, Masson M, Xie X, Cornelius A, Herati R, Haberman R, Scher J, Guttmann A, Blank R, Plotz B, Haj-Ali M, Banbury B, Stream S, Hasan G, Ho G, Rackoff P, Blazer A, Belmont H, Saxena A, Mulligan M, Clancy R, Buyon J. Evaluation of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Response in a Multi-Racial/Ethnic Cohort of Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-sars-cov-2-vaccine-response-in-a-multi-racial-ethnic-cohort-of-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-sars-cov-2-vaccine-response-in-a-multi-racial-ethnic-cohort-of-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/