Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment II: Emerging Therapies (2023–2027)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 11:00AM-11:50AM
Background/Purpose: Tildrakizumab (TIL), a high-affinity anti–interleukin-23p19 monoclonal antibody, is approved to treat moderate to severe plaque psoriasis.1 The efficacy and safety of TIL up to week (W)52 in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) was evaluated in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multiple-dose, phase 2b study (NCT02980692).
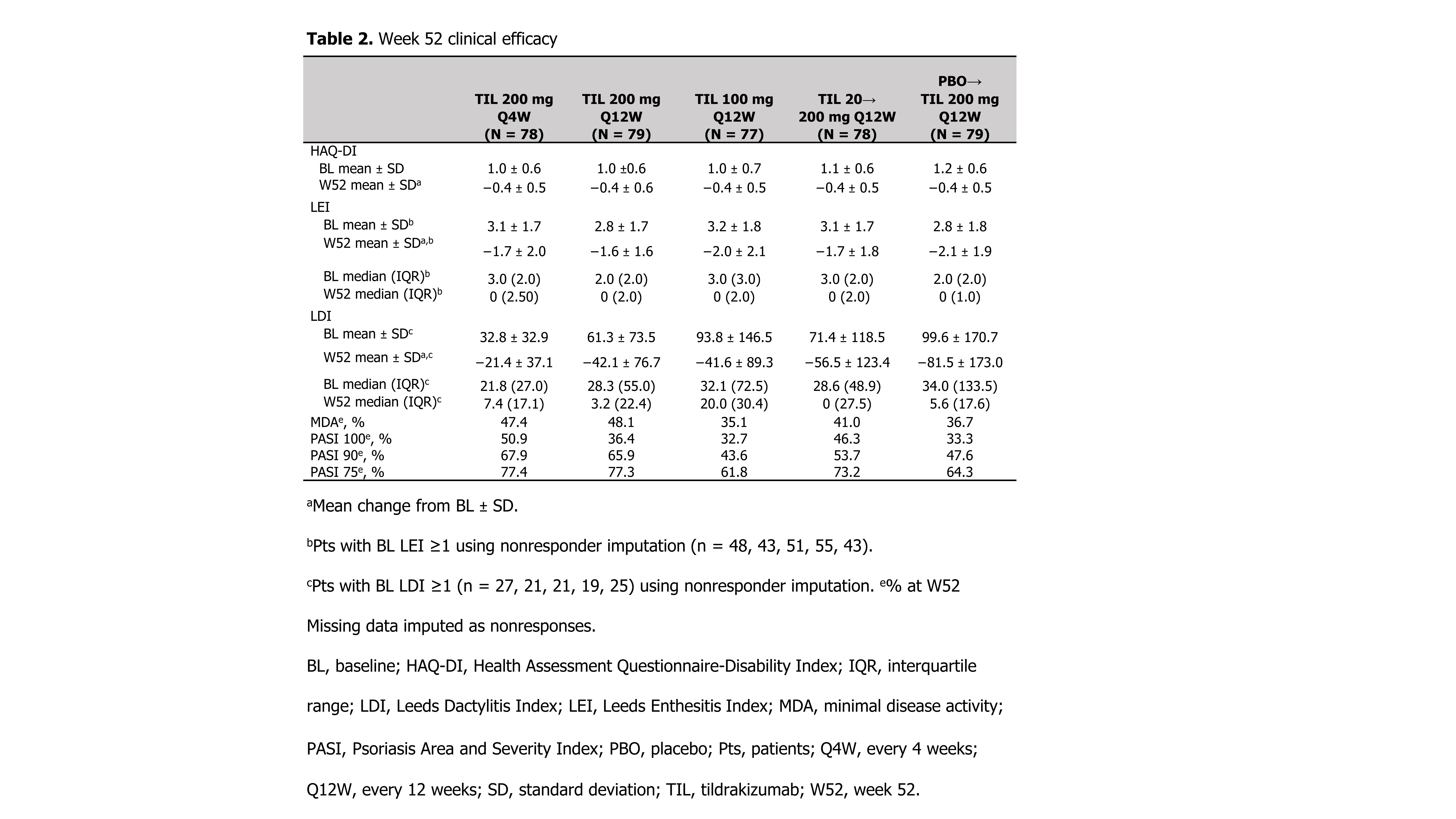
Methods: Patients (pts) ≥18 years with active PsA2 were randomized 1:1:1:1:1 to TIL 200 mg every 4 weeks (Q4W) to W52, TIL 200 mg Q12W to W52, TIL 100 mg Q12W to W52, TIL 20 mg Q12W until W24 then TIL 200 mg Q12W to W52, or placebo Q4W until W24 then TIL 200 mg Q12W to W52. Efficacy assessments included ACR20/50/70, 75%/90%/100% improvement in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index, proportion of pts with residual minimal disease activity response; and mean change from baseline (BL) in HAQ-Disability Index, Leeds Dactylitis Index (LDI, pts with BL LDI ≥1), and Leeds Enthesitis Index (LEI, pts with BL LEI ≥1) to W52. Treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were recorded.
Results: Of 500 pts screened, 391 were randomized and received ≥1 dose of drug. Demographics and baseline disease characteristics were generally consistent across treatment arms (Table 1). Proportions of ACR20/50/70 responders were superior with TIL vs PBO through W24; after W24 rates of responses further increased for TIL 20→200 mg Q12W and PBO→200 mg Q12W through W52 (Figure). Other efficacy results are shown in Table 2. Overall, 252 (64.5%) patients had a TEAE, the most common being nasopharyngitis (8.4%) and upper respiratory tract infection (6.4%). Most TEAEs, including infections, were mild. One (0.3%) malignancy (intraductal proliferative breast lesion) occurred in the TIL 20→200 mg Q12W arm. Serious TEAEs were observed in 13 (3.3%) patients. One serious infection (chronic tonsillitis) was reported in the TIL 20 mg Q12W arm during the first 24 weeks. One case each of pyelonephritis and urinary tract infection were reported as TEAEs of special interest (both in the same patient in the TIL 100 mg Q12W arm). No deaths or major adverse cardiac events occurred.
Conclusion: TIL was well tolerated and improved musculoskeletal and skin manifestations of PsA through W52.
References
- Reich, et al. Lancet 2017;390:276−88.
- Taylor, et al. Arthritis Rheum 2006;54:2665–73.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mease P, Chohan S, García Fructuoso F, Gottlieb A, Luggen M, Rahman P, Raychaudhuri S, Chou R, Mendelsohn A, Rozzo S, Orbai A. Efficacy and Safety of Tildrakizumab, a High-Affinity Anti–Interleukin-23p19 Monoclonal Antibody, in Patients with Active Psoriatic Arthritis in a Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Multiple-Dose, Phase 2b Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-tildrakizumab-a-high-affinity-anti-interleukin-23p19-monoclonal-antibody-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-in-a-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-tildrakizumab-a-high-affinity-anti-interleukin-23p19-monoclonal-antibody-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-in-a-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled/