Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 23, 2018
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Clinical Poster III: Treatment
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a heterogeneus disease. Patients with PsA may have predominant axial (axPsA) or peripheral (pPsA) manifestations but the factors influencing on this are unknown. Recently, the recommended disease activity indexes have been updated, being these ASDAS for axial manifestations and DAPSA for peripheral manifestations. However, the impact of these changes in the outcomes of patients treated with biological therapies is unclear. Our objective is to analyse the efficacy of treatment in patients with axPsA and pPsA starting TNFi and the predictive factors of clinical presentation in clinical practice.
Methods: An observational study analysing data from a prospective cohort including 93 patients (pts) with axPsA or pPsA treated with TNFi from 2002-2018 was conducted. Demographic information, disease activity indexes (ASDAS for axPsA and DAPSA for pPsA) and laboratory tests were collected before starting TNFi (baseline visit) and 6 months later (6 m visit). At 6 m, the percentage of pts achieving inactive disease (ASDAS <1.3) and low disease activity (LDA) (ASDAS 1.3-2.1) for axPsA, or remission (DAPSA < 4) and LDA (DAPSA 4.1-15) for pPsA as well as the percentage of pts achieving clinical improvement (defined as ASDAS-clinically important improvement= delta-ASDAS>1.1- or delta-DAPSA50) was determined. Baseline predictor factors for developing axial or peripheral manifestations were identified using a univariable and multivariable binary regression models adjusted for confounder factors.
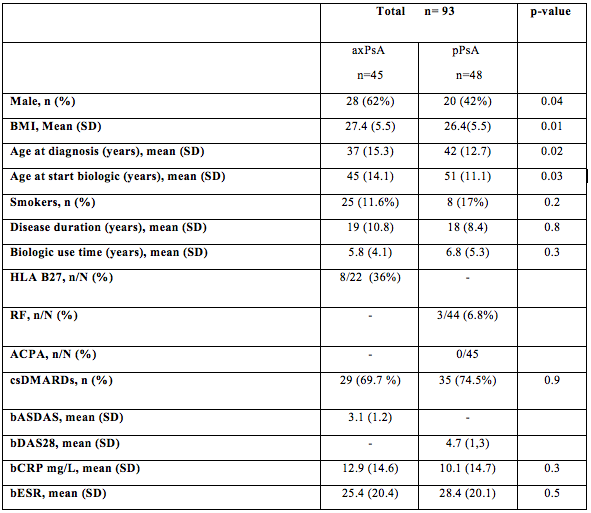
Results: Out of 93 included pts, 45 pts had predominant axPsA and 48 pPsA. Administered TNFi were etanercept for most pts (42%), infliximab in 29%, adalimumab in 22% and golimumab in 7%. Baseline characteristics are shown in Table 1. In axPsA, 49% clinically improved, 56 % pts reached LDA and 35% reached inactive disease. In pPsA, 56% pts clinically improved, 67% pts reached LDA and 25% pts were on remission at 6 m. The univariate analysis demonstrated in our cohort of patients with PsA that patients with younger age at diagnosis (OR, p=3.5; p=0.03), younger age at starting the biologic (OR, p=4.9; p=0.03), obesity (OR, p=6.4; p=0.03), and male gender (OR, p=3.0; p=0.03) had more risk to present axPsA. After multivariable analysis, only the obesity reached signification (p=0.01) for risk of presenting axPsA.
Conclusion: According to newly recommended disease activity indexes (ASDAS and DAPSA) 1 out of 3 pts with axPsA and 1 out of 4 in pPsA is on remission 6 m later after initiating a TNFi in clinical practice. Additionally, around 1 out of 2 clinically improve in both groups. The presence of obesity, male gender and younger age at diagnosis or when initiating TNFi are associated with developing axial predominant manifestations inPsA.
Table 1
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Benavent D, Plasencia C, Navarro-Compán V, Hernández-Breijo B, Villalba A, Peiteado D, Fernández E, Bogas P, de Diego M, Balsa A. Efficacy of TNF Inhibitors and Predictive Factors of Clinical Presentation in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-tnf-inhibitors-and-predictive-factors-of-clinical-presentation-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-tnf-inhibitors-and-predictive-factors-of-clinical-presentation-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis/