Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is one of the most prevalent autoimmune and prototypic inflammatory diseases. It is a heterogeneous autoimmune disease with local and systemic features. The molecular triggers for the synovium transition from healthy to inflammatory and then to rheumatoid arthritis are still not clearly defined. Recently, studying synovial tissue in RA is gaining more attention in order to have a better understanding of the early stages of the disease. Transcriptomic profiling of synovial samples is a promising approach to identify reliable biomarkers, assess the effects of medical interventions, and predict the outcomes. One limitation of such an approach is the masking effect of the local gene expression signature by the infiltrating immune cells, thus making it difficult to distinguish the trigger from the consequence. We aimed to establish a combined bioinformatical approach using in house pipeline to process, filter, and combine microarray transcriptomic data to identify novel synovium related biomarkers. The filtered transcriptomic profile was tested by ESTIMATE R package (Estimation of Stromal and Immune cells in MAlignant Tumor tissues using Expression data) to estimate the difference in immune cells infiltration in healthy, Osteoarthritis (OA) and RA.
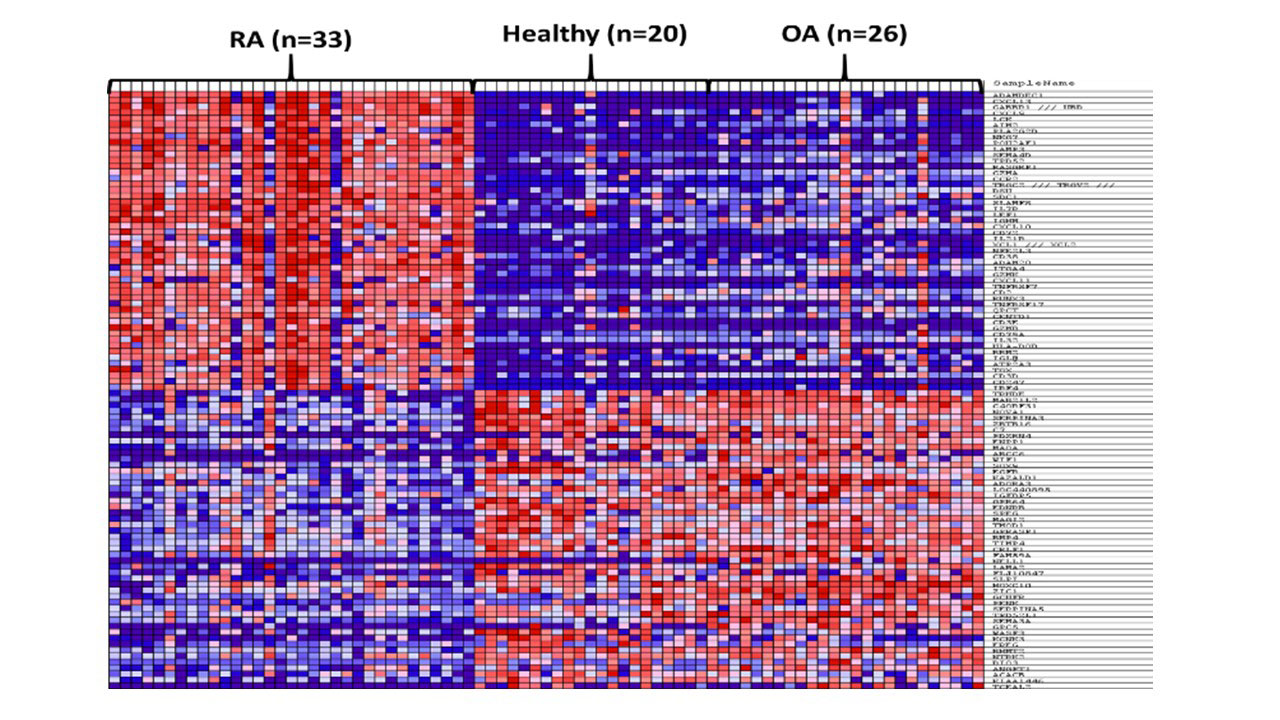
Methods: Gene expression profile of synovial tissue from 33 RA, 26 OA, and 20 healthy controls from three datasets (GSE55235, GSE55457, GSE55584) were extracted using the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) public repository. Raw cell files were re-analyzed using in house pipeline for normalization and variant filtration. Gene Set Enrichment analysis was used to identify genes that are differentially expressed (DEG) between the three groups, as shown in Figure 1.
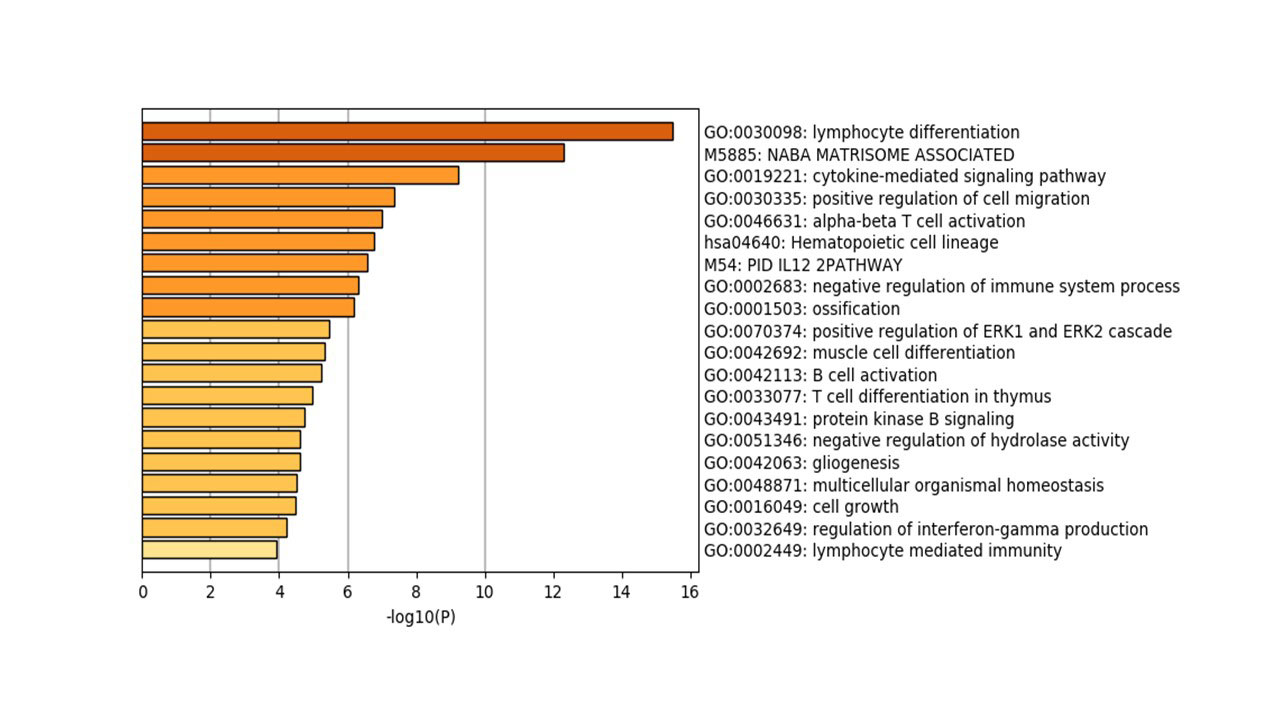
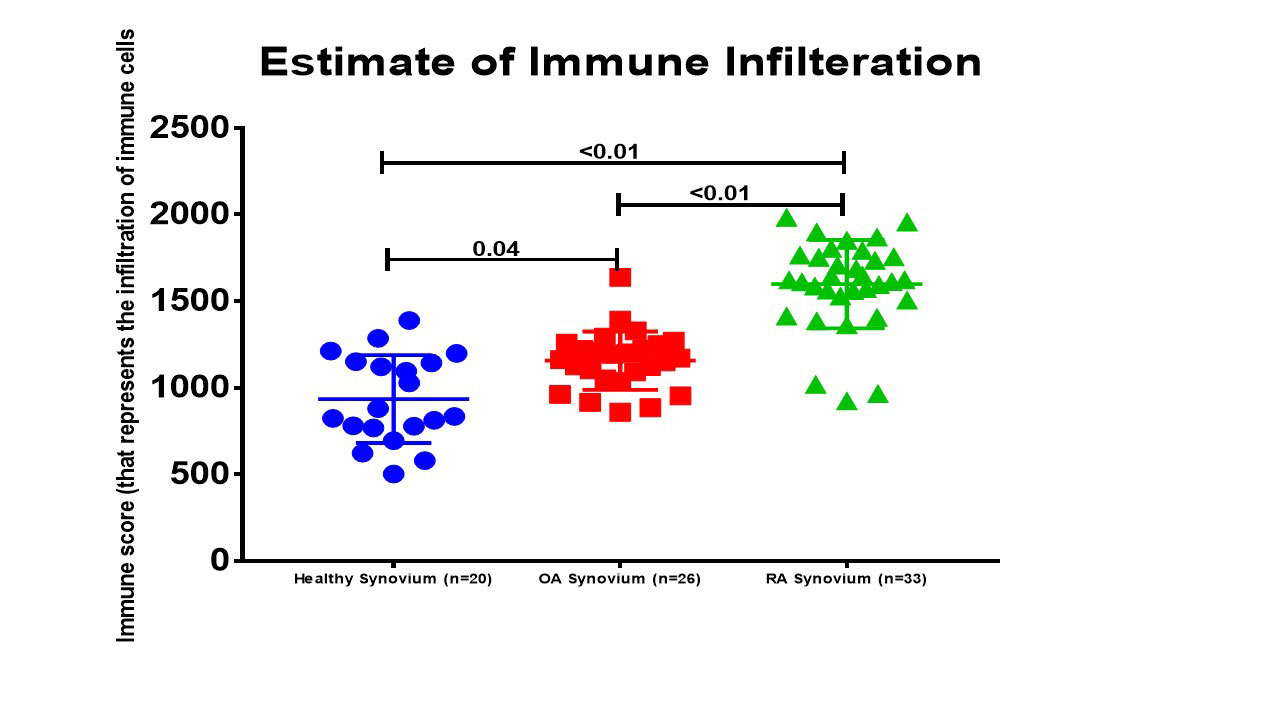
Results: In comparison to OA and healthy controls, RA synovium showed significant enrichment for immune-related pathways namely: lymphocytes differentiation, aβT cell activation, IL12 pathway, B cell activation, T cell differentiation, regulation of interferon-gamma production and lymphocytes mediated immunity, Figure (2). The most immune-related genes significantly altered in RA were chemokines (CXCL13, CXCL9, CCR2, CXCL10, XCL1, XCL2, and CXCL11), interleukins (IL7R, IL21R, IL32, and IRF4), and B cell related (TPD52, SLAMF8, IGHM, CD27, CD79A). Interestingly, NK related gene NKG7 (natural killer cell granule protein 7) was significantly upregulated in RA patients. Using ESTIMATE, it was shown that RA synovium contains more infiltrating immune cells than OA or healthy synovium, Figure (3). Healthy synovium contained the highest nonimmune cells (64±5%), compared to OA (58±2%), and RA (52±3%). One of the identified biomarkers to be synovium specific marker is CXCL13, a potent homing chemoattractant for B lymphocytes. CXCL13 was shown previously to be upregulated in RA synovium and can predict the recruitment of Follicular Dendritic Cells and synovial germinal centers formation, pathognomonic features in RA.
Conclusion: Using proper bioinformatical analysis of the synovium in RA to identify synovium specific biomarkers that are not masked by infiltrating immune cells may pave the way for understanding the molecular basis of RA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hachim M, Elemam N, Hachim I, Hannawi S, Hamoudi R, Maghazachi A. Estimating the Infiltration of Immune Cells in Synovium of Rheumatoid Arthritis Compared to Osteoarthritis and Healthy Control Using Transcriptomic Profiling [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/estimating-the-infiltration-of-immune-cells-in-synovium-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-compared-to-osteoarthritis-and-healthy-control-using-transcriptomic-profiling/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/estimating-the-infiltration-of-immune-cells-in-synovium-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-compared-to-osteoarthritis-and-healthy-control-using-transcriptomic-profiling/