Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Title: Spondyloarthropathies and Psoriatic Arthritis – Pathogenesis, Etiology Poster I
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Genetic research in axSpA is performed in patients with longstanding ankylosing spondylitis (AS). Early axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) is a diverse patient group in which a minority of the patients have AS. Therefore, it is not known if recently identified genetic risk factors for AS are also risk factors for early axSpA. The aim is to evaluate if ERAP1 and HLA-B*4001 are susceptibility factors for early axSpA.
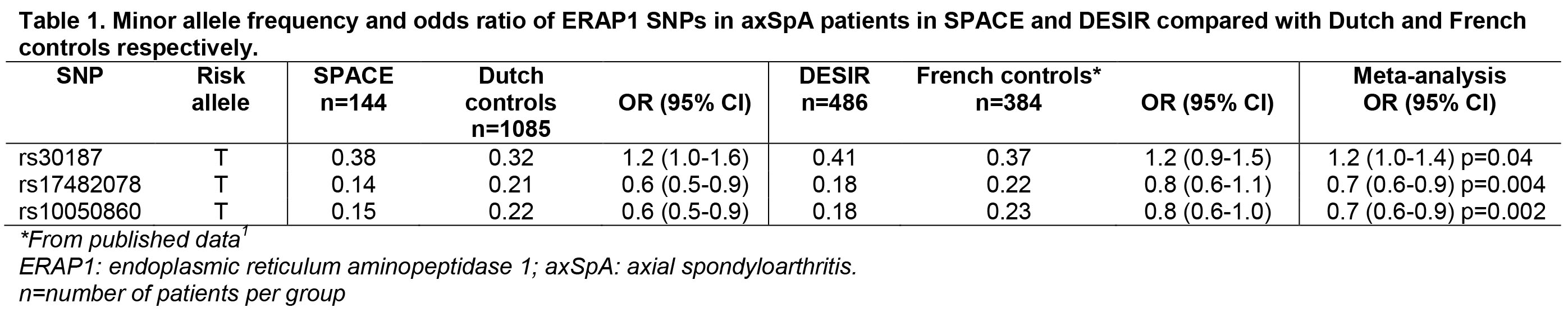
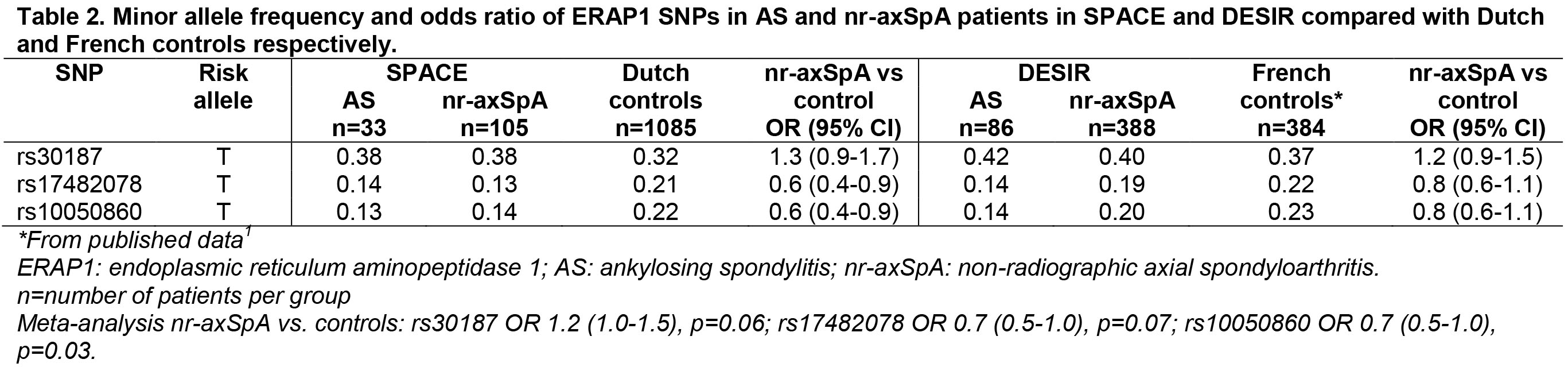
Methods: Patients with early axSpA meeting the ASAS classification criteria from the SPondyloArthritis Caught Early (SPACE) cohort (inclusion criteria: back pain for ≥3 months, ≤2 years, onset <45 years) and the DEvenir des Spondyloarthrites Indifférenciées Récentes (DESIR) cohort (inclusion criteria: inflammatory back pain for ≥3 months, ≤3 years, age <50) were typed for two well established AS genetic risk factors: ERAP1 SNPs (rs30187 (susceptibility), rs17482078 (protective) and rs10050860 (neutral)1) and HLA-B*4001. Subsequently, for ERAP1 SNPs sub analyses were performed for AS and non-radiographic axSpA (nr-axSpA) patients. Analysis of weaker AS risk factors was limited by sample size. For ERAP1, genotyped Dutch healthy controls (n=1085) (data kindly provided by C. Wijmenga and A. Zhernakova (UMCG)) and published French subjects1 were used as controls. For HLA-B*4001 healthy blood bank donors from the Netherlands (n=5584) and France (n=10177) were used as controls.
Results: In 486 DESIR patients (mean age 32.5 (SD 8.6); 50% male; 84% HLA-B27+; 18% X-SI+) and 144 SPACE patients (mean age 29.5 (SD 8); 51% male; 88% HLA-B27+; 24% X-SI+) ERAP1 SNP rs30187 was more common than in controls (OR 1.2, p=0.01 in meta-analysis; table 1). rs17482078 and rs10050860 were negatively associated with early axSpA (both OR 0.7 (0.6-0.9) p<0.01 in meta-analysis). Minor allele frequencies were similar for AS patients and nr-axSpA patients (table 2). Although both cohorts were sufficiently powered, HLA-B*4001 was not positively associated with early axSpA (OR 0.6 (0.4-0.9) in meta-analysis).
Conclusion: ERAP1 rs30187 is a genetic risk factor for early axSpA patients with and without radiographic sacroiliitis. To our knowledge this is the first report of genetic risk factor research in early axSpA patients meeting the ASAS criteria. Larger cohorts are needed to study additional AS risk factors.
ADDIN EN.REFLIST 1. Kadi A, Izac B, Said-Nahal R, Leboime A, Van Praet L, de Vlam K, et al. Investigating the genetic association between ERAP1 and spondyloarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013;72(4):608-13.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
de Koning A, Hameetman M, Miceli-Richard C, Dougados M, van der Heijde D, Kurreeman F, van Gaalen F. Endoplasmic Reticulum Aminopeptidase 1 (ERAP1) Is a Susceptibility Factor for Early Axial Spa Meeting the ASAS Classification Criteria: Results from the Spondyloarthritis Caught Early and DEvenir des Spondyloarthrites Indifférenciées Récentes Cohorts [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/endoplasmic-reticulum-aminopeptidase-1-erap1-is-a-susceptibility-factor-for-early-axial-spa-meeting-the-asas-classification-criteria-results-from-the-spondyloarthritis-caught-early-and-devenir-des/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/endoplasmic-reticulum-aminopeptidase-1-erap1-is-a-susceptibility-factor-for-early-axial-spa-meeting-the-asas-classification-criteria-results-from-the-spondyloarthritis-caught-early-and-devenir-des/