Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Undertreatment of RA can lead to cumulative joint damage as well as negatively impact emotional health. Recent evidence favors a treat-to-target strategy to achieve remission or low disease activity (DA) using objective scores such as the clinical disease activity index (CDAI) or the DAS28. We hypothesized that integration of CDAI and DAS28 calculators into electronic medical records (EMR) would improve treatment to target.
Methods: We performed a retrospective chart review of all RA patients in our academic rheumatology clinic who had a documented DA score, comparing treatment practices for 18 months before and after calculator implementation (March 2015). We identified patients using ICD-9 and ICD-10 codes for RA. Before implementation, we used natural language processing to search note text for CDAI, DAS, DAS28, DAS 28, and “disease activity score.” After implementation, we searched for results of DAS28-ESR, DAS28-CRP, and CDAI calculators in patient charts. We analyzed charts for a step-up/switch (addition or increase in dose of steroid or addition, dose increase, or change of synthetic or biologic DMARD), no change, or step down in therapy in response to the first moderate or high score for each patient.
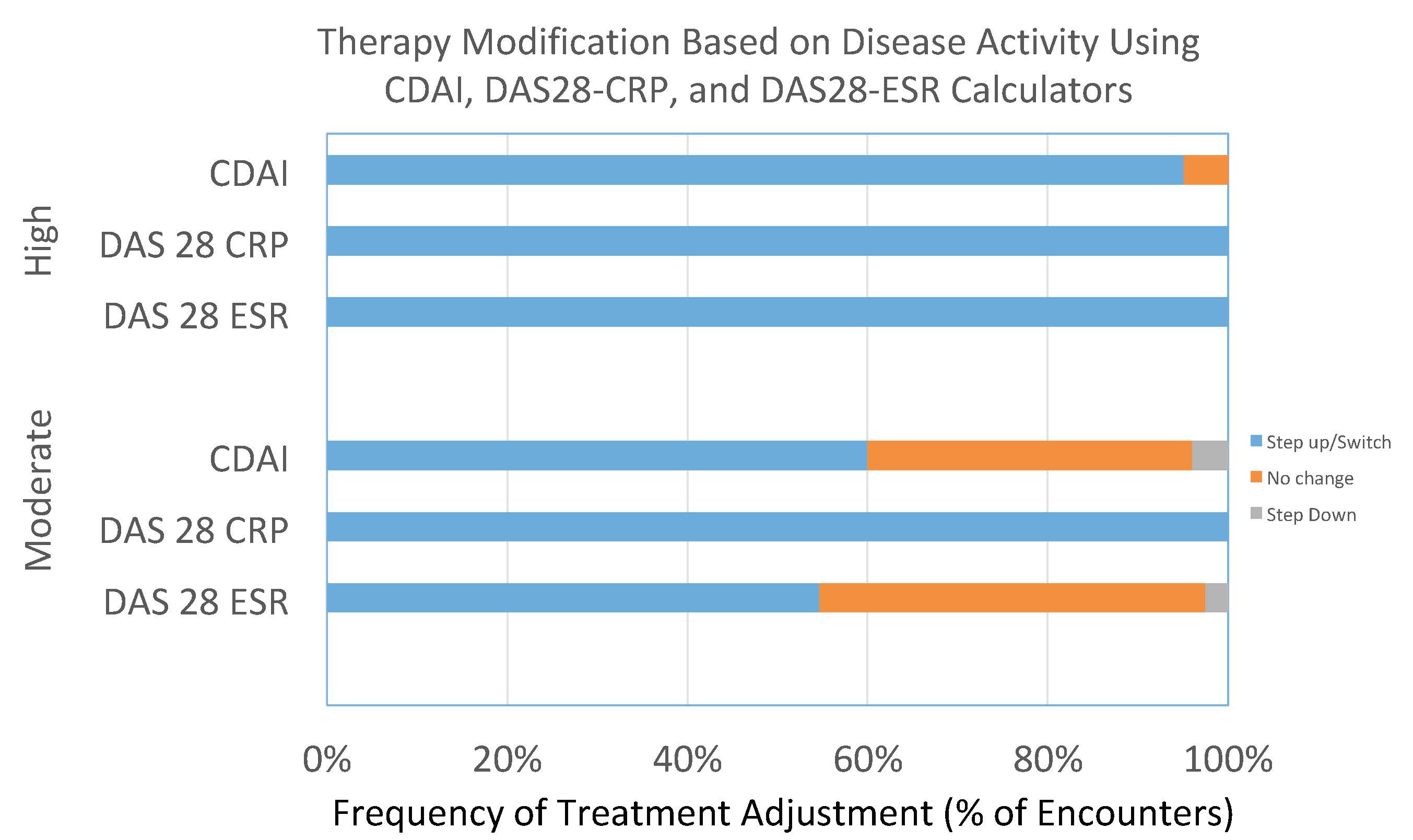
Results: Prior to incorporation of DA calculators in the EMR, out of 732 patients, 14% had at least one recorded CDAI and 4% had at least one DAS28, respectively. After implementation, out of 895 patients, 23% , 2.6%, and 17% had at least one recorded CDAI, DAS28-CRP, and DAS28-ESR, respectively. Both before and after calculator implementation, therapy was intensified the majority of the time in patients with moderate (50-60%) or high activity (80-100%) (see figures 1 and 2).
Conclusion: As expected, implementation of EMR-integrated DA calculators greatly improved DA score documentation. However, even after calculator integration in our EMR, scores were recorded < 25% of the time, with CDAI being the most commonly used measure. For patients in whom DA calculators are used, providers in our clinic adjusted therapy in response to DA level about 50-60% of the time after a moderate DAS and about 90% of the time after a high DA score, suggesting that they are following the treat-to-target recommendations. Targeted education to increase provider use of existing DA calculators may thus lead to improved patient outcomes. We plan to systematically examine charts to understand why there was no change or a step down in therapy in patients with moderate or high DA. Future studies include examining the time to initiation of biologic therapy in newly diagnosed RA patients before and after implementation of EMR DA calculators to assess impact on prescribing practices.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Barbera G, Kahlon J, Patel M, Pompa S, Jayatilleke A. EMR-integrated Disease Activity Calculators Improve Treatment to Target in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/emr-integrated-disease-activity-calculators-improve-treatment-to-target-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/emr-integrated-disease-activity-calculators-improve-treatment-to-target-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/