Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: Plenary I
Session Type: Plenary Session
Session Time: 9:15AM-10:45AM
Background/Purpose: The objective was to assess the efficacy and safety of UPA vs placebo (PBO), in combination with a GC taper regimen, in patients with GCA.
Methods: SELECT-GCA is a double-blind, randomized PBO-controlled phase 3 trial conducted in 24 countries, consisting of two 52-week periods. Results from the first 52-week period (primary analysis) are reported here, in which patients received either UPA 7.5 mg or 15 mg (UPA7.5 or UPA15) once daily in combination with a 26-week GC taper regimen or PBO with a 52-week GC taper regimen. Eligible patients were aged ≥50 yrs, diagnosed with new-onset or relapsing GCA, and had received prior GCA treatment with ≥40 mg prednisone or equivalent daily before baseline (BL) and were taking prednisone ≥20 mg daily at BL. The primary endpoint was sustained remission, defined as the absence of signs or symptoms of GCA from week 12 through week 52 and adherence to the protocol-defined GC taper regimen. Secondary endpoints included sustained complete remission (defined as achievement of sustained remission with normalization of ESR and CRP), disease flare-related endpoints, several patient-reported outcomes including FACIT-Fatigue, and cumulative GC exposure. Exposure-adjusted treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were documented through 52 weeks.
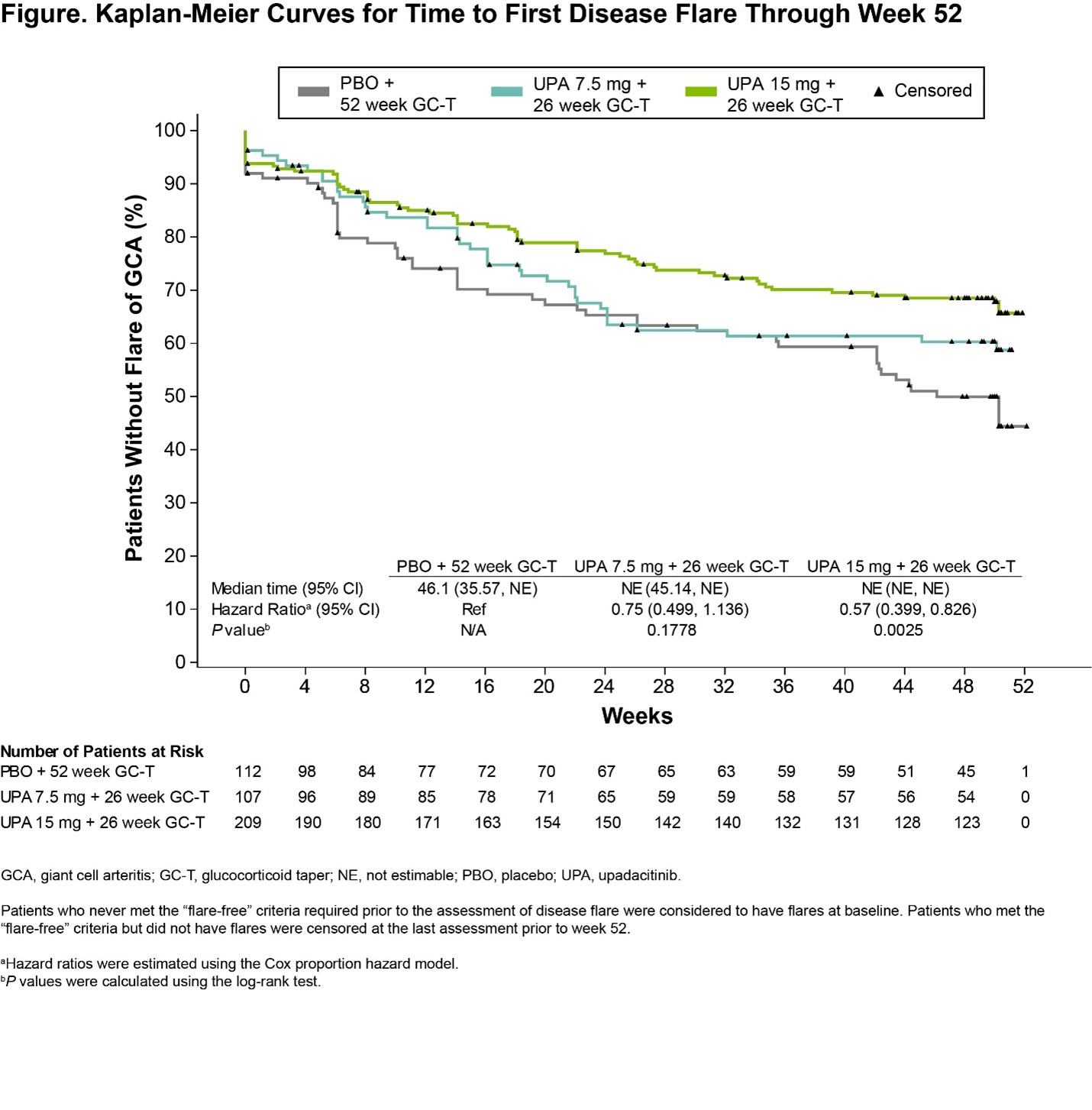
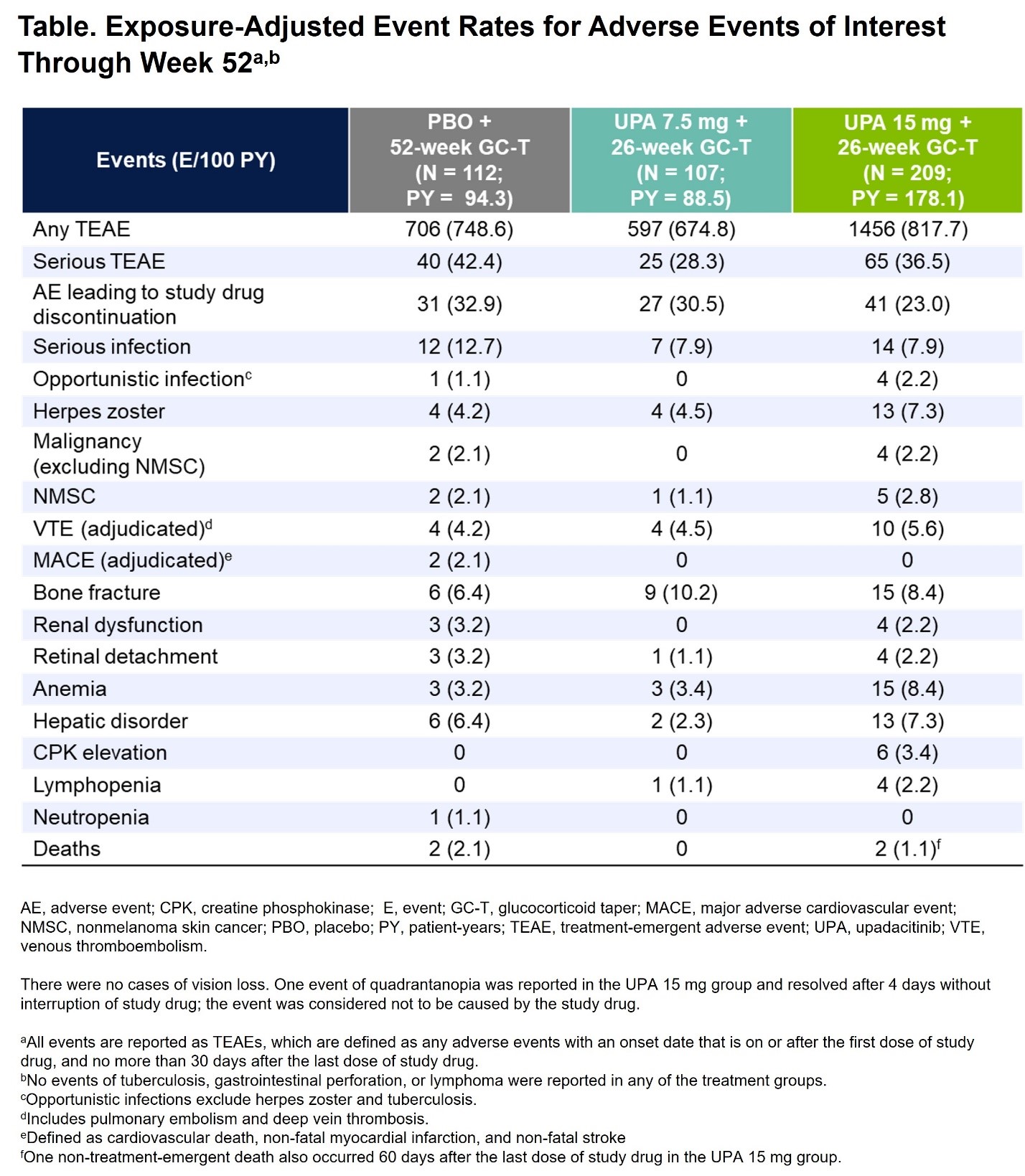
Results: A total of 428 patients were randomized and treated (PBO, N=112; UPA7.5, N=107; UPA15, N=209). BL characteristics were balanced across treatment groups, with 70% and 30% of patients having new-onset and relapsing GCA, respectively. The primary endpoint of sustained remission at week 52 was achieved with UPA15 vs PBO (46% vs 29%, P=.0019). Additionally, the study met 9 out of 11 multiplicity-controlled secondary endpoints with UPA15 including achievement of sustained complete remission from week 12 through week 52 (37% vs 16%, P< .0001). UPA15 resulted in a decreased risk for flare through 52 weeks relative to those receiving PBO (Figure). Additionally, UPA15 led to significantly greater improvements in FACIT-Fatigue scores from BL to week 52 (least-squares mean change: UPA15, 1.7; PBO, -2.4; P=.0036). Cumulative GC exposure over 52 weeks was significantly lower with UPA15 vs PBO (median exposure of 1615mg vs 2882mg, P< .0001). Across most endpoints, UPA7.5 showed numerically better efficacy compared to PBO but did not reach statistical significance. Safety outcomes over 52 weeks were generally similar among the UPA groups and PBO (Table), with numerically higher rates of serious infections and MACE observed in the PBO group and no MACE reported in the UPA groups. Rates of herpes zoster, lymphopenia, anemia, and nonmelanoma skin cancer (NMSC) were numerically higher with UPA15 than PBO. Rates of VTE were comparable across treatment groups. Rates of serious TEAEs and malignancy, excluding NMSC, were similar between UPA15 and PBO. Four treatment-emergent deaths were reported.
Conclusion: UPA15 combined with a 26-week GC taper demonstrated superior efficacy and reduced GC use compared to PBO with a 52-week GC taper. No new safety signals were identified with UPA as compared to its known safety profile.1 UPA15 provided a favorable benefit-risk profile and represents a potential new oral targeted therapy for patients with GCA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Merkel P, Penn S, Setty A, Schmidt W, Rubbert-Roth A, Hauge E, Keen H, Ishii T, Khalidi N, Meng L, zhao w, Lagunes I, Romero A, Wung P, blockmans d. Efficacy and Safety of Upadacitinib in Patients with Giant Cell Arteritis (SELECT-GCA): A Double-Blind, Randomized Controlled Phase 3 Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-upadacitinib-in-patients-with-giant-cell-arteritis-select-gca-a-double-blind-randomized-controlled-phase-3-trial/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-upadacitinib-in-patients-with-giant-cell-arteritis-select-gca-a-double-blind-randomized-controlled-phase-3-trial/