Session Information
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: There is a dearth of epidemiological studies on Adult Onset Still’s Disease (AOSD) and no consensus on its incidence and prevalence. Most studies report a majority of patients below the age of 35 [Sakata et al, Rheumatol Int 2016]. Our objective is to describe the demographics, complications and mortality of hospitalized patients with AOSD in USA.
Methods: Adult (>18 years) hospitalized patients between 2009 and 2013 from a nationwide inpatient sample (NIS) database were captured. AOSD patients were identified using the ICD-9 code 714.2 that was in use before 2015. Patients also coded for RA, SLE, Myositis, PMR, AS and Psoriatic Arthritis were excluded. This was done in order to capture patients with strictly AOSD. NIS is the largest all-payer inpatient care database in the United States with approximately 8 million hospitalizations each year. Discharge weights were used to enable nationwide estimates. Descriptive statistics were represented as means/medians for continuous and as frequencies (%) for categorical variables.
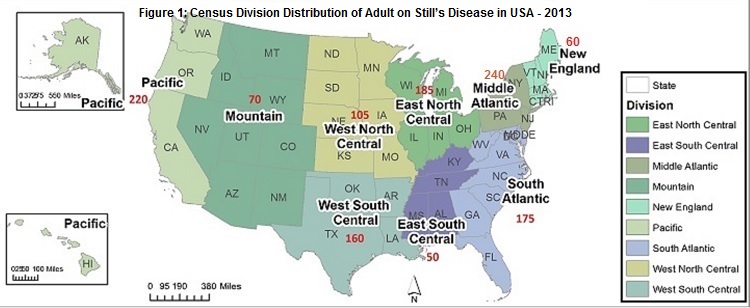
Results: Between 2009 and 2013, 5,820 AOSD patients were hospitalized (Table 1). AOSD patients had a mean age of 53.6 (SE – 0.6) years and 3817 (70.4%) were females. The racial/ethnic distribution showed that 56% white, 15% African American, 11.7% Hispanic and 3% Asian patients were affected. 37.6% of patients were hospitalized in urban teaching hospitals. The Mid-Atlantic census division had the highest number of patients (Figure 1). 100 (1.7%) developed Macrophage Activating Syndrome (MAS), 66 (1.1%) patients had disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) and 25(0.4%) had thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP). The mean length of stay was 6.9 (SE- 0.3) days. There were 154 inpatient deaths in 5 years (mortality 2.6%) (Table 2). The patients who died during hospitalization were more likely to be older, mean age of 62.4 (SE- 3.1) years, women (69.2%) and/or Asian (13.9%).
Conclusion: In hospitalized US AOSD patients, the average age was higher than previously described in cross sectional studies. This may indicate an aging population with a higher number of comorbidities that prompt hospitalization. Mortality increased with age and was higher among women and Asians. To our knowledge, this is the largest epidemiological study of AOSD today in the USA.
|
Table 1: Characteristics of the Hospitalized Adult Onset Still’s Disease over 5 years. |
||||||
|
Year |
2009 |
2010 |
2011 |
2012 |
2013 |
Total |
|
N |
846 |
995 |
1,434 |
1,280 |
1,265 |
5,820 |
|
Age in Years, Mean (SE) |
53.4(1.3) |
52.3(1.6) |
54.9(1.1) |
52.8(1.2) |
53.9(1.1) |
53.6(0.6) |
|
Female |
520 (61.4%) |
645 (64.8%) |
892 (62.2%) |
870 (68%) |
890 (70.4%) |
3817 (65.6%) |
|
Race |
||||||
|
White |
437 (51.6%) |
515 (51.8%) |
819 (57.1%) |
760 (59.4%) |
730 (57.7%) |
3261 (56%) |
|
Black |
117 (13.9%) |
168 (16.9%) |
243 (16.9%) |
180 (14.1%) |
165 (13%) |
874 (15%) |
|
Asian |
25 (3%) |
47 (4.7%) |
29 (2%) |
25 (2%) |
50 (4%) |
175 (3%) |
|
Expected primary payer |
||||||
|
Medicare |
311 (36.7%) |
338 (34%) |
589 (41.1%) |
525 (41%) |
570 (45.1%) |
2333 (40.1%) |
|
Medicaid |
104 (12.3%) |
157 (15.7%) |
170 (11.8%) |
145 (11.3%) |
160 (12.6%) |
735 (12.6%) |
|
Private including HMO |
351 (41.5%) |
373 (37.5%) |
474 (33.1%) |
475 (37.1%) |
375 (29.6%) |
2048 (35.2%) |
|
Self-pay |
60 (7.1%) |
79 (7.9%) |
95 (6.6%) |
85 (6.6%) |
80 (6.3%) |
398 (6.8%) |
|
Median household income national quartiles for patient’s ZIP Code |
||||||
|
$1 – $38999 |
205 (24.2%) |
276 (27.7%) |
294 (20.5%) |
340 (26.6%) |
315 (24.9%) |
1430 (24.6%) |
|
$39000 – $47999 |
217 (25.7%) |
222 (22.3%) |
253 (17.6%) |
255 (19.9%) |
315 (24.9%) |
1262 (21.7%) |
|
$48000 – $62999 |
166 (19.6%) |
275 (27.7%) |
370 (25.8%) |
325 (25.4%) |
305 (24.1%) |
1442 (24.8%) |
|
$63000+ |
236 (27.9%) |
188 (18.9%) |
498 (34.7%) |
335 (26.2%) |
315 (24.9%) |
1572 (27%) |
|
Bed size of the hospital |
||||||
|
Small |
51 (6%) |
78 (7.8%) |
123 (8.5%) |
175 (13.7%) |
140 (11.1%) |
566 (9.7%) |
|
Medium |
169 (20%) |
158 (15.9%) |
230 (16.1%) |
305 (23.8%) |
270 (21.3%) |
1133 (19.5%) |
|
Large |
341 (40.3%) |
384 (38.5%) |
462 (32.2%) |
640 (50%) |
610 (48.2%) |
2436 (41.9%) |
|
Location / teaching status of hospital |
||||||
|
Rural |
60 (7.1%) |
93 (9.4%) |
88 (6.2%) |
65 (5.1%) |
100 (7.9%) |
406 (7%) |
|
Urban non-teaching |
233 (27.6%) |
240 (24.2%) |
379 (26.4%) |
345 (27%) |
340 (26.9%) |
1538 (26.4%) |
|
Urban teaching |
267 (31.6%) |
286 (28.8%) |
347 (24.2%) |
710 (55.5%) |
580 (45.8%) |
2191 (37.6%) |
|
Transferred in from a different hospital/ facility |
71 (8.4%) |
72 (7.2%) |
138 (9.6%) |
130 (10.2%) |
125 (9.9%) |
535 (9.2%) |
|
In-Hospital death |
16 (1.9%) |
35 (3.6%) |
27 (1.9%) |
40 (3.1%) |
35 (2.8%) |
154 (2.6%) |
|
Length of Stay in days, Mean (SE) |
6.1 (0.5) |
8.7 (1.1) |
7 (0.4) |
6.6 (0.4) |
6.3 (0.4) |
6.9 (0.3) |
|
Cost of hospitalization in USD, Mean (SE) |
$ 33,152 (2,406) |
$ 25,501 (3,024) |
$ 29,633 (2,450) |
$ 32,080 (2,590) |
$ 31,367 (2,137) |
$ 30,857 (516) |
|
*The values are presented as Number (%) unless indicated otherwise |
||||||
|
Table 2: Description of patients who died in the hospital |
|
|
N |
154 |
|
Age in yrs, Mean (SE) |
62.4 (3.1) |
|
Age Distribution |
|
|
18 – 39 yrs |
21 (13.4%) |
|
39 – 54 yrs |
15 (9.9%) |
|
54 – 67 yrs |
50 (32.5%) |
|
67 – 90 yrs |
68 (44.3%) |
|
Female |
106 (69.2%) |
|
Race |
|
|
White |
81 (52.8%) |
|
Asian |
21 (13.9%) |
|
Others |
26 (19.8%) |
|
Expected primary payer |
|
|
Medicare |
92 (59.6%) |
|
Medicaid |
21 (13.4%) |
|
Private insurance / Self-pay |
41 (26.9%) |
|
Median household income – national quartiles for patient’s ZIP Code |
|
|
$1 – $38,999 |
15 (9.9%) |
|
$39,000 – $47,999 |
35 (23.1%) |
|
$48,000 – $62,999 |
36 (23.5%) |
|
$63,000+ |
61 (40%) |
|
Bed size of the hospital |
|
|
Small |
16 (10.6%) |
|
Medium |
45 (29.5%) |
|
Large |
50 (32.7%) |
|
Location/teaching status of hospital |
|
|
Rural |
20 (13.2%) |
|
Urban non-teaching |
15 (9.8%) |
|
Urban teaching |
77 (49.8%) |
|
Transferred in from a different hospital/ facility |
22 (14.6%) |
|
Length of Stay in days, Mean (SE) |
13.4(4.4) |
|
Total Charges during hospitalization in USD (SE) |
$ 66,083 (18,346) |
|
*The values are presented as Number (%) unless indicated otherwise |
|
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mehta BY, Briggs W, Efthimiou P. Epidemiology of Hospitalized Adult Onset Still’s Disease in United States [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/epidemiology-of-hospitalized-adult-onset-stills-disease-in-united-states/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/epidemiology-of-hospitalized-adult-onset-stills-disease-in-united-states/