Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 12, 2019
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster III: Comorbidities
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Paraoxonase 1 (PON1) is a high density lipoprotein (HDL)-associated enzyme, which promotes the anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of HDL. We previously associated low PON1 activity with increased atherosclerotic risk in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The current work investigates the relationship of PON1 activity to a lipidomics panel of pro-inflammatory bioactive lipid mediators (BLM) in patients with RA and arthritic K/BxN mice.
Methods: Group A included 16 RA patients with carotid atherosclerosis (RA-ATH), 16 RA patients without carotid ATH (RA), and 16 healthy controls (HC). Group B included 29 arthritic K/BxN mice, (9 weeks (n=10), 14 weeks (n=12), 21 weeks (n=7)), and 21 non-arthritic control mice, (14 weeks, KRN (n=10), Ag7 (n= 11)). Circulating PON1 activity was measured using 3 different substrates: phenylacetate (arylesterase assay), dihydrocoumarin (lactonase assay), and paraoxon (paraoxonase assay). Liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization, tandem mass spectroscopy was performed for a panel of 10 circulating BLM including TXB2, 13 HODE, 9 HODE, 17S-HDHA, 15 HETE, 14 S-HDHA, 11 HETE, 12 HETE, 5 HETE, and 5-oxoETE.
Results: PON1 activity was lower in patients with RA compared to HC and was significantly lower in the RA-ATH group compared to the RA group by both paraoxonase and lactonase assays. Similarly, PON1 activity was lower in arthritic K/BxN mice compared to KRN/Ag7 non-arthritic controls. Multiple BLMs were elevated in RA patients and K/BxN mice compared to controls, with trends for highest levels in the RA-ATH group compared to RA and HC groups (Table 1). Lower PON1 activity by arylesterase and lactonase assays correlated with higher levels of several BLMs in both humans and mice (Table 2).
Conclusion: Low circulating activity of the HDL-associated enzyme PON1 associates with higher pro-inflammatory BLMs in both RA patients and arthritic K/BxN mice. This work suggests a potential mechanism for increase atherosclerotic risk in patients with active RA via suppression of PON1 activity and elevation in pro-inflammatory lipid mediators. Further work is warranted to determine if PON1 represents a potential “dual” therapeutic target in patients with RA.
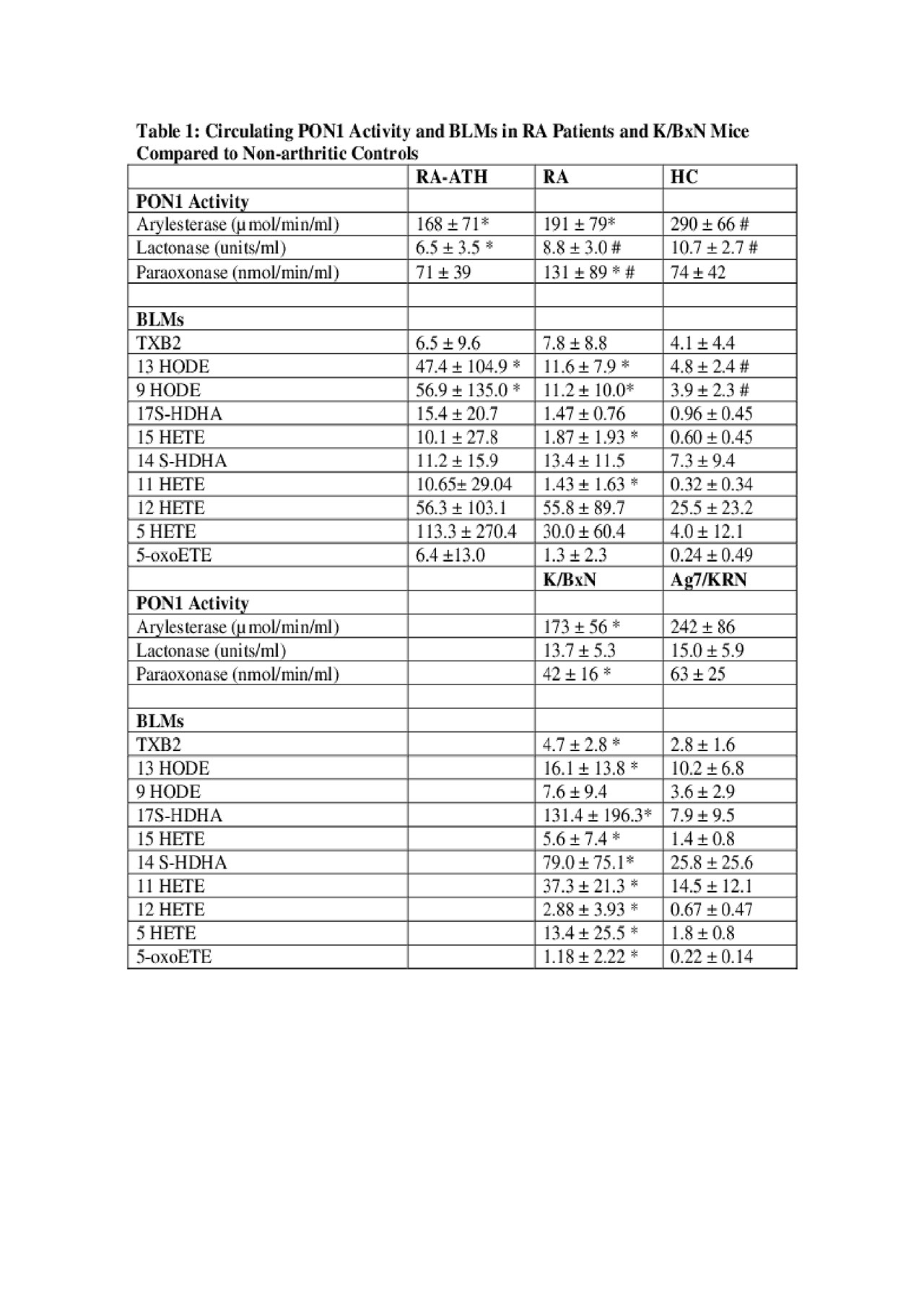
Lipidomics abstract Table 1 6-3-19.3
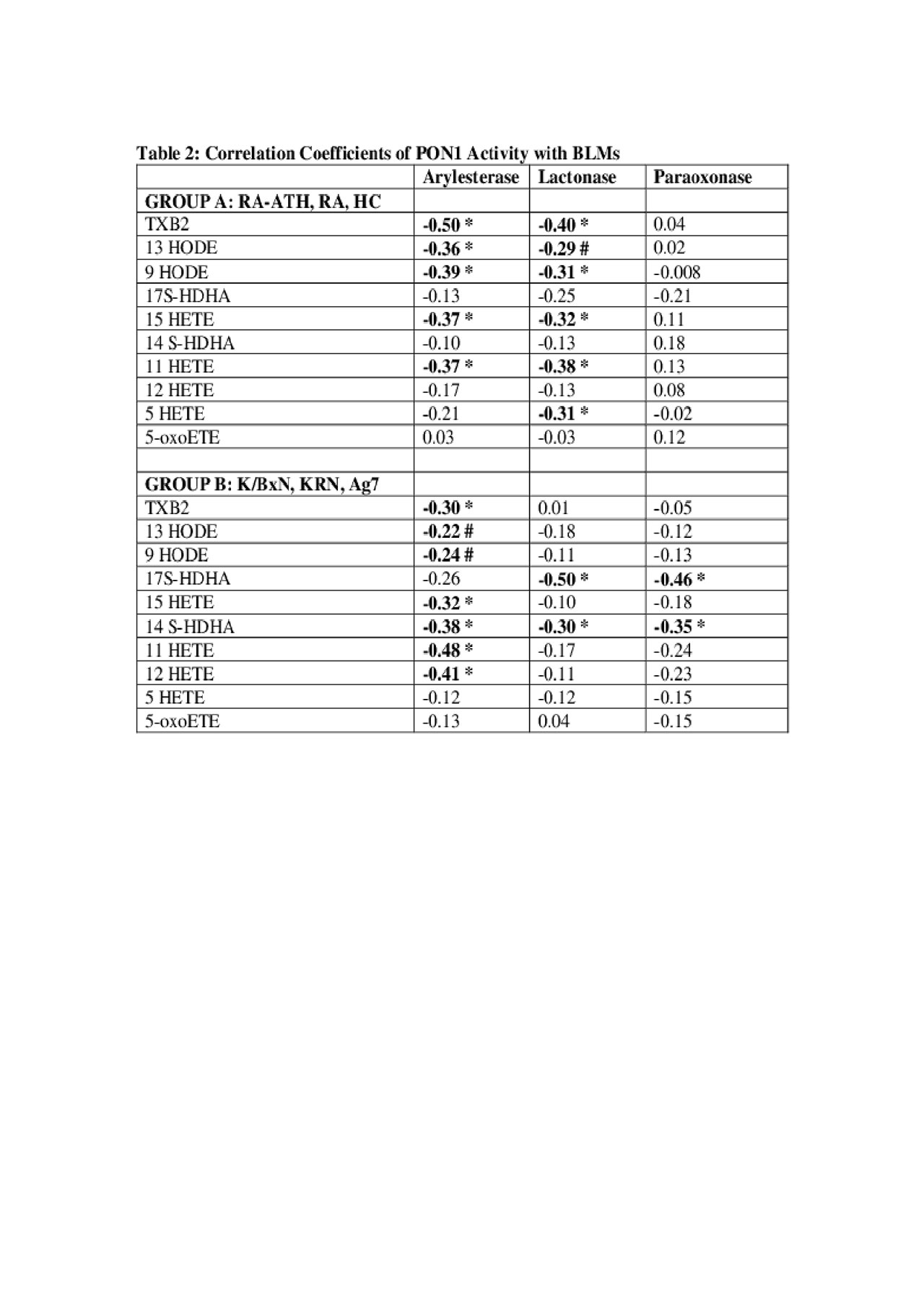
Lipidomics Abstract Table 2 6-3-19.3
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Charles-Schoeman C, Wang J, Shahbazian A, Papesh J, Reddy S. Elevated Pro-inflammatory Lipid Mediators Associate with Low Paraoxonase 1 Activity in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Arthritic K/BxN Mice [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/elevated-pro-inflammatory-lipid-mediators-associate-with-low-paraoxonase-1-activity-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-arthritic-k-bxn-mice/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/elevated-pro-inflammatory-lipid-mediators-associate-with-low-paraoxonase-1-activity-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-arthritic-k-bxn-mice/
