Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0510–0542) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment: AxSpA Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Acute anterior uveitis (AAU) is the most common extra-musculoskeletal manifestation in axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA), affecting more than a third of patients. However, long-term interventional placebo-controlled studies are lacking due to ethical challenges. This study aimed to evaluate anterior uveitis flares rate in patients with axSpA who are at high risk of recurrent uveitis when treated with the PEGylated Fc-free TNF inhibitor certolizumab pegol (CZP) compared with standard non-biologic care.
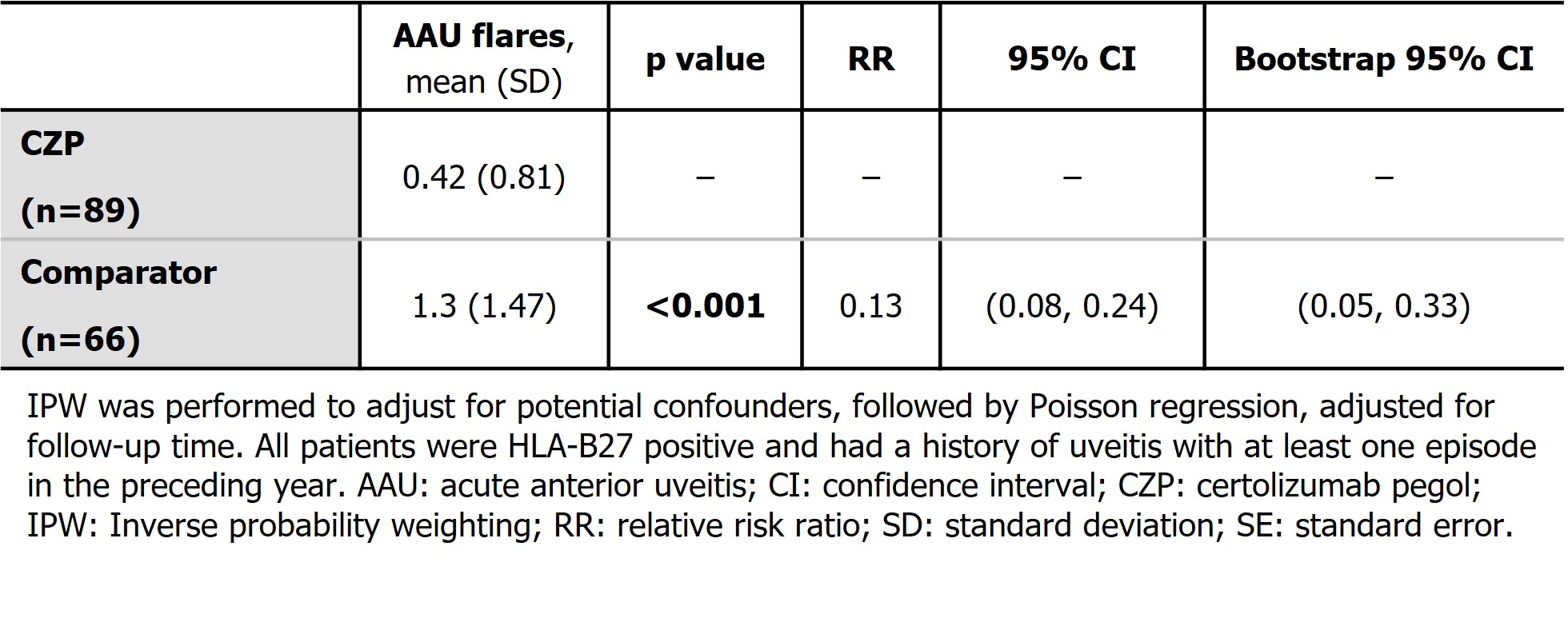
Methods: In the C-VIEW study (NCT03020992), CZP was administered to patients with a high risk of uveitis flares (i.e., those with active axSpA, human leukocyte antigen-B27 [HLA-B27] positivity, and a history of recurrent AAU [≥2 AAU flares in total; ≥1 in the year prior to baseline]). This was an open-label, multicenter study where patients received CZP for 96 weeks; data up to Week 48 were used in the present analysis. The number of AAU flares in C-VIEW were compared to those seen in matched high-risk patients with non-biologic standard care from two North American axSpA centers who were followed up for 48 weeks. Inverse probability weighting (IPW) was performed to adjust for potential confounders, followed by Poisson regression, adjusted for follow-up time, to test the effect of treatment with CZP.
Results: A total of 89 patients received CZP and completed the C-VIEW study, while 66 bio-naïve patients (40 from the University of California, San Francisco and 26 from the University of Toronto) qualified as comparator with no exposure to biologic therapy during the 48-week follow-up period. All patients were HLA-B27 positive and had at least one episode of AAU before the baseline visit. Symptom duration and baseline CRP levels were similar in the two groups. Following IPW, there were no statistically significant differences in mean BASDAI and distribution of ASDAS disease activity states at baseline between the CZP treatment and comparator groups. Conventional synthetic DMARD use was similar between groups at baseline and during follow-up. The mean number of AAU flares (mean ± standard deviation) was significantly lower (p< 0.001) with CZP (0.42±0.81) than in the matched comparator population (1.3±1.47). In the final model after IPW, there was an 87% reduction in AAU flares (p≤0.001) associated with CZP treatment (Table).
Conclusion: This matched control study supports the benefit of CZP over standard non-biologic treatment in reducing anterior uveitis flares among high-risk patients with axSpA, highlighting its potential as a promising therapeutic option in managing this debilitating ocular manifestation in axSpA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Haroon N, Baskurt Z, Chim T, Inman R, Paez D, Kumke T, Tham R, Kim M, van der Horst-Bruinsma I, Gensler L. Efficacy of Certolizumab Pegol in Preventing Anterior Uveitis Flares Compared with Standard Non-Biologic Treatment: A Matched Control Study in High-Risk Patients with Axial Spondyloarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-certolizumab-pegol-in-preventing-anterior-uveitis-flares-compared-with-standard-non-biologic-treatment-a-matched-control-study-in-high-risk-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-certolizumab-pegol-in-preventing-anterior-uveitis-flares-compared-with-standard-non-biologic-treatment-a-matched-control-study-in-high-risk-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis/