Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 13, 2022
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: PsA is a systemic disease involving multiple domains. Peripheral joints are frequently affected, and patients often initially present with asymmetrical oligoarthritis (2-4 swollen joints). KEEPsAKE 1 and KEEPsAKE 2 are double-blind, phase 3 clinical trials that evaluated the efficacy of risankizumab (RZB) versus placebo (PBO) for the treatment of adults with active PsA and at least 5 tender and swollen joints. RZB is a humanized monoclonal antibody that binds specifically to the p19 subunit of interleukin 23 and is approved to treat PsA. Here we assess response rates in PsA patients with limited (5 to ≤ 8) and extensive (≥ 9) swollen joint count (SJC) after treatment with RZB to examine whether its efficacy differed according to the extent of joint involvement.
Methods: In KEEPsAKE 1 and KEEPsAKE 2, patients were originally randomized 1:1 to receive RZB 150 mg or PBO at weeks 0, 4, 16 and every 12 weeks thereafter with an open label extension beginning for all patients at week 24 and is currently ongoing. Integrated efficacy results are reported for continuous endpoints by mixed-effect model repeated measure for week 24 and by as observed for week 52. Categorical endpoints are reported by non-responder imputation.
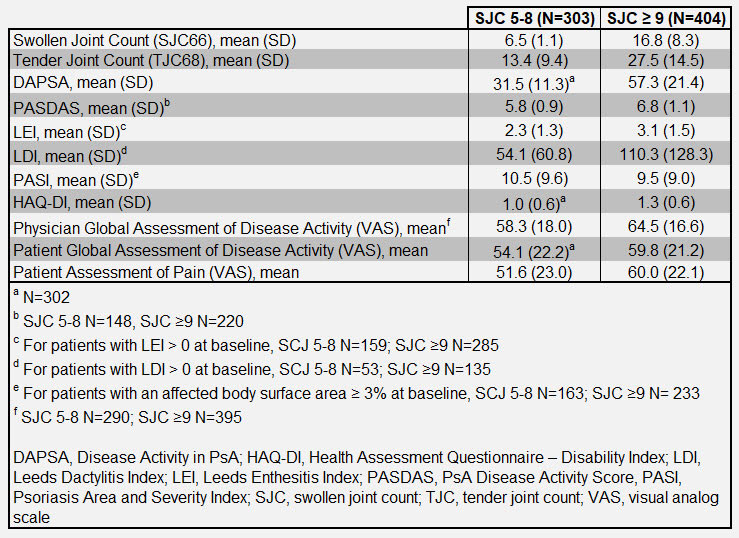
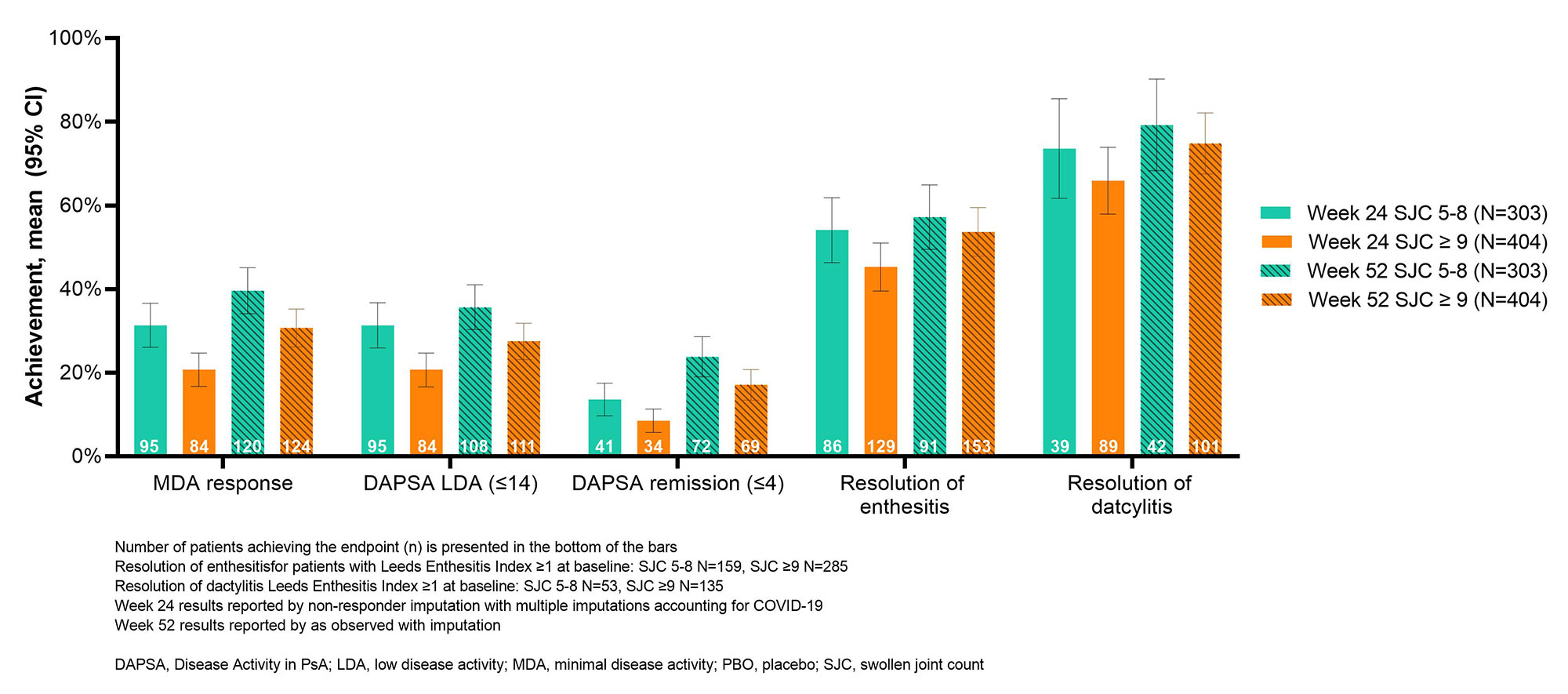
Results: Of the 707 patients initially randomized to RZB across both trials, 303 had a limited (5 to ≤ 8) SJC and 404 had extensive SJC (≥ 9) at baseline. Baseline characteristics for each group are presented in Table 1. At baseline, both groups of patients had high disease activity with a mean Disease Activity in PsA (DAPSA) score of 31.47 in the limited joint involvement population and 57.31 in the extensive joint involvement population (Table 1). In both groups, patients achieved minimal disease activity (MDA), Disease Activity in PsA (DAPSA) remission or low disease activity and resolution of enthesitis and dactylitis at weeks 24 and 52 (Figure 1). A higher proportion of patients in the limited joint involvement population achieved these stringent end points than did patients with extensive joint involvement (Figure 1). Both patient groups also had a decreased total number of swollen or tender joints at weeks 24 and 52 compared to baseline and showed improved scores for PsA disease activity (PASDAS), Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI), Physician and Patient’s Global Assessment of Disease Activity, pain, and HAQ-Disability Index (Figure 2). As expected, a greater reduction in swollen and tender joints was seen in patients in the extensive joint involvement population, due to a higher baseline joint involvement. Efficacy results were maintained or further improved from week 24 to 52 for both limited and extensive SJC patients (Figure 1 and 2).
Conclusion: RZB is efficacious in reducing signs and symptoms of PsA in patients, regardless of patterns of joint involvement. More patients in the limited joint involvement group achieved stringent treatment targets such as MDA and DAPSA remission at both weeks 24 and 52.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ogdie A, Ritchlin C, Nakasato P, Liu R, Kaufmann C, Padilla B, Gossec L. Efficacy of Risankizumab in the Treatment of PsA Patients with Limited and Extensive Joint Involvement [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-risankizumab-in-the-treatment-of-psa-patients-with-limited-and-extensive-joint-involvement/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-risankizumab-in-the-treatment-of-psa-patients-with-limited-and-extensive-joint-involvement/