Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Evidence on the efficacy of advanced therapies for axial involvement in PsA (axPsA) is scarce, largely due to the lack of a widely accepted axPsA definition. Guselkumab, an IL-23p19 inhibitor, showed early and sustained improvements in Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) and Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) among patients (pts) from the DISCOVER-1 and DISCOVER-2 studies (D1+D2) with imaging-confirmed sacroiliitis consistent with axial involvement1. Using unsupervised machine learning (ML), a cluster of D1+D2 pts with axial involvement was previously identified2. We sought to contrast pt profiles across axPsA cohorts defined by imaging and ML criteria and to evaluate the efficacy of GUS in improving disease activity across cohorts.
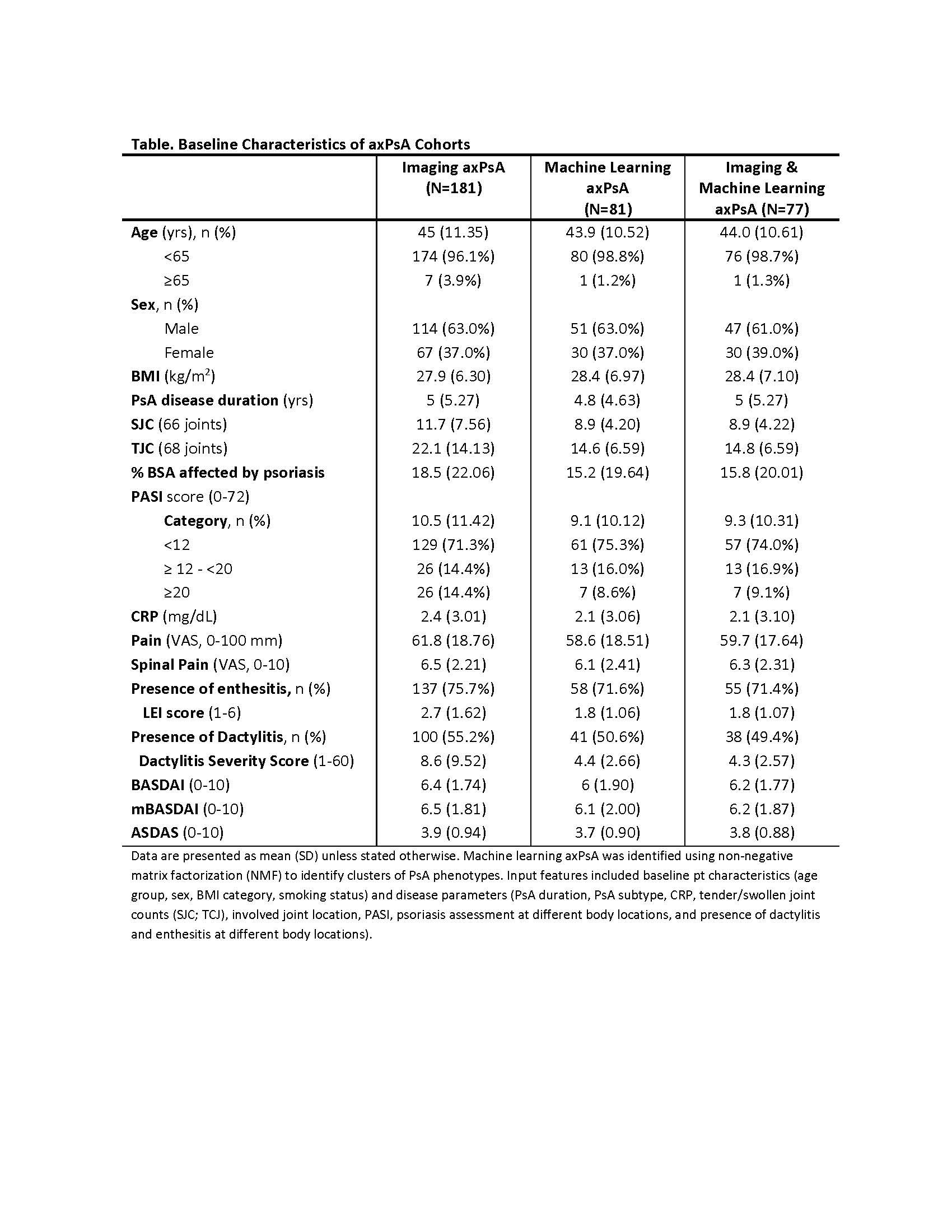
Methods: Pts enrolled in D1+D2 were adults with active PsA despite standard therapies. Pts were randomized 1:1:1 to GUS 100 mg every 4 weeks (Q4W); GUS 100 mg at W0, W4, then Q8W; or placebo. The current post hoc analysis included only bio-naïve GUS-treated pts (pooled GUS Q4W and Q8W) who met one of the following axPsA definitions: (1) Presence of spondylitis based on imaging confirmation (Imaging axPsA); (2) ML-identified axial cluster2 (ML axPsA); (3) fulfilment of both the Imaging & ML axPsA definitions. Efficacy assessments included least squares mean changes in BASDAI, modified BASDAI (mBASDAI; excluding peripheral joint pain), spinal pain (BASDAI Q2), morning stiffness (BASDAI Q5/6) scores and ASDAS, as well as achievement (employing non-responder imputation for missing data) of ≥50% (BASDAI50) or ≥70% (BASDAI70) improvement in BASDAI, and ASDAS response of low disease activity (LDA; < 2.1), inactive disease (ID; < 1.3), clinically important improvement (CII; change of ≥1.1), and major improvement (MI; change of ≥2.0).
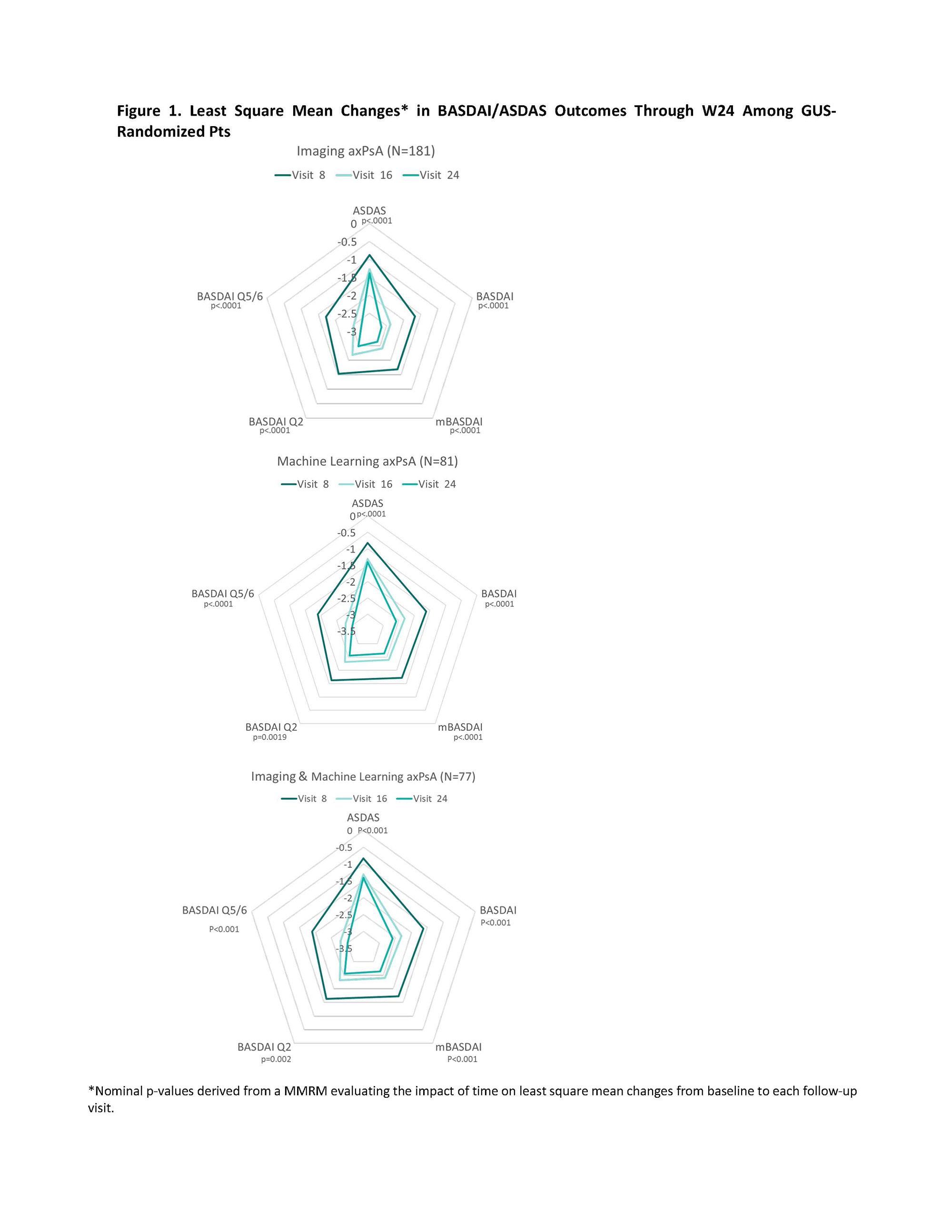
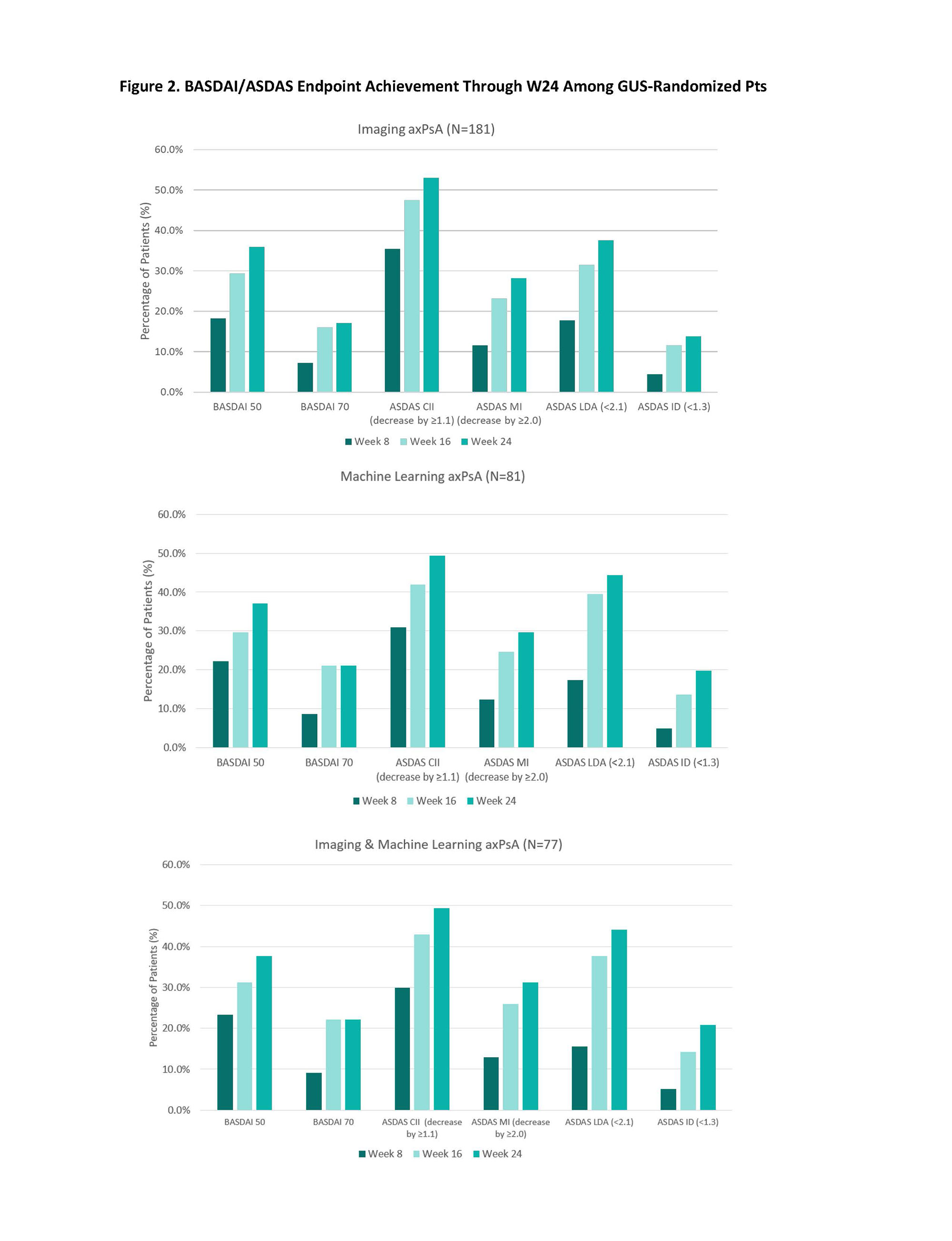
Results: Of the 669 bio-naïve GUS-treated pts in D1+D2, 185 (28%) were included; 181 met the Imaging axPsA, 81 the ML axPsA, and 77 both definitions. Some numerical differences in baseline characteristics were observed (e.g., swollen and tender joint counts); however, remaining characteristics were comparable across the 3 cohorts (Table). Irrespective of axPsA definition, GUS treatment was associated with significant (nominal p< 0.001) improvements in BASDAI, mBASDAI, spinal pain, morning stiffness, and ASDAS at W8 that continued being enhanced through W24 (Figure 1). The proportion of pts achieving categorical BASDAI & ASDAS endpoints also increased through W24, with W24 response rates of 36-38% for BASDAI50, 17-22% for BASDAI70, 49-53% for ASDAS CII, 28-31% for ASDAS MI, 38-44% for ASDAS LDA, and 14-22% for ASDAS ID across the 3 cohorts (Figure 2).
Conclusion: Irrespective of different definitions, pts with active axPsA treated with GUS had significant and clinically meaningful improvements in BASDAI score, mBASDAI score, and ASDAS as early as W8, including in the axial-specific domain of spinal pain, that continued to improve through W24. These results further support the efficacy of GUS in treating PsA pts with axial involvement.
References:
1. Mease PJ et al. Lancet Rheumatol 2021; 3: e715–23.
2. Richette P et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 10).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mease P, Tillett W, Ohrndorf S, Perate M, Medysky M, Zimmermann M, Shawi M, Rampakakis E, Bird P, Zabotti A, Deodhar A, Gladman D. Efficacy of Guselkumab in Three Cohorts of Biologic-Naïve PsA Patients with Axial Involvement Defined Based on Imaging and Machine-Learning Criteria: Pooled Analysis of Two Phase 3 Studies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-guselkumab-in-three-cohorts-of-biologic-naive-psa-patients-with-axial-involvement-defined-based-on-imaging-and-machine-learning-criteria-pooled-analysis-of-two-phase-3-studies/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-guselkumab-in-three-cohorts-of-biologic-naive-psa-patients-with-axial-involvement-defined-based-on-imaging-and-machine-learning-criteria-pooled-analysis-of-two-phase-3-studies/