Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (2387–2424) Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The relapse rate of treated patients with giant cell arteritis (GCA) varied widely in observational series and randomized controlled trials. This study aimed to estimate the frequency and timing of relapse, the prevalence of multiple relapses, the characteristics of flares, and the predictors of relapse in a large cohort of Spanish patients with GCA.
Methods: All patients in the ARTESER (Registry of Giant Cell Arteritis Patients of the Spanish Society of Rheumatology) were reviewed. ARTESER is a multicentre observational retrospective longitudinal study conducted in 26 hospitals that included all consecutive patients diagnosed with GCA between 1 June 2013 and 29 March 2019. All cases were aged 50 years or older and had a confirmed diagnosis of GCA, that is, they met at least one of the following criteria: objective confirmation of the presence of vasculitis in a diagnostic test, at least three 1990 ACR criteria for GCA satisfied, and/or a diagnosis made based on the clinical judgment of the investigator. We diagnosed disease relapses if all the following criteria were satisfied: 1) reappearance of signs/symptoms of GCA and/or polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR); 2) resolution of signs/symptoms after increasing glucocorticoids; 3) presence of raised acute-phase reactants ESR and/or CRP, and 4) exclusion of other causes. The data were obtained by review of medical records.
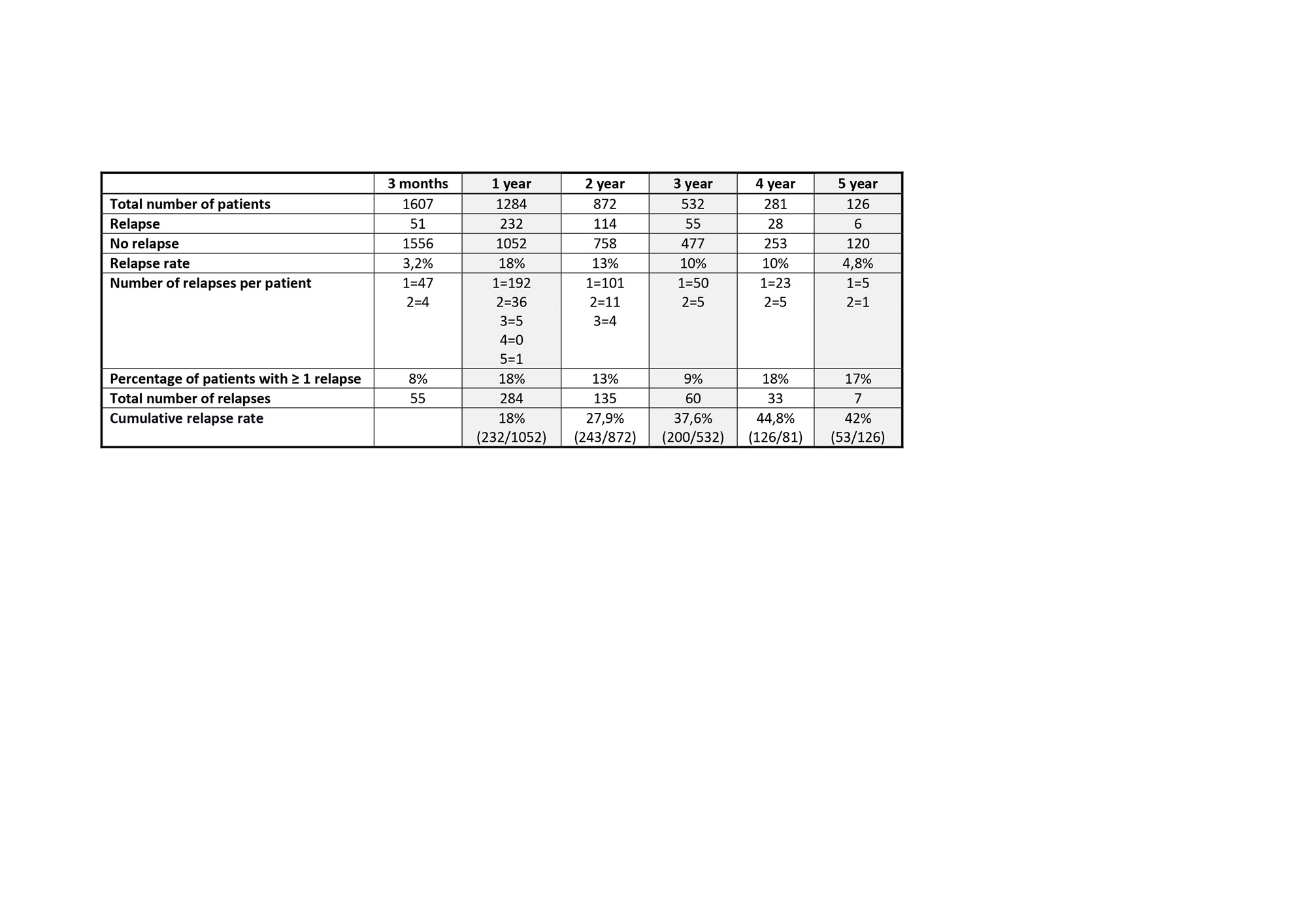
Results: In total, 1675 patients were included. They were predominantly female (70.3%), with a mean (±SD) age at diagnosis of 76.9±8.1 years. Of them, 1284 patients were followed up for one or more years. During follow-up, 574 relapses were observed in 334 (26%) patients. One-year, 2-year, 3-year, and 4-year cumulative relapse rates were 18%, 27.9%, 37.6%, and 44.8%, respectively (see Table 1). Most relapses (81.2%) occurred within the first two years after diagnosis (55.3% in the first year and 26% during the second). The mean dose of prednisone at the first relapse was 13.95 mg/day (IQR25%-75%: 5-20 mg). Fifteen percent (34/232) of patients experienced > 1 flare within the first year of treatment and 10.5% (12/114) during the second year. The majority of flares corresponded to a minor relapse according to the EULAR consensus definitions for disease activity states in GCA (minor relapses 73% / major relapses 27%) In the multivariate analysis, we did not identify any clinical factor at diagnosis that was a predictor of relapse during the first three years of evolution: nor the age, sex, presence of cranial manifestations, severe ischemic complications, large vessel involvement, or a strong initial systemic inflammatory response. By contrast, the administration of intravenous (IV)methylprednisolone (MP) boluses was negatively associated with the occurrence of relapses (OR: 0.356, 95% CI 0.182 to 0.696; p< 0.01).
Conclusion: Relapses among patients with GCA are common, mainly during the first two years after diagnosis. Between 8 and 18% of patients had multiple relapses. Despite the relevance of this problem, we do not yet have any predictive factors to identify patients with a higher risk of flare. Induction treatment with high-dose IV MP boluses appears to decrease the risk of relapses.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Narvaez J, Sanchez-Costa J, Hernández-Rodríguez I, Melero-Gonzalez R, De Miguel E, Monjo I, silva díaz M, SILVA FERNANDEZ L, Belzunegui Otano J, Valero-Jaimes J, Moriano Morales C, González I, Sanchez Martin J, Almorza Hidalgo T, Lluch J, Galindez-Agirregoikoa E, Calvo-Zorrilla I, Aldasoro V, Mendizabal J, ABASOLO L, LOIS P, Loricera J, Garrido-Puñal N, RUIZ ROMAN A, Castañeda S, Valero C, Moya Albarado P, Corominas H, García-Villanueva M, Larena C, Estrada-Alarcón P, Navarro V, Galisteo C, Riveros-Frutos A, Ortiz Sanjuan F, Labrada-Arrabal S, Alcalde M, Molina Almela C, Garcia Porrua C, García-González M, Rocha M, Mas A, Gonzalez-Gay M, Blanco R. Epidemiology and Predictors of Relapse in Giant Cell Arteritis: Results of the ARTESER Register [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/epidemiology-and-predictors-of-relapse-in-giant-cell-arteritis-results-of-the-arteser-register/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/epidemiology-and-predictors-of-relapse-in-giant-cell-arteritis-results-of-the-arteser-register/