Session Information
Date: Monday, November 6, 2017
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy I: Outcomes Therapy
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-4:00PM
Background/Purpose: Clinical guidelines recommend pneumococcal and tetanus vaccinations in patients (pts) with RA.1 Baricitinib (bari) is an oral, selective Janus kinase (JAK) 1/JAK 2 inhibitor and is approved in the EU for the treatment of moderately to severely active RA in adults. The objective of this substudy was to evaluate pneumococcal conjugate and tetanus toxoid vaccine responses in pts with RA receiving bari. These vaccines elucidate predominantly T-cell-dependent humoral antibody responses.2
Methods: Eligible RA pts in a Phase 3 long-term extension (LTE) trial (RA-BEYOND) in US/Puerto Rico receiving bari 2 or 4 mg with or without concomitant MTX were enrolled. Baseline antibody titers were measured and pts were vaccinated with Prevnar 13® (Pneumococcal 13-valent Conjugate Vaccine [Diphtheria CRM197 Protein]; Wyeth; PCV13) and Boostrix® (Tetanus Toxoid Vaccine, Reduced Diphtheria Toxoid, and Acellular Pertussis Vaccine, Adsorbed; GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals; Tdap). The primary endpoints were the proportion of pts achieving a satisfactory humoral response defined as 1) a ≥2-fold increase in anti-pneumococcal antibody titers in ≥6/13 serotypes and 2) a ≥4-fold increase in anti-tetanus titers at 5 wks post-vaccination.
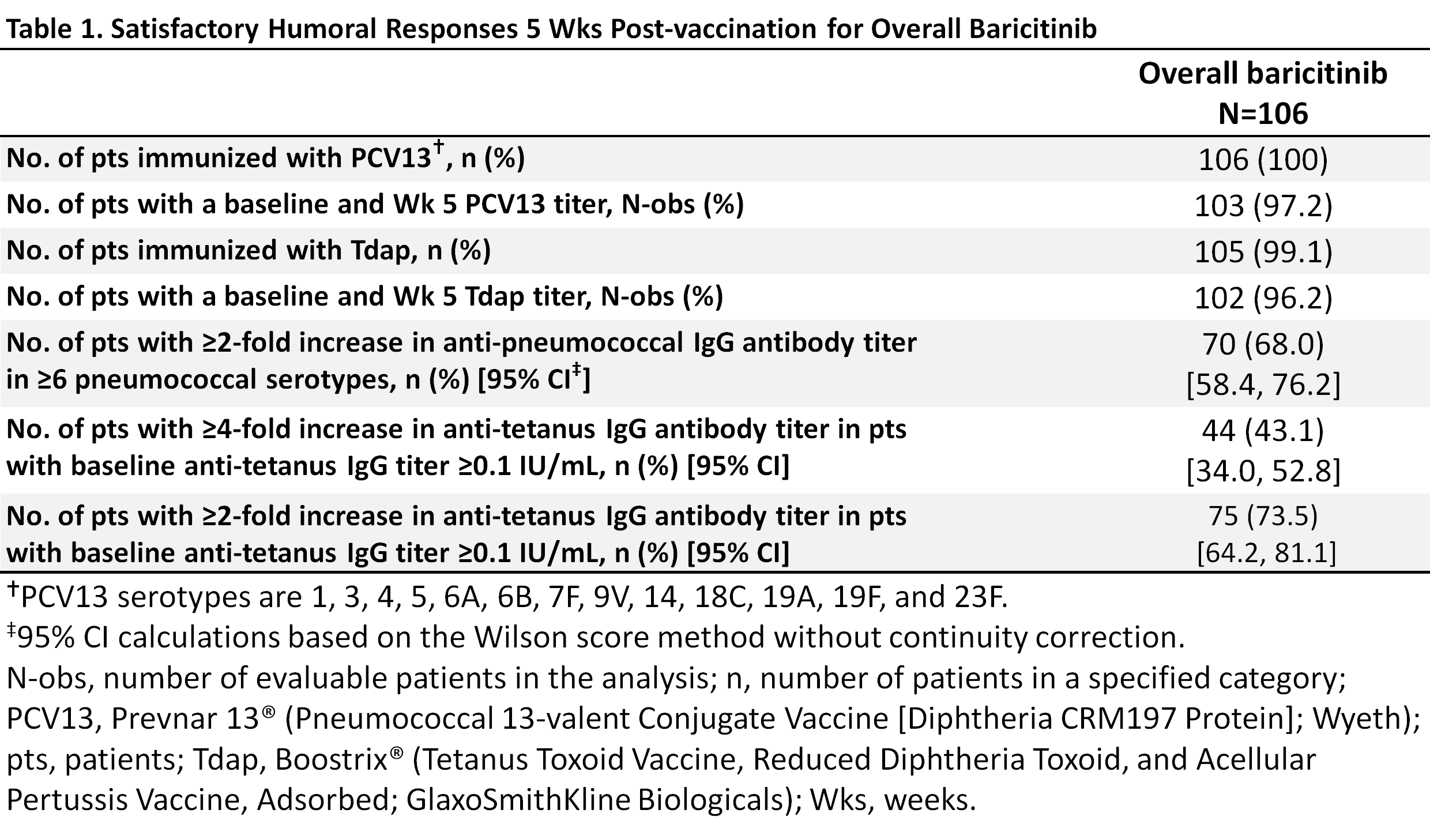
Results: Of the 106 pts, 80% were female, 32 (30.2%) were taking glucocorticoids, with a mean age of ~55 yrs and a mean duration of RA ~12 yrs; 89% (N=94) were taking bari+MTX and 11% (N=12) were taking bari without MTX. Most pts (97% PCV13/96% Tdap) completed the evaluations (Table 1). The small size of the bari without MTX group precluded subgroup analysis; response in the overall group is reported here. Over two-thirds of pts (68.0%; 95% CI, 58.4, 76.2) achieved a positive response in ≥6/13 PCV13 serotypes (Table 1). Forty-three percent (43.1%; 34.0, 52.8) achieved a ≥4-fold increase in anti-tetanus titers and 73.5% (64.2, 81.1) achieved a ≥2-fold increase (Table 1). Through 12 weeks post-vaccination, 7 pts (6.6%) reported injection site events possibly related to vaccination. Two pts reported moderate pain. There were no serious adverse events (AE) related to the vaccine. (AE monitoring in the LTE trial was on-going.)
Conclusion: The proportions of pts on long-term bari (89% were on concomitant MTX) who achieved satisfactory humoral response five weeks post-vaccination were 68% for pneumococcal conjugate vaccine and 43% for tetanus toxoid vaccine (a ≥4-fold increase). These responses are broadly in line with responses to PCV13,3 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23),4,5 and tetanus toxoid vaccines2,5 described for other contemporary RA therapies.
References:
1Singh JA et al. Arthritis Care Res 2016;68:1-25.
2Bingham CO et al. 2010 Arthritis Rheum 2010;62:64‑74.
3Rakoczi E et al. Joint Bone Spine 2016;83:675-9.
4Winthrop KL et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2016;75:687-95.
5Bingham CO et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2015;74:818–22.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Winthrop K, Bingham III CO, Bradley JD, Issa M, Klar R, Kartman CE. Evaluation of Pneumococcal and Tetanus Vaccine Responses in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Receiving Baricitinib: Results from a Long-Term Extension Trial Substudy [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-pneumococcal-and-tetanus-vaccine-responses-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-receiving-baricitinib-results-from-a-long-term-extension-trial-substudy/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-pneumococcal-and-tetanus-vaccine-responses-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-receiving-baricitinib-results-from-a-long-term-extension-trial-substudy/