Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Only a few small case series, case reports, and one small clinical trial suggested some benefit of leflunomide (LEF) in ANCA-associated vasculitis and other vasculitides. We analyzed the clinical efficacy and tolerability of LEF in a large cohort of patients with various vasculitides.
Methods: This was a retrospective analysis of patients who received LEF for treatment of their vasculitis enrolled in the Vasculitis Clinical Research Consortium (VCRC) Longitudinal Study and in 3 additional centers from the Canadian vasculitis research network (CanVasc). Efficacy was defined as a response to LEF at 6 months after its initiation, as per the treating physician, with the ability to taper glucocorticoids (GC), if applicable, the relief of symptoms for which LEF was started, or the maintenance of remission without the need to add or substitute another agent. Efficacy was further analyzed at 12 and 24 months. The validation of efficacy also required the absence of active disease, corresponding to a Birmingham Vasculitis Activity Score of 0.
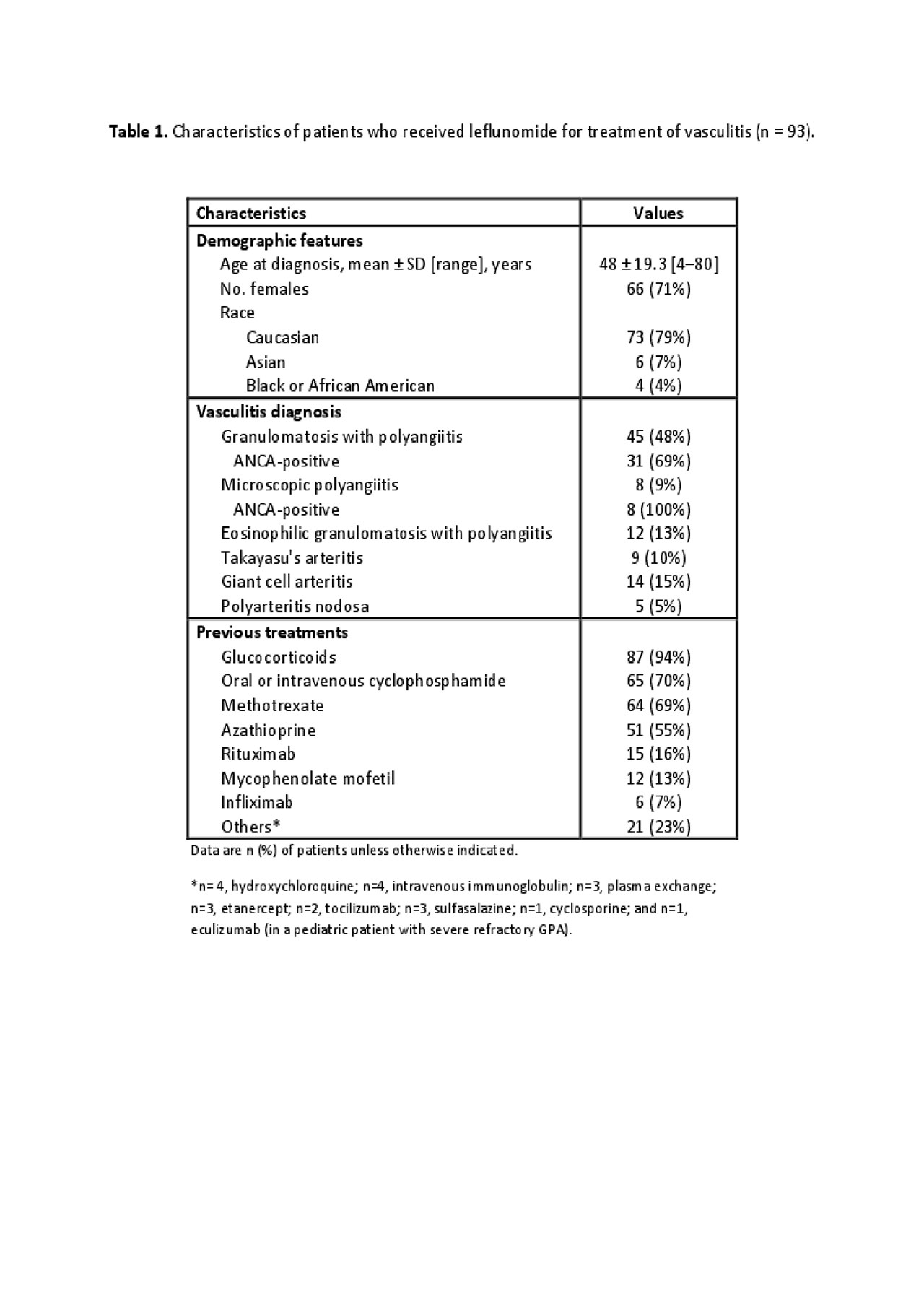
Results: Data for 93 patients were analyzed. As shown in Table 1, 45 patients had granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA), 8 microscopic polyangiitis (MPA), 12 eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA), 14 giant-cell arteritis (GCA), 9 Takayasu’s arteritis (TAK) and 5 polyarteritis nodosa (PAN). The main reason for initiation of LEF was active disease (89%). The mean duration of treatment with LEF was 2.3±2.3 years; it was used with GC (mostly low-dose prednisone), at least initially, for 79% of patients; as monotherapy without GC for 18%; and in addition to another non-GC immunosuppressive sparing agent for 27%. As shown in Table 2, LEF was efficacious for remission induction or maintenance at 6 months for 62 (67%) patients (64% with GCA, 89% with TAK, 80% with PAN, 69% with GPA, 33% with EGPA); 20% discontinued LEF before achieving remission because of persistent disease activity. Five (5.4%) patients experienced nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea. Neuropathy was reported in 4, which resolved after cessation of LEF in 1 (3 had symptoms of minor sensory neuropathy and stopped LEF). Infections were reported in 4 patients (1 with GCA, also on GC, died from sepsis before month 6 of LEF) and mild transient elevation of transaminase levels in 3 patients. High blood pressure was reported in 1 patient after 12 months of use. Overall, 22 adverse events led to drug discontinuation in 18 (19%) patients, of which 6 stopped LEF before month 12 and before showing any benefit in 8/12 of these patients.
Conclusion: LEF can be an effective therapeutic option for various vasculitides, especially for non-severe refractory or relapsing ANCA-associated vasculitis or large-vessel vasculitis, and for maintenance in GPA or MPA. No new safety signals for LEF were identified in this population.
-n = 93-.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
MUSTAPHA N, Barra L, Carette S, Cuthbertson D, Khalidi N, Koening C, Langford C, McAlear C, Milman N, Moreland L, Monach P, Seo P, Specks U, Sreih A, Ytterberg S, Merkel P, Pagnoux C, Canadian Vasculitis Research Network C, Vasculitis Clinical Research Consortium V. Efficacy of Leflunomide for Treatment of Vasculitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-leflunomide-for-treatment-of-vasculitis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-leflunomide-for-treatment-of-vasculitis/