Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Growing utilization of musculoskeletal ultrasound (MSUS) for the management of rheumatologic disorders has led to integration of dedicated MSUS clinics in many rheumatology practices. However, there is limited published data on patient/physician satisfaction with such clinics and their clinical impact. This study aimed to analyze the performance of our MSUS clinic by assessing (1) reasons for referral, (2) patient/physician satisfaction and (3) subsequent diagnostic and therapeutic impact.
Methods: Patients (pts) and referring rheumatologists anonymously completed and returned a single written in-office questionnaire-based survey, at the end of the visit or study, respectively. For all pts seen for diagnostic MSUS, a retrospective chart review was conducted, and post-MSUS diagnosis and management were documented. Positive MSUS findings, indicative of inflammatory arthritis (IA), were defined as synovitis, tenosynovitis, dactylitis, erosions, synovial thickening or crystal deposition.
Results: Of 48 total pts, seen over 5 months, 23% (n=11) received US guided joint injections and 77% (n=37) had diagnostic US for disease monitoring/management of established IA (n=9) or assessment of subclinical/suspected IA (n=28). Of the 28 pts with suspected IA, 46% (n=13) had MSUS findings of IA, prompting initiation of DMARD (n=8) or prednisone (n=3). Remaining 54% of pts (n=15) had no inflammation on MSUS, leading to de-escalation (n=1) or no escalation of management (n=14). Of 9 pts with established IA, 78% (n=7) showed no active synovitis, with no consequent escalation of management (figure ).
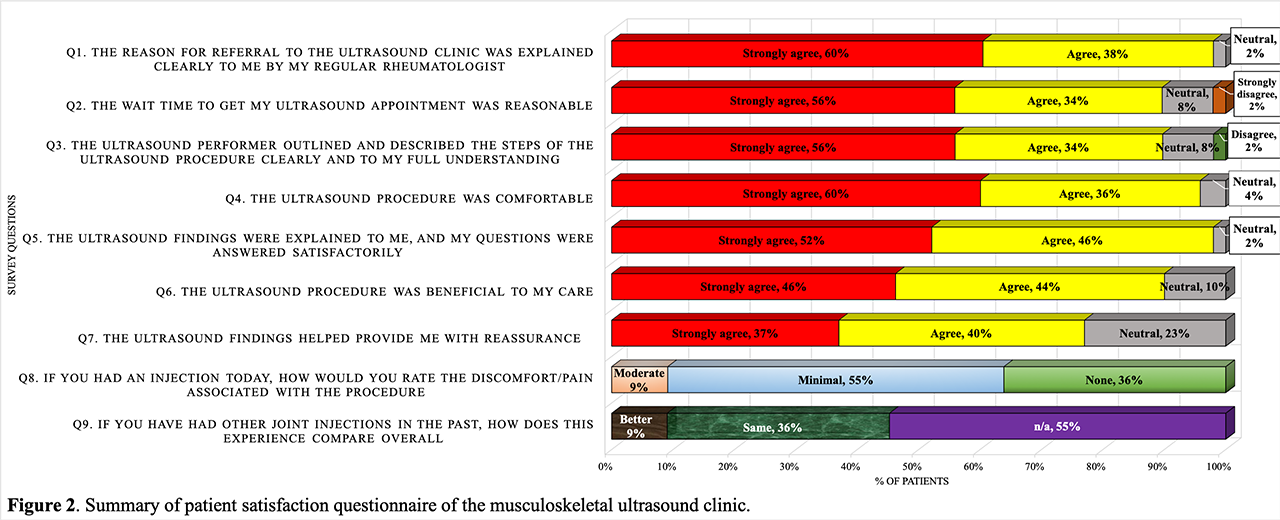
The patient survey had 100% response rate, 9.6 mean satisfaction score (1-10 scale) and > 75% positive feedback (strongly agree or agree) for every question (Q); 89-98% explanation of procedure/results (Q1, 3, 5), 89% appointment wait time (Q2), 95% comfort (Q4), 90% benefit to care (Q6), 77% reassurance (Q7). Of pts who received injections, 82% had minimal to no pain, and 100% had similar to improved overall experience, compared to prior injections (figure 2).
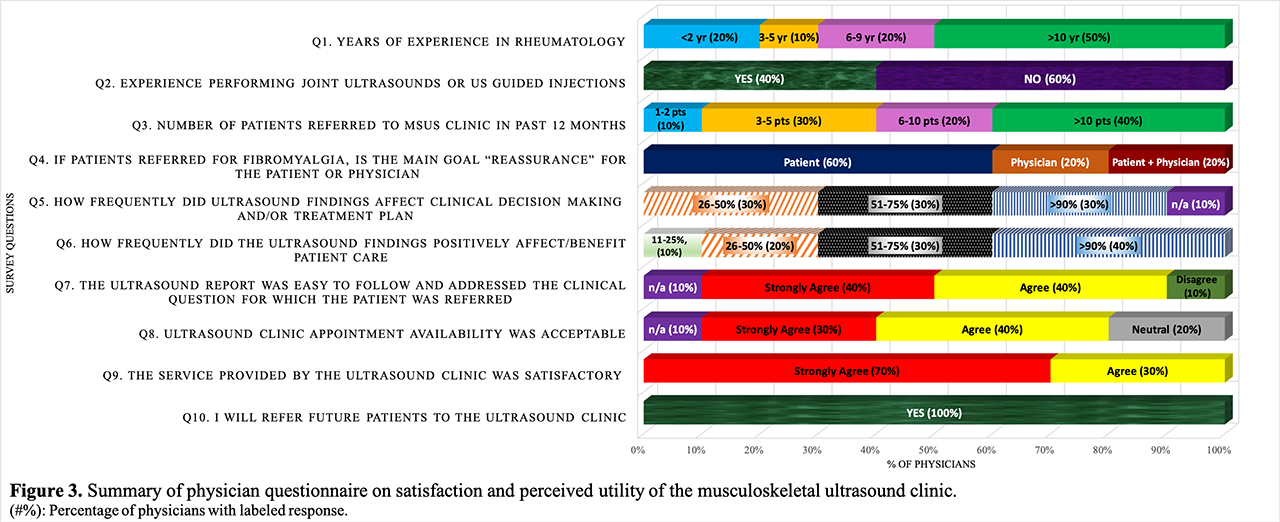
Of the 83% (n=10) physician survey response, 100% indicated plan for future referral (figure 3). The most frequent reason given for referral was assessment of subclinical/suspected IA (n=10), followed by US injections (n=9) and disease monitoring (n=4). The majority of physicians (75%, n=3) with experience performing MSUS referred most often ( >10 pts/12 months). However, in regards to perceived impact on clinical decision making or benefit to patient care, there was no statistical difference between physicians with more MSUS or rheumatology experience, compared to their less experienced colleagues.
Conclusion: The MSUS clinic was most impactful in the evaluation of patients with subclinical/suspected IA. This group of patients comprised the most referrals to the clinic and 46% of patients had positive US findings, which helped to confirm a new diagnosis of IA. Overall, the MSUS clinic received high patient and physician satisfaction scores and was perceived as beneficial to patient care by both patients and referring rheumatologists.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Nensey N, Hassan S. Evaluating the Performance of a Single-site Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Clinic Associated with an Academic Rheumatology Practice: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Impact on Patient Care and Survey of Patient and Physician Satisfaction [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluating-the-performance-of-a-single-site-musculoskeletal-ultrasound-clinic-associated-with-an-academic-rheumatology-practice-diagnostic-and-therapeutic-impact-on-patient-care-and-survey-of-patient/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluating-the-performance-of-a-single-site-musculoskeletal-ultrasound-clinic-associated-with-an-academic-rheumatology-practice-diagnostic-and-therapeutic-impact-on-patient-care-and-survey-of-patient/