Session Information
Date: Friday, November 6, 2020
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Ixekizumab (IXE), a high-affinity anti-interleukin-17A monoclonal antibody, is effective in patients (pts) with active non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA), who had elevated C-reactive protein (CRP) and/or active sacroiliitis on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).1 The objective was to determine if disease activity and patient-reported outcomes at Week 16 were similar between groups after stratifying pts by CRP/sacroiliac joint (SIJ) MRI status at baseline.
Methods: COAST-X (NCT02757352) included pts with active nr-axSpA and objective signs of inflammation, that is, presence of sacroiliitis on MRI (Assessment of Spondyloarthritis International Society [ASAS]/Outcome Measures in Rheumatology criteria) or elevation of serum CRP ( >5.0 mg/L). Pts were randomized 1:1:1 to receive subcutaneous 80 mg IXE every 4 weeks (Q4W) or every 2 weeks (Q2W), or placebo (PBO). Depending on the baseline values of CRP and MRI SIJ (Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada [SPARCC] score), pts in the intent-to-treat population (N=239) were divided into 3 subgroups (CRP >5 and MRI ≥2; CRP ≤5 and MRI ≥2; CRP >5 and MRI < 2). Logistic regression analysis with treatment, subgroup, and treatment-by-subgroup interaction was used to detect treatment group differences in ASAS40, Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) < 2.1 (low disease activity), and Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index 50 (BASDAI50) responses at Week 16. Analysis of covariance model with baseline value, treatment, subgroup, and treatment-by-subgroup interaction was used to detect the treatment group difference in change from baseline in Short Form-36 physical component score (SF-36 PCS).
Results: The proportion of pts achieving ASAS40 (primary endpoint), ASDAS < 2.1, and BASDAI50 (secondary endpoints) was higher in IXE treatment groups compared to PBO at Week 16 (Figure 1). The response rates in IXE-treated subjects were higher in all subgroups (CRP >5 and MRI ≥2; CRP ≤5 and MRI ≥2; CRP >5 and MRI < 2) without consistent differences in efficacy between the subgroups. Similarly, pts in the IXE groups showed improvement in SF-36 PCS scores (secondary endpoint) versus pts on PBO at Week 16 (Figure 2).
Conclusion: Pts with active nr-axSpA and objective signs of inflammation at baseline who were treated with IXE showed an overall improvement in the signs and symptoms of the disease. The efficacy was not different between pts with both elevated CRP and active sacroiliitis on MRI and pts with either elevated CRP or active sacroiliitis on MRI.
Reference:
1. Deodhar A, et al. Lancet. 2020;395(10217):53-64.
 *p < 0.05 as compared to PBO. Data from ITT population in 3 subgroups, N=239. Baseline CRP is defined as the last CRP value prior to first study injection. ASAS40=Assessment of Spondyloarthritis International Society 40; ASDAS=Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score; BASDAI50=Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index 50; CRP=C-Reactive Protein; ITT=intent-to-treat; IXE Q4W=ixekizumab every 4 weeks; IXE Q2W=ixekizumab every 2 weeks; MRI=magnetic resonance imaging; N=number of patients in the analysis population; NRI=non-responder imputation; Ns=number of patients in each subgroup; PBO=placebo; SIJ=sacroiliac joints; SPARCC=Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada Score.
*p < 0.05 as compared to PBO. Data from ITT population in 3 subgroups, N=239. Baseline CRP is defined as the last CRP value prior to first study injection. ASAS40=Assessment of Spondyloarthritis International Society 40; ASDAS=Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score; BASDAI50=Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index 50; CRP=C-Reactive Protein; ITT=intent-to-treat; IXE Q4W=ixekizumab every 4 weeks; IXE Q2W=ixekizumab every 2 weeks; MRI=magnetic resonance imaging; N=number of patients in the analysis population; NRI=non-responder imputation; Ns=number of patients in each subgroup; PBO=placebo; SIJ=sacroiliac joints; SPARCC=Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada Score.
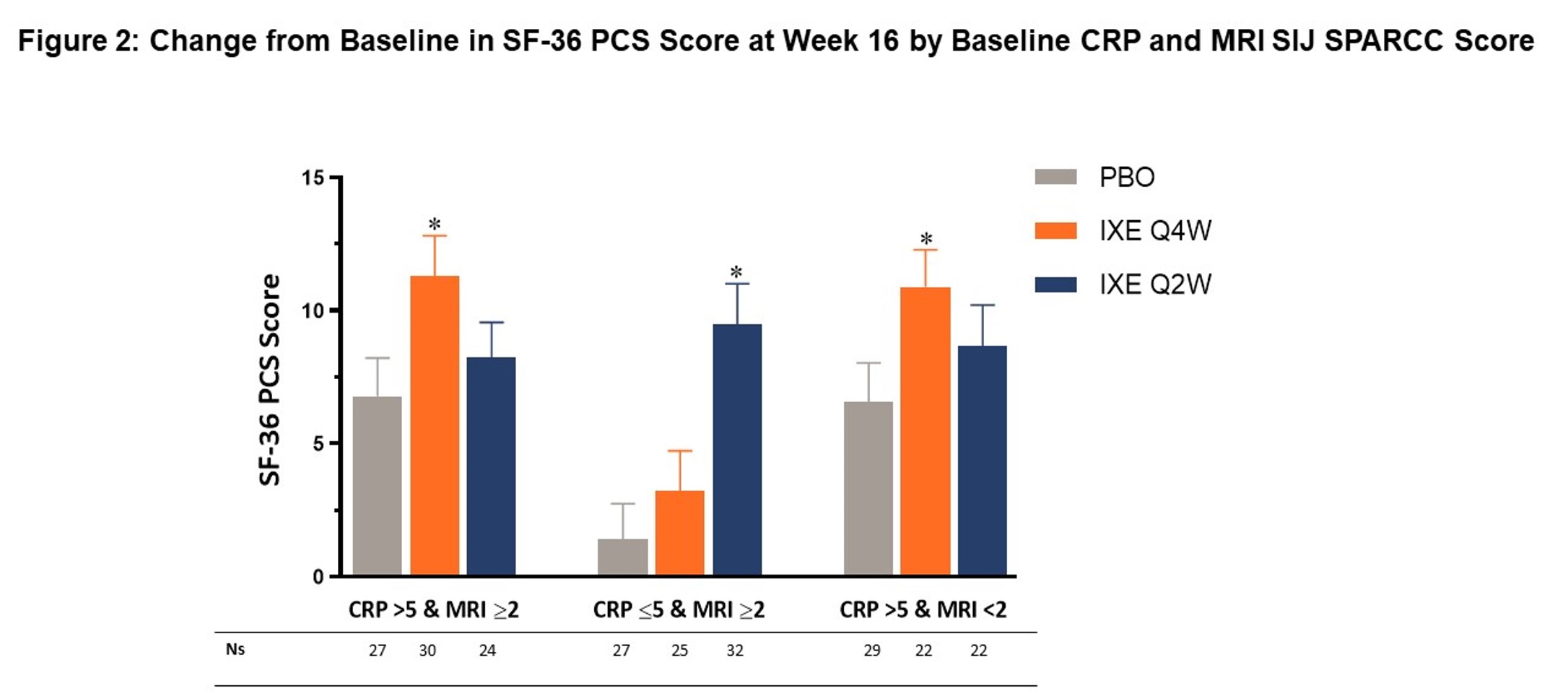 *p < 0.05 as compared to PBO. mBOCF data provided as least square mean ± standard error from ITT population in 3 subgroups, N=239. Baseline CRP is defined as the last CRP value prior to first study injection. CRP=C-Reactive Protein; ITT=intent-to-treat; IXE Q4W=ixekizumab every 4 weeks; IXE Q2W=ixekizumab every 2 weeks; mBOCF=modified baseline observation carried forward; MRI=magnetic resonance imaging; N=number of patients in the analysis population; Ns=number of patients in each subgroup; PBO=placebo; SF-36 PCS=Short Form-36 physical component score; SIJ=sacroiliac joints; SPARCC=Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada Score.
*p < 0.05 as compared to PBO. mBOCF data provided as least square mean ± standard error from ITT population in 3 subgroups, N=239. Baseline CRP is defined as the last CRP value prior to first study injection. CRP=C-Reactive Protein; ITT=intent-to-treat; IXE Q4W=ixekizumab every 4 weeks; IXE Q2W=ixekizumab every 2 weeks; mBOCF=modified baseline observation carried forward; MRI=magnetic resonance imaging; N=number of patients in the analysis population; Ns=number of patients in each subgroup; PBO=placebo; SF-36 PCS=Short Form-36 physical component score; SIJ=sacroiliac joints; SPARCC=Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada Score.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Maksymowych W, Marzo-Ortega H, Ǿstergaard M, Gensler L, Ermann J, Deodhar A, Poddubnyy D, Sandoval D, Bolce R, Kronbergs A, Liu-Leage S, Doridot G, Geneus V, Leung A, Adams D, Rudwaleit M. Efficacy of Ixekizumab on Disease Activity and Quality of Life in Patients with Active Nonradiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis and Objective Signs of Inflammation, Stratified by Baseline CRP/Sacroiliac Joint MRI Status [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-ixekizumab-on-disease-activity-and-quality-of-life-in-patients-with-active-nonradiographic-axial-spondyloarthritis-and-objective-signs-of-inflammation-stratified-by-baseline-crp-sacroilia/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-ixekizumab-on-disease-activity-and-quality-of-life-in-patients-with-active-nonradiographic-axial-spondyloarthritis-and-objective-signs-of-inflammation-stratified-by-baseline-crp-sacroilia/
