Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: Abstracts: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment II: Biologic Therapies (1943–1946)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-4:45PM
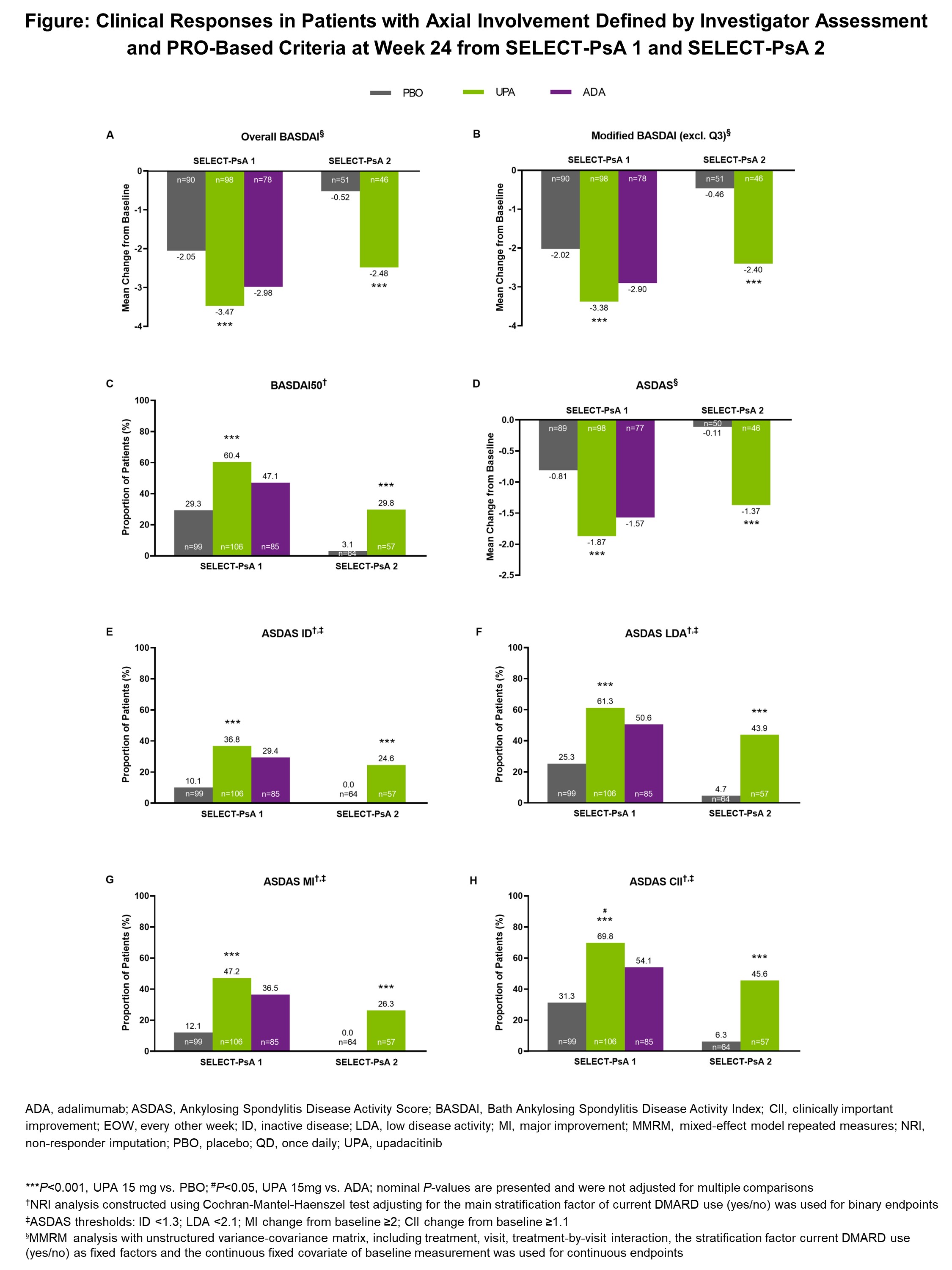
Background/Purpose: Patients with PsA and axial involvement have higher disease activity and greater reductions in quality of life;1 however, there are no accepted criteria for identifying axial involvement in PsA. The objective of this post-hoc analysis is to assess the efficacy of upadacitinib (UPA), a Janus kinase inhibitor, on axial symptoms in patients with active PsA and axial involvement defined by investigator assessment and PRO-based criteria from two phase 3 SELECT trials.2,3
Methods: Patients with active PsA (≥3 swollen joints and ≥3 tender joints) and prior inadequate response or intolerance to ≥1 non-biologic (SELECT-PsA 1) or ≥1 biologic (SELECT-PsA 2) DMARD were randomly assigned to once daily oral UPA 15 mg or 30 mg, placebo (PBO), or every other week subcutaneous adalimumab (ADA) 40 mg (SELECT-PsA 1 only).2,3 At baseline, axial involvement in PsA was determined by investigator assessment based on the totality of clinical information, such as duration and character of back pain, age of onset, and previous imaging. In addition to investigator assessment, PRO-based criteria for axial involvement (BASDAI ≥4 and BASDAI Question 2 ≥4 at baseline) were applied for this analysis to identify patients with active disease. Efficacy in the sub-group of patients defined using both investigator assessment and PRO-based criteria was evaluated at week 24 for UPA 15 mg vs PBO and ADA (SELECT-PsA 1 only). Data were analyzed using mixed-effect model repeated measures (MMRM) or non-responder imputation (NRI), with nominal P-values shown.
Results: Based on investigator assessment alone, 31.3% (n=534/1704) of patients in SELECT-PsA 1 and 34.2% (n=219/641) in SELECT-PsA 2 were defined as having axial involvement. When both investigator assessment and PRO-based criteria were applied, 23.1% (n=393/1704) of patients in SELECT-PsA 1, or 73.6% (n=393/534) of those defined using investigator assessment alone, and 27.5% (n=176/641) in SELECT-PsA 2, or 80.4% (n=176/219) using investigator assessment alone, met the combined criteria for axial involvement. In both studies, UPA 15 mg showed significantly greater clinical responses vs PBO at week 24 across all endpoints assessed (Figure). In SELECT-PsA 1, UPA showed numerically greater responses than ADA at week 24 across all BASDAI and Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) endpoints. The proportion of patients achieving ASDAS clinically important improvement (CII) at week 24 was significantly greater with UPA vs ADA based on nominal P-value.
Conclusion: Patients with active PsA and axial involvement defined by both investigator assessment and PRO-based criteria demonstrated statistically greater clinical responses related to their axial involvement with UPA 15 mg compared to PBO, and consistently numerically higher responses compared to ADA, at week 24 in the SELECT-PsA trials. Findings from this post-hoc analysis are consistent with previous data based on investigator assessment alone.4
References:
1. Mease PJ et al. J Rheumatol. 2018; 45(10):1389-96
2. McInnes IB et al. N Engl J Med. 2021; 384(13):1227-39
3. Mease PJ et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020; 80(3):312-20
4. Deodhar A et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72(Suppl 10)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Baraliakos X, Ranza R, Ostor A, Ciccia F, Coates L, Rednic S, Walsh J, Gao T, Lertratanakul A, Song I, Ganz F, Douglas K, Deodhar A. Efficacy of Upadacitinib on Psoriatic Arthritis with Axial Involvement Defined by Investigator Assessment and PRO-Based Criteria: Results from Two Phase 3 Studies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-upadacitinib-on-psoriatic-arthritis-with-axial-involvement-defined-by-investigator-assessment-and-pro-based-criteria-results-from-two-phase-3-studies/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-upadacitinib-on-psoriatic-arthritis-with-axial-involvement-defined-by-investigator-assessment-and-pro-based-criteria-results-from-two-phase-3-studies/