Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Patients (pts) with RA generally receive conventional synthetic DMARDS (csDMARDs) as first-line therapy, and inadequate responders (IR) to csDMARDs generally receive biological DMARDs (bDMARDs). We evaluated the efficacy and safety of tofacitinib in 3 RA pt populations (popns) who had incomplete response or were intolerant to prior lines of therapy (both referred to as IR).
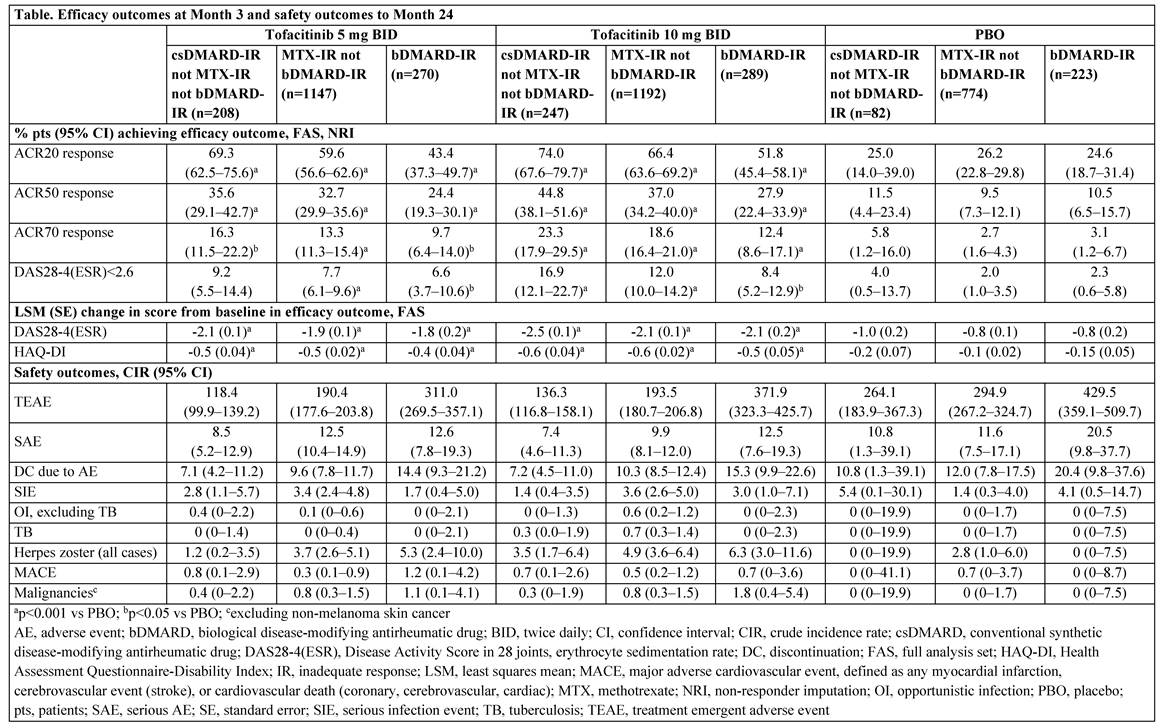
Methods: Data from pts who were 1) non-MTX csDMARD-IR but not bDMARD-IR; 2) MTX-IR but not bDMARD-IR; and 3) bDMARD-IR (referred to as non-MTX csDMARD-IR, MTX-IR, and bDMARD-IR) were pooled from 8 Phase 2 and 6 Phase 3 trials evaluating the efficacy and safety of tofacitinib 5 or 10 mg BID vs placebo (PBO) in RA. Pts may have received >1 prior csDMARD, and in ~60% of the studies tofacitinib was given in combination with a csDMARD, commonly MTX. Month (M)3 efficacy outcomes included % of pts achieving ACR20/50/70 responses or Disease Activity Score in 28 joints, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (DAS28-4[ESR])<2.6 (remission), and change from baseline (BL) in DAS28-4(ESR) or HAQ-DI scores. No multiplicity adjustments were made. Crude incidence rates (CIR; unique pts with events/100 pt-yrs) based on adverse events (AEs) through M24 were calculated as safety outcomes.
Results: The non-MTX csDMARD-IR, MTX-IR, and bDMARD-IR popns comprised a total of 537, 3113, and 782 pts, respectively (Table; the non-MTX csDMARD-IR and bDMARD-IR popns were substantially smaller). Prior csDMARDs received by the total non-MTX csDMARD-IR, MTX-IR, and bDMARD-IR popns were chloroquine (17.7%, 13.8%, 4.1%), hydroxychloroquine (37.2%, 21.2%, 19.8%), leflunomide (19.4%, 20.5%, 24.2%), MTX (7.3% [not IR to MTX], 100%, 95.5%), sulfasalazine (31.1%, 26.8%, 18.0%), and others (8.0%, 10.7%, 10.4%), respectively. BL characteristics were similar between non-MTX csDMARD-IR, MTX-IR, and bDMARD-IR popns except for mean RA duration (5.2–7.2, 8.1–8.6, and 11.6–12.2 yrs, respectively). Most pts were female (80.3–85.4%), mean age range was 49.7–54.6 yrs, and mean DAS28-4(ESR) score ranged from 6.2–6.5. Significantly higher ACR response rates and greater changes from BL in DAS28-4(ESR) and HAQ-DI scores at M3 were recorded with tofacitinib 5 and 10 mg BID in all popns vs PBO (Table). A trend was observed for numerically higher proportions of non-MTX csDMARD-IR pts achieving efficacy outcomes vs MTX-IR and bDMARD-IR popns. CIRs for TEAEs, SAEs, and DC due to AEs were numerically lower in the non-MTX csDMARD-IR popn vs the MTX-IR popn and both popns had lower CIRs vs the bDMARD-IR popn. For numerical differences, 95%CIs generally overlap. AEs of special interest are reported (Table).
Conclusion: Tofacitinib is associated with improved efficacy and most safety outcomes vs PBO in each of the non-MTX csDMARD-IR, MTX-IR, and bDMARD-IR popns, and may be more efficacious when used in earlier lines of therapy.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tesser J, Gül A, Olech E, Oelke K, Lukic T, Murray CW, Zang C, Takiya L. Efficacy and Safety of Tofacitinib in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Inadequate Response or Intolerance to Prior Therapies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-tofacitinib-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-inadequate-response-or-intolerance-to-prior-therapies/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-tofacitinib-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-inadequate-response-or-intolerance-to-prior-therapies/