Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 10, 2019
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster I: Risk Factors, Predictors, & Prognosis
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: To evaluate the performance of the EULAR definition of arthralgias suspicious for progression to rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in a group of patients admitted to “Reuma-check” ® program with hand arthralgias and to estimate the added value of ultrasound (US) and the determination of antibodies.
Methods: Consecutive patients older than 18 years admitted for predominantly hand arthralgias to “Reuma-check” ® program were included. At baseline, laboratory tests (including ESR, CRP, RF and anti-CCP), US of hands and wrists with power Doppler (PD) technique including 22 joints (bilateral wrist, MCP and PIP) and X-ray of hands and feet were performed. Sociodemographic, clinical and clinimetry data were also collected. EULAR defined characteristics describing arthralgia at risk for RA were recorded: history taking: Joint symptoms of recent onset (duration < 1 year), symptoms located in MCP joints, duration of morning stiffness ≥60 min, most severe symptoms present in the early morning, presence of a first-degree relative with RA; physical examination: difficulty with making a fist, positive squeeze test of MCP joints. Each evaluator (laboratory, images and clinician) was blinded to the data of the other studies. In successive visits, definitive diagnosis of RA according to the ACR/EULAR 2010 criteria was established or not. Only patients with at least 2 visits were included for the final analysis.
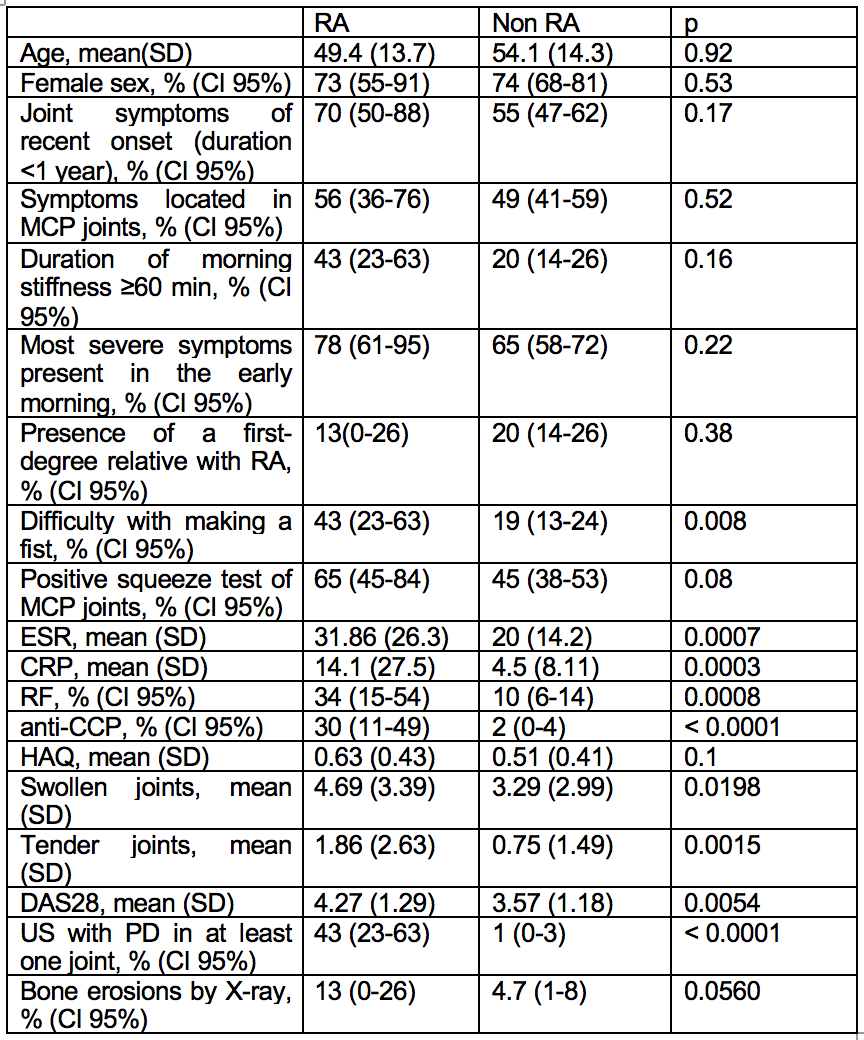
Results: A total of 192 patients were included. 74% were women and mean age was 53 years (SD 14.2). Of the 192 patients, 23 (12%, 95% CI: 7-16) were diagnosed with RA at follow-up. Mean of baseline characteristics describing arthralgia at risk for RA was 3.7 (SD 2.2) in patients with final diagnosis of RA vs 2.7 (SD 1.7) in non-RA patients (p= 0.02). The area under the ROC curve for the EULAR defined characteristics describing arthralgia at risk for RA for the final diagnosis of RA was 0.6302, adding US with PD and anti-CCP data, the area under the ROC curve were 0.6845 (p= 0.0009) and 0.6554 (p= 0.02), respectively. Table shows features associated with final diagnosis of RA. In the multivariate regression logistic analysis, the only features associated with a final diagnosis of RA were anti-CCP (OR: 11, CI 95%: 1.6-74.3) and US with PD in at least one joint assessed (OR: 22.1, CI 95%: 3.7-129.5).
Conclusion: The EULAR definition of arthralgia suspicious for progression to rheumatoid arthritis had an acceptable performance to predict the development of RA in patients with arthralgias in our cohort of patients and improves adding information of both US with PD and anti-CCP. 12% of patients (23/192) were diagnosed as RA at follow-up. Anti-CCP and US with PD were the main features associated with final diagnosis of RA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Torres Chichande J, Ruta S, Sanchez Prado E, Ruta A, Magri S, Salvatori F, Garcia Salinas R. EULAR Definition of “Arthralgia Suspicious for Progression to Rheumatoid Arthritis” in a Cohort of Patients Included in a Program for Rapid Diagnosis: Role of Ultrasound and Antibodies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/eular-definition-of-arthralgia-suspicious-for-progression-to-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-a-cohort-of-patients-included-in-a-program-for-rapid-diagnosis-role-of-ultrasound-and-antibodies/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/eular-definition-of-arthralgia-suspicious-for-progression-to-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-a-cohort-of-patients-included-in-a-program-for-rapid-diagnosis-role-of-ultrasound-and-antibodies/