Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Disease activity of psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is affected by many parameters including joint, spinal and skin involvement, enthesitis, dactylitis and pain. According to disease activity indices such as DAPSA, DAS28 and MDA, some patients may not be in remission even though they do not have joint involvement and arthritis.
The aim of this study was to assess the clinical parameters that affect remission in patients with PsA
Methods: This study involved patients with PsA consistent with CASPAR criteria from Turkish League Against Rheumatism (TLAR) Network multi-centre study. The demographic and clinical parameters of patients (pain VAS, patient global VAS, doctor global VAS, tender and swollen joint) were recorded. Maastricht Ankylosing Spondylitis Enthesitis Score (MASES), Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI), fatigue with the VAS (0-10), Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HAD), Fibromyalgia Rapid Screening Tool (FIRST), Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) and Health Assesment Questionnaire (HAQ) were evaluated. DAS28, DAPSA and minimally disease activity (MDA) were used to asses the disease activity and remission. The patients were classified into two groups, according to their remission status and swollen joint count. (group 1 are in remission and no swollen joint; group 2 patients are not in remission and no swollen joint). The Spearman correlation coefficient was used to evaluate the correlations between variables. The Mann-Whitney-U test and Chi-squared test were used for comparison between the groups. P< 0.05 was considered statistically significant. The SPSS22.0 statistic package was used for statistical analysis.
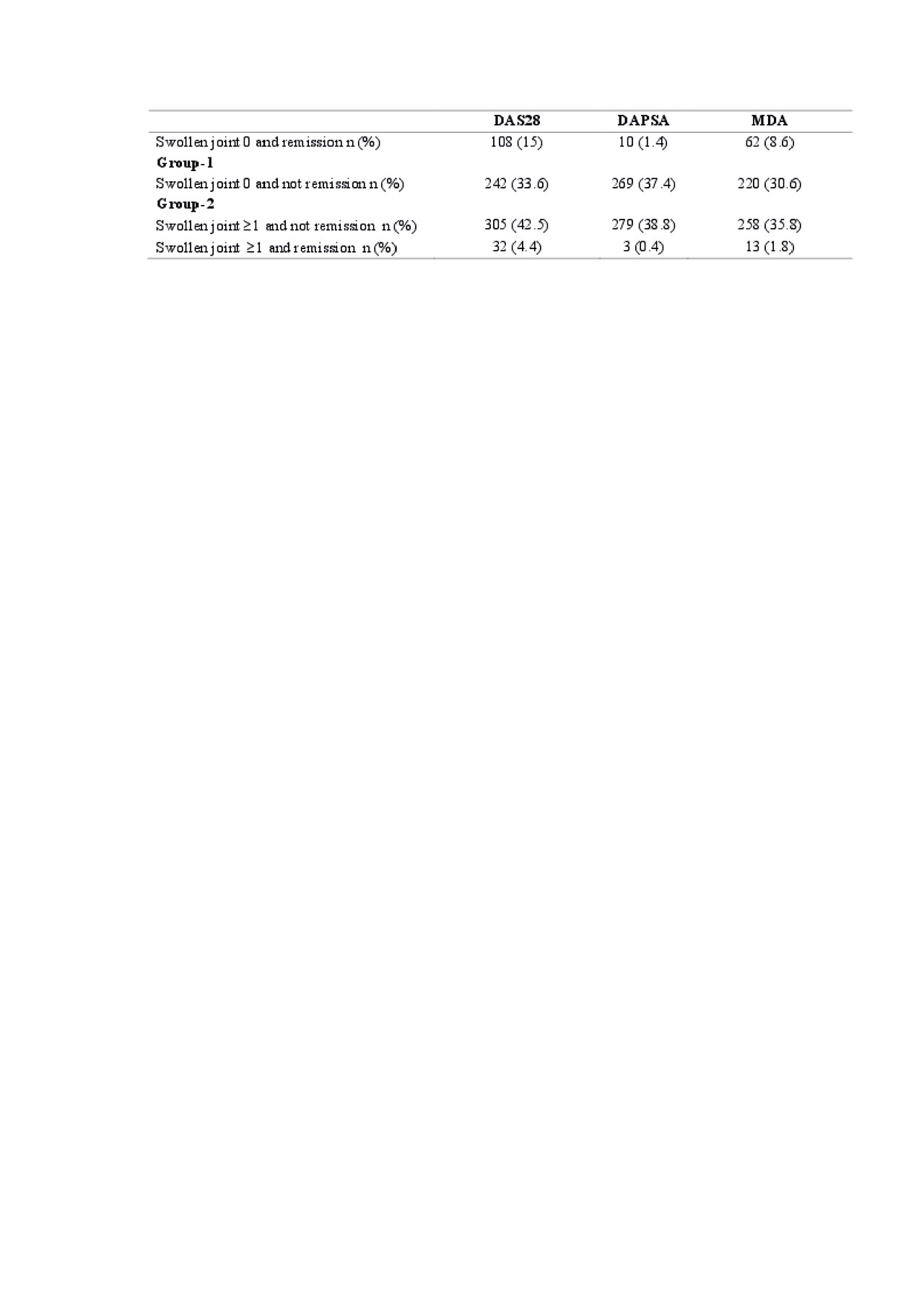
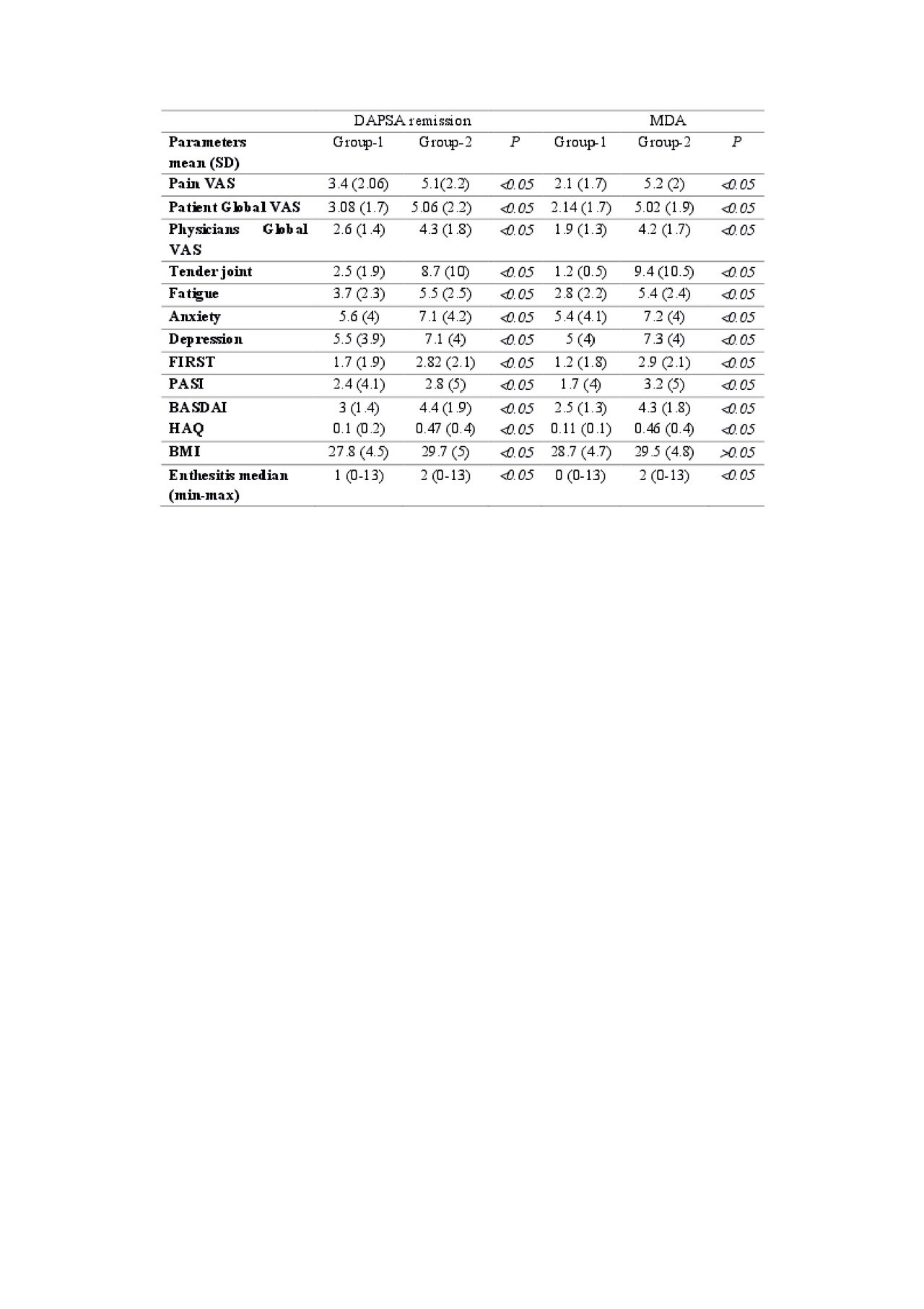
Results: Of 1134 patients diagnosed with PsA, 720 patients ( 471 female (%65.4), 249 male (%34.6) were found to have peripheral involvement. The mean age was 47,6 years (SD:12.03). The median disease duration was 6.47 years (min:0, max:44). DAPSA, DAS28 and MDA scores were obtained in 561, 687 and 553 patients (Table 1). The two groups were similar in terms of age, gender, educational status, disease duration (P >0.05). Group 1 and 2 differed significantly in terms of VAS pain, VAS global pain, VAS doctor global, tender joint count, fatigue, anxiety, depression, FIRST score, PASI, BASDAI, enthesitis and HAQ score (p< 0.05) (Table-2)
Conclusion: PSA may not be in remission even though joint involvement has been controlled. In these patients fatigue, pain, anxiety, depression, fibromyalgia, functional disorders, skin lesions, enthesitis, tender joint and spinal involvement more often than the patients in remission and no active joint involvement. In the evaluation of the disease activity, it is necessary to make evaluations by using composite scales.
References:
1. Coates LC, FitzGerald O, Merola JF, Smolen J, van Mens LJJ, Bertheussen H, et al. Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis/Outcome Measures in Rheumatology Consensus-Based Recommendations and Research Agenda for Use of Composite Measures and Treatment Targets in Psoriatic Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(3):345-55
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gezer H, Duruoz M, Nas K, Kilic E, Sargin B, Acer Kasman S, Alkan H, Sahin N, Cengiz G, Cuzdan N, Albayrak Gezer I, Keskin D, Mulkoglu C, Resorlu H, Sunar I, Bal A, Kucukakkas O, Yurdakul O, Alkan Melikoglu M, Aydin Y, Ayhan F, Bodur H, Calis M, Capkin E, Devrimsel G, Gök K, Hizmetli S, Kamanli A, Keskin Y, Kocabas H, Kutluk O, Sen N, Sendur O, Tekeoglu I, Tolu S, Toprak M, Tuncer T. Evaluation of Clinical and Functional Parameters by Joint Involvement and Remission in Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-clinical-and-functional-parameters-by-joint-involvement-and-remission-in-psoriatic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-clinical-and-functional-parameters-by-joint-involvement-and-remission-in-psoriatic-arthritis/