Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 9:15AM-9:30AM
Background/Purpose: Both efficacy and safety data regarding COVID vaccines in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) are lacking. We conducted the international Vaccination Against COvid in systemic LUPus study (VACOLUP) to evaluate the efficacy and tolerance of the vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) in SLE. Our main objective was to describe the tolerance of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in SLE patients, and to assess the risk of post-vaccination flare.
Methods: VACOLUP was designed as a cross-sectional study which consisted of 43 web-based questions. The study took place from March 22, 2021 to May 17, 2021. Main study outcomes included: demographical characteristics; history of COVID-19; history of vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 and tolerance. Self-reported side-effects, medically-confirmed lupus flare or COVID-19 after vaccination were analyzed.
Results: The study included 696 participants (669 [96.1%] women and 27 [3.9%] men), with a median age of 42 years [IQR: 34-51]), from 29 countries. Side-effects were reported by 316 patients (45.4%) after the first dose of COVID-19 vaccine and 181 (52.8%) of those who received a second dose of vaccine. There was no difference in the occurrence of side effects according to gender (p=0.11), age (p=0.08) or by mechanism of action (mRNA vaccines versus others, p=0.69). The type and intensity of side effects are shown in figure 1, being minor or moderate in intensity (i.e., with no consequence on the ability to perform daily tasks) in more than 80% of cases. Taking into account all vaccine doses together (n=1039), side effects required a medical consultation in 81 cases (7.8%), an emergency consultation in 14 cases (1.3%) and an hospitalization in 5 cases (0.5%), including 4 for the occurrence of a SLE flare. A total of 21 patients (3.0%) reported a medically-confirmed lupus flare, typically with predominant musculoskeletal symptoms (90.5%) and fatigue (85.7%). Of note these symptoms were reported to occur after a median delay of 3 days (IQR: 0-29) following COVID-19 vaccination. This led to a change in lupus treatment in 15/21 cases.
Conclusion: Side effects are common but minor or moderate in 80% of the cases. Only 21 (3.0%) self-reported a medically confirmed SLE flare. These flares were mainly represented by musculoskeletal symptoms (90.5%) and fatigue (85.7%) and occurred early after COVID-19 vaccination, suggesting it might be difficult to distinguish between lupus flares and common side-effects of vaccination in SLE patients. Disseminating these reassuring data should therefore help clinicians to increase vaccine coverage in SLE patients.
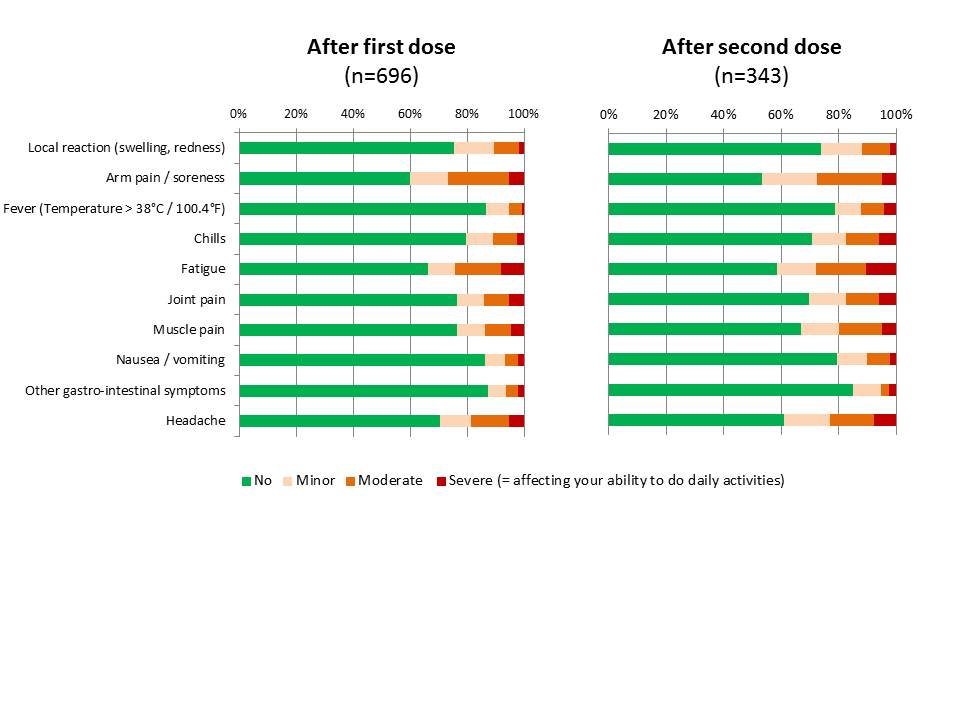 Figure 1. Type and intensity of side effects after COVID_19 vaccination Cumulative plot showing the proportion of minor, moderate and severe reaction for each adverse event (as self-reported by patients, with severe manifestations defined as affecting the ability to do daily activity)
Figure 1. Type and intensity of side effects after COVID_19 vaccination Cumulative plot showing the proportion of minor, moderate and severe reaction for each adverse event (as self-reported by patients, with severe manifestations defined as affecting the ability to do daily activity)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Felten R, KAWKA L, DUBOIS M, Ugarte-Gil M, Fuentes-Silva Y, PIGA M, Arnaud L. Efficacy and Tolerance of Vaccination Against COVID-19 in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: The International VACOLUP Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-tolerance-of-vaccination-against-covid-19-in-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-the-international-vacolup-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-tolerance-of-vaccination-against-covid-19-in-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-the-international-vacolup-study/
