Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2015
Title: Pediatric Rheumatology - Clinical and Therapeutic Aspects I: Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-4:00PM
Background/Purpose: Efficacy and safety of canakinumab
(CAN) in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (SJIA) have been demonstrated
in two phase III trials.1 In these trials, over 60% of the patients
(pts) had received a previous biologic and were switched to CAN for either lack
of efficacy or safety reasons and may be more refractory to another biologic
therapy. Here, we examine CAN efficacy in CAN-naïve SJIA pts, previously
exposed to anakinra (ANK) and tocilizumab (TCZ).
Methods: This was an open-label extension study
with details reported earlier.2 Adapted (a) ACR 30/50/70/90/100
responses with CAN were assessed at Day 29 and 12 months. Pts with prior
exposure to ANK or TCZ exposure were compared to biologic naïve pts. Reasons
for discontinuation of ANK and TCZ were recorded and safety noted.
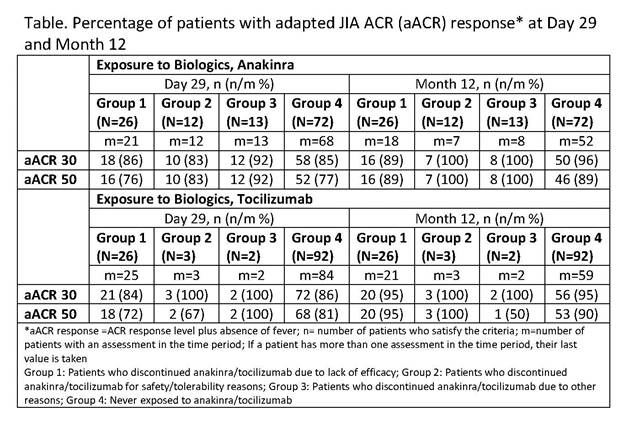
Results: Among the 123 pts considered in this
analysis, 51 pts (42%) previously received ANK and 31 (25%) TCZ, respectively.
The main reason for ANK/TCZ discontinuation was lack of efficacy (ANK, 21%;
TCZ, 21%). At Day 29, aACR 30/50 response rates were similar for both ANK-naïve
pts and those who discontinued ANK for lack of efficacy(Table); aACR30 but not
aACR50 response rates were slightly higher in ANK-naïve vs those who
discontinued ANK for lack of efficacy. In the TCZ-exposed pts, aACR 30 response
rates were comparable at Day 29 in TCZ naïve pts vs those who discontinued TCZ
for lack of efficacy. At month 12, aACR 50 response rates were higher in pts who
discontinued TCZ due to lack of efficacy vs TCZ naïve pts.
Conclusion:
There is a comparable
initial and 12 month aACR-JIA response to CAN among SJIA patients who switched
from ANK or TCZ due to lack of efficacy compared to those without previous use.
These results support the consistent efficacy of CAN across different patient
subtypes and demonstrate efficacy in prior biologic non-responders.
References:
1.
Ruperto N, et al. N Engl J Med 2012;367(25):2396–406.
2.
Ruperto et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(2):608
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Brunner HI, Ruperto N, Quartier P, Constantin T, Berkun Y, Calvo-Penedes I, Erguven M, Goffin L, Hofer M, Kallinich T, Oliveira S, Uziel Y, Viola S, Nistala K, Wouters C, Leon K, Speziale A, Lheritier K, Junge G, Lovell D, Martini A. Efficacy of Canakinumab in Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Patients Previously Exposed to Biologics [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-canakinumab-in-systemic-juvenile-idiopathic-arthritis-patients-previously-exposed-to-biologics/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-canakinumab-in-systemic-juvenile-idiopathic-arthritis-patients-previously-exposed-to-biologics/