Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
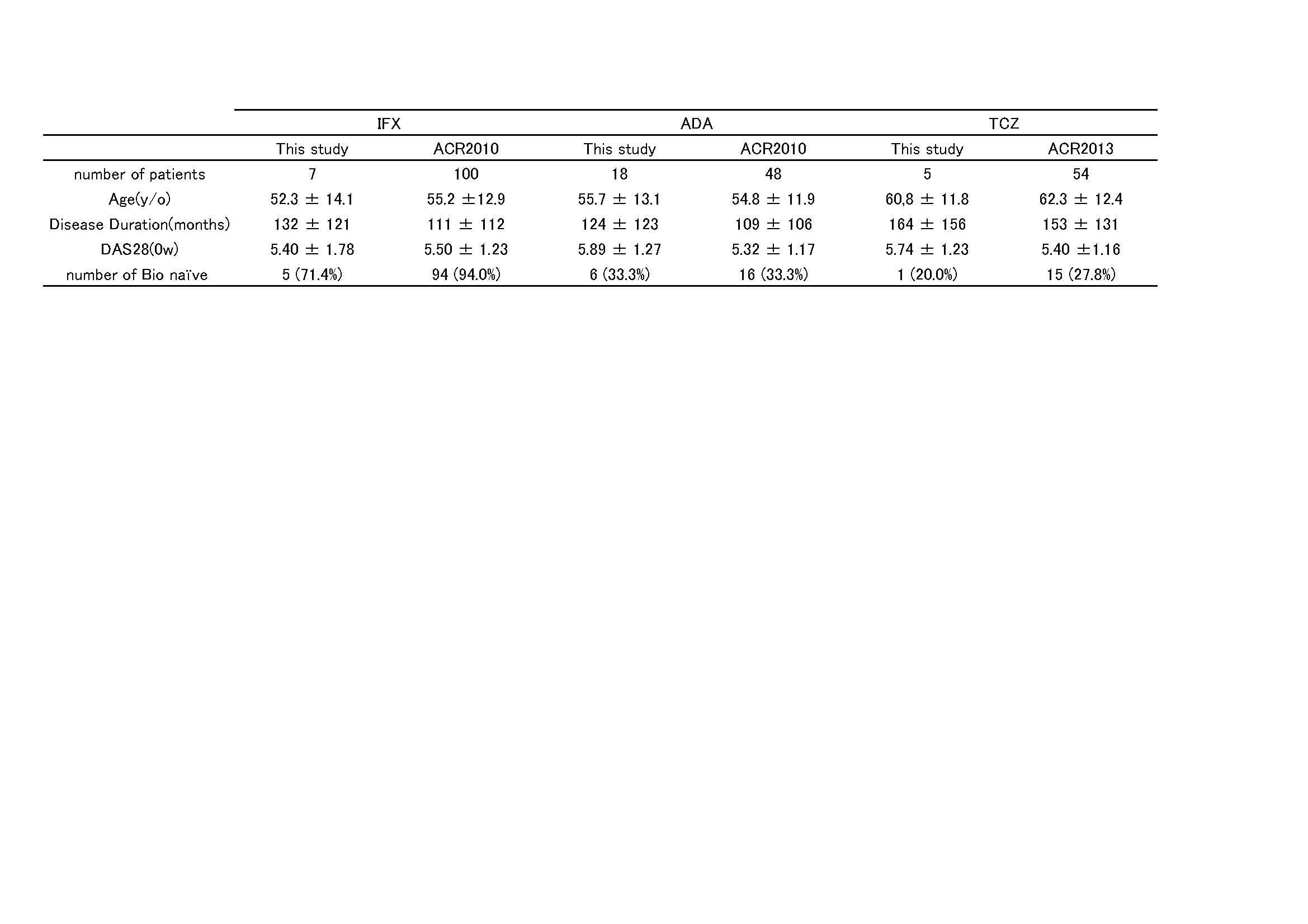
Background/Purpose: We have previously (2010ACR, 2013ACR) reported that the efficacy of biologics, infliximab, adalimumab, and tocilizumab can be predictable using baseline blood a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 5 (ADAMTS5) mRNA level. In this study presented here, we investigated whether the efficacy of these biologics could be improved if they were administered to RA patients who were diagnosed as effective of those biologics using the baseline ADAMTS5 mRNA levels. Methods: Whole blood was collected from 41 RA patients at baseline and total RNA was isolated. ADAMTS5 mRNA was quantified using real-time PCR (BiologicMate®) followed by the reverse transcription. ADAMTS5 mRNA was calculated as the ratio against b-actin mRNA (Index). Out of 41 patients, 12 (29.3%) have been refractory to infliximab (IFX). IFX, adalimumab (ADA), and tocilizumab (TCZ) was administered if the baseline ADAMTS5 was lower than 1.2, higher than 1.7, and higher than 1.6 Index, respectively. Efficacy of IFX at 14 weeks, ADA at 20 weeks, and TCZ at 12 weeks was estimated using EULAR response. Clinical data (Clinical remission rate, etc) of the RA patients treated with these biologics according to the baseline ADAMTS5 mRNA was compared with those of our data presented at ACR2010 (IFX and ADA) and ACR2013 (TCZ). Results: All of 12 patients refractory to IFX revealed high level (> 1.2 Index) of the baseline ADAMTS5 mRNA. Out of 41 RA patients, 7 (5 bio-naïve and 2 bio-switch), 18 (6 bio-naïve and 12 bio-switch), and 5 patients (1 bio-naïve and 4 bio-switch), were received IFX, ADA, and TCZ according to the baseline ADAMTS5 mRNA levels (ADAMTS5 selection). As a result, the clinical remission (DAS28-ESR<2.6) rate (4/7; 57.1%) with IFX under ADAMTS5 selection was higher than that with IFX of ACR 2010 data (32/100; 32.0%). On the other hand, the clinical remission rate (12/18; 66.7%) with ADA under ADAMTS5 selection was significantly (p=0.0002) higher than that with ADA of ACR 2010 data (9/48; 18.8%). Furthermore, the clinical remission rate (4/5; 80.0%) with TCZ under ADAMTS5 selection was significantly (p=0.0083) higher than that with TCZ of ACR 2013 data (13/54; 24.0%). Conclusion: Thus the efficacy of infliximab, adalimumab, and tocilizumab can be improved with the baseline ADAMTS5 selection.
Disclosure:
K. Tsuzaka,
Kaytee Bio, CoLtd,
1;
Y. Akiyama,
None;
M. Nagata,
None.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-infliximab-adalimumab-and-tocilizumab-can-be-improved-under-the-baseline-adamts5-selection/