Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Upadacitinib (UPA) has shown efficacy and safety in patients (pts) with active PsA in the Phase 3 SELECT-PsA 1 and SELECT-PsA 2 clinical trials.1,2 Historically efficacy has been lower with second- and third-line therapy compared with first-line anti-TNF therapy in PsA;3,4 however, clinical trial data that describe efficacy in pts who have had an inadequate response (IR) to multiple biologic DMARDs (bDMARDs) are limited. This analysis assessed the effects of prior bDMARD failure on UPA efficacy in the SELECT-PsA 2 trial.
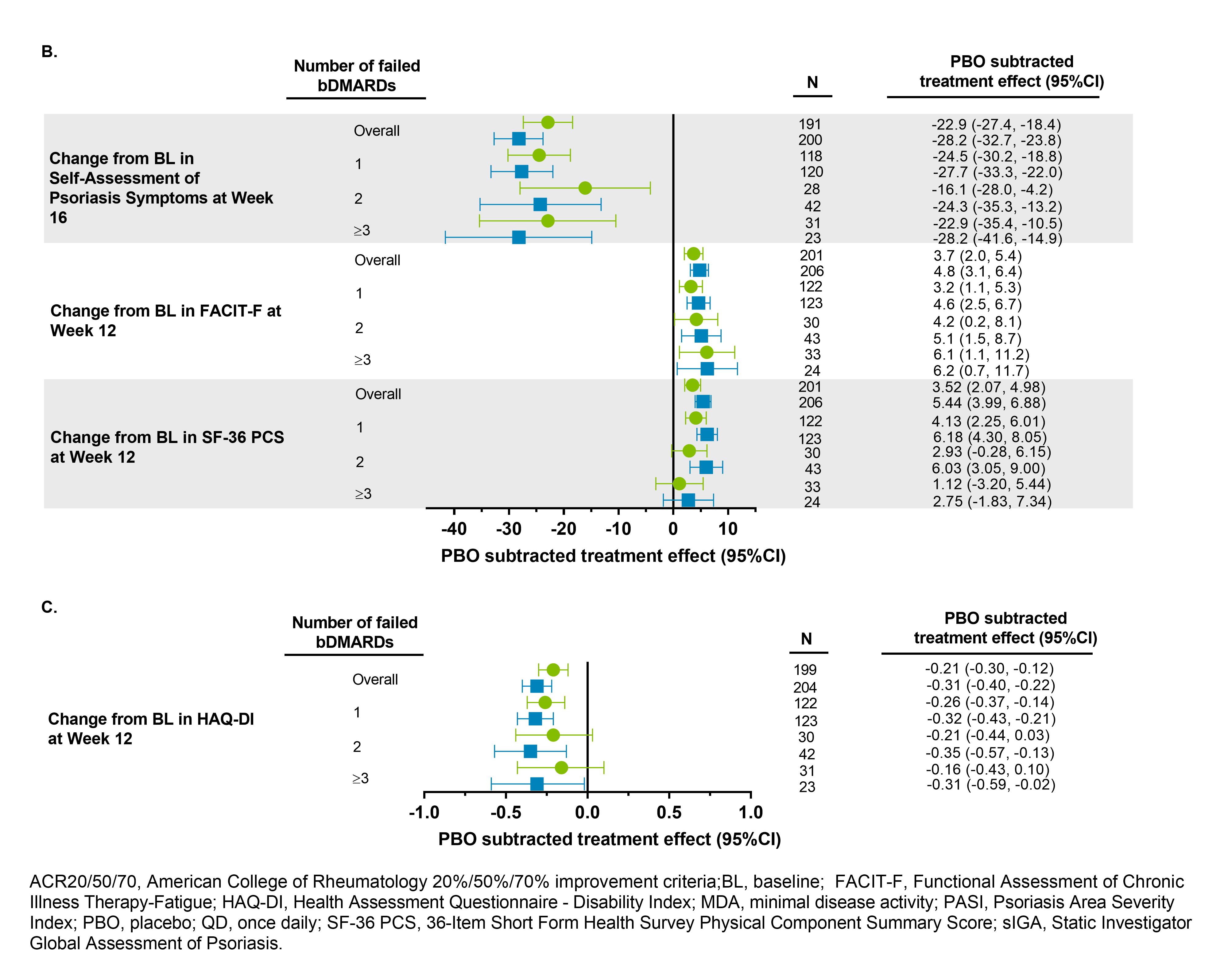
Methods: The SELECT-PsA 2 study enrolled pts with prior IR or intolerance to ≥1 bDMARD (N=642). Pts were randomized to placebo (PBO), UPA 15 mg once daily (QD, UPA15), or UPA 30 mg QD (UPA30). Stable background treatment of ≤2 non-bDMARDs was permitted; background therapy was not required. Only the pts who had IR to ≥1 bDMARD were included in this analysis; pts were subgrouped based on the number of bDMARDs failed prior to enrollment (1, 2, or ≥3). This analysis includes assessment of proportion of pts achieving ACR20/50/70, and change in HAQ-DI, FACIT-Fatigue, and SF-36 Physical Component Summary at Wk 12; static Investigator Global Assessment of Psoriasis of 0 or 1 and at least a 2-point improvement from baseline, PASI75, and change in Self-Assessment of Psoriasis Symptoms at Wk 16; and proportion of pts achieving minimal disease activity (MDA) at Wk 24. Non-responder imputation was used for binary endpoints. Mixed-effects model for repeated measures was used for continuous endpoints. Point estimates and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) of the PBO subtracted treatment effect were calculated.
Results: 641 pts were randomized and received study drug; 92% were bDMARD-IR: 391 (61%) of pts failed 1 bDMARD, 116 (18%) failed 2 bDMARDs, and 83 (13%) failed ≥3 bDMARDs.
In the overall study population, UPA15 and UPA30 demonstrated superiority vs placebo for all endpoints evaluated. In this post hoc analysis, the PBO subtracted treatment effect demonstrates generally consistent efficacy as compared to the overall study population for UPA15 and UPA30 across efficacy endpoints in the subgroups of pts with IR to 1, 2, or ≥3 prior bDMARDs (Figure). Due to limited sample sizes for pts with IR to >1 bDMARD and the pt subsets analyzed for psoriasis-related endpoints, results should be interpreted with caution.
Conclusion: Upadacitinib demonstrated consistent efficacy in treating clinical manifestations of PsA including musculoskeletal symptoms, psoriasis, physical function, fatigue, and quality of life in pts with IR to 1 or multiple prior bDMARDs. In addition, comprehensive disease control as measured by MDA, was generally consistently achieved with upadacitinib regardless of number of prior bDMARDs tried.
References
1. McInnes IB, et al. Ann Rheum Dis, 2020; 79:12.
2. Genovese MC, et al. Ann Rheum Dis, 2020; 79:139.
3. Costa L, et al. Drugs R D. 2017;17:509‐522.
4. Reddy SM, et al. 2016;35:2955‐2966.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mease P, Lertratanakul A, Strober B, Tsuji S, Richette P, Lovan C, Feng D, Anderson J, Van den Bosch F. Efficacy of Upadacitinib in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis Stratified by Number of Prior Biologic Disease-modifying Anti-rheumatic Drugs [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-upadacitinib-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-stratified-by-number-of-prior-biologic-disease-modifying-anti-rheumatic-drugs/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-upadacitinib-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-stratified-by-number-of-prior-biologic-disease-modifying-anti-rheumatic-drugs/