Session Information
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-4:00PM
Background/Purpose: Peficitinib (ASP015K), a novel oral JAK inhibitor, demonstrated efficacy as once-daily monotherapy in patients with moderate to severe RA in a phase 2b study (NCT01649999). In this phase 3 study (NCT02308163), we report efficacy and safety data for peficitinib alone or in combination with DMARDs in patients with RA who had an inadequate response to DMARDs.
Methods: This multicenter, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo (PBO)-controlled study was conducted in Japan, Korea, and Taiwan. All patients had RA diagnosed according to 1987 ACR or 2010 ACR/EULAR criteria. Patients with active RA (defined as ≥6 tender and painful joints and ≥6 swollen joints, using 68 and 66-joint assessment respectively, and CRP >0.50 mg/dL) and inadequate response to DMARDs (administered for ≥90 days) were randomized in a 1:1:1:2 ratio to 52 weeks’ treatment with PBO, peficitinib 100 mg/day, peficitinib 150 mg/day or etanercept 50 mg/week (open-label reference arm). At week 12, patients initially assigned to PBO were switched (under blinded conditions) to either peficitinib 100 mg/day or peficitinib 150 mg/day until end of treatment. Concomitant stable dose of DMARDs was permitted. The primary efficacy variable was ACR20 response rate at week 12/early termination (ET).
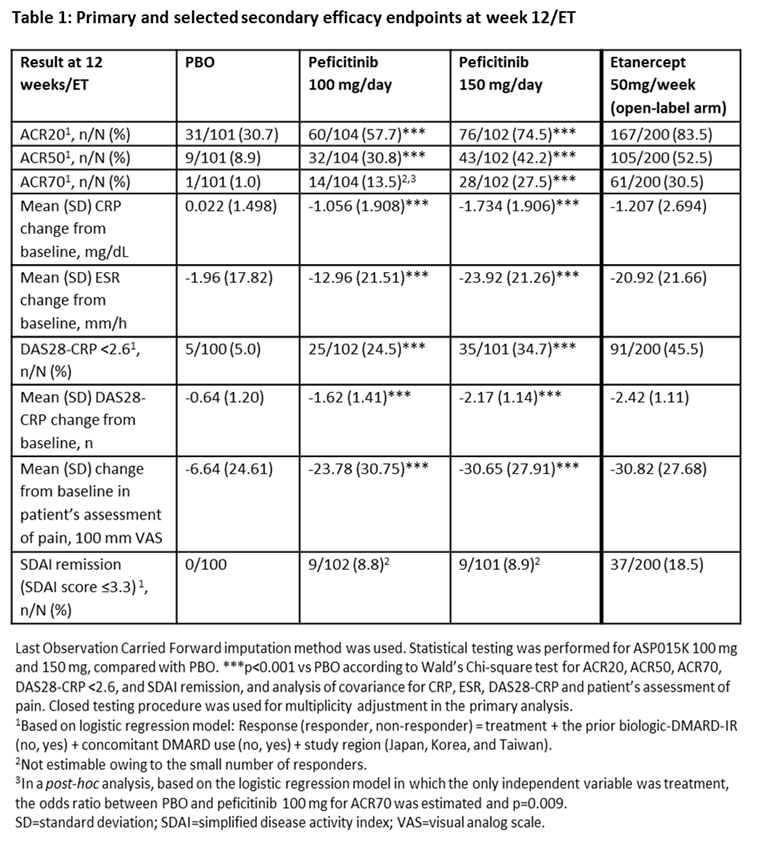
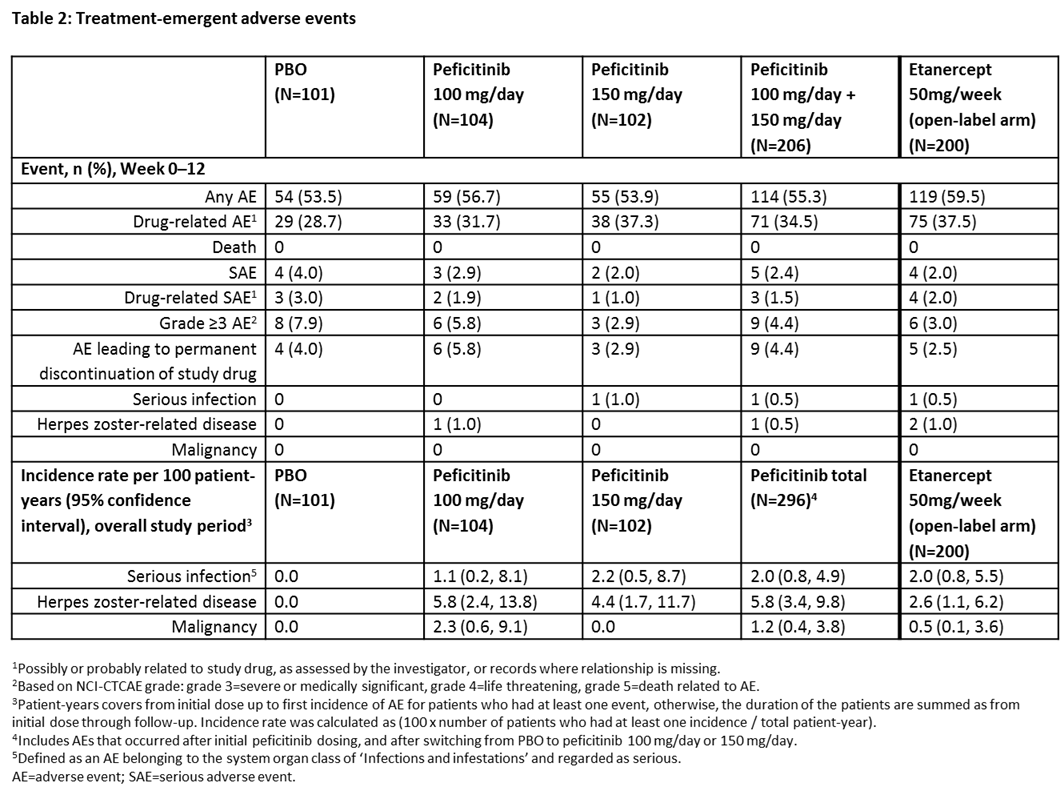
Results: In total, 507 patients were randomized and treated: PBO (n=101), peficitinib 100 mg/day (n=104), peficitinib 150 mg/day (n=102) and etanercept (n=200). Regarding efficacy at week 12/ET, significant differences were observed with peficitinib 100 mg/150 mg vs PBO (p<0.001) in the proportion of patients achieving ACR20, ACR50, ACR70 (150 mg/day dose only) and DAS28-CRP <2.6, and for change from baseline to week 12/ET in DAS28-CRP (Table 1). Week 0–12 safety results were similar between treatment groups, while serious adverse events were more common with PBO than other study treatments (Table 2). For the overall study period, the incidence rate of serious infections per 100 patient-years was higher with peficitinib 100 mg/150 mg than PBO (Table 2). There were no deaths during the study.
Conclusion: In patients with RA who had an inadequate response to DMARDs, 100 mg/day and 150 mg/day peficitinib doses significantly reduced RA symptoms according to clinical and patient assessment scores. The proportion of patients achieving the primary efficacy variable (ACR20 at week 12/ET) was significantly greater for both peficitinib doses versus PBO. Peficitinib 100 mg/day and 150 mg/day showed acceptable safety and tolerability, with no new safety signals detected compared with other JAK inhibitors.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tanaka Y, Takeuchi T, Tanaka S, Kawakami A, Iwasaki M, Song YW, Chen YH, Rokuda M, Izutsu H, Ushijima S, Kaneko Y, Shiomi T, Yamada E. Efficacy and Safety of the Novel Oral Janus Kinase (JAK) Inhibitor, Peficitinib (ASP015K), in a Phase 3, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Randomized Study of Patients with RA Who Had an Inadequate Response to Dmards [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-the-novel-oral-janus-kinase-jak-inhibitor-peficitinib-asp015k-in-a-phase-3-double-blind-placebo-controlled-randomized-study-of-patients-with-ra-who-had-an-inadequate-re/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-the-novel-oral-janus-kinase-jak-inhibitor-peficitinib-asp015k-in-a-phase-3-double-blind-placebo-controlled-randomized-study-of-patients-with-ra-who-had-an-inadequate-re/