Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The increased risk of herpes zoster (HZ) in older adults is attributable to age-related decline in immunity. In 2 pivotal studies, ZOE-50 (NCT01165177) and ZOE-70 (NCT01165229), the adjuvanted recombinant zoster vaccine (RZV) proved to be efficacious against HZ in adults ≥50 years of age (YOA), with no identified safety concerns, irrespective of the pre-existing medical conditions at enrollment.1 This post-hoc analysis was performed to evaluate the impact of any pre-existing potential immune mediated diseases (pIMDs) on RZV efficacy (VE) against the first or only episode of HZ and on RZV safety. pIMDs included autoimmune diseases and other inflammatory and/or neurologic disorders of interest, which may or may not have an autoimmune etiology.
Methods: The ZOE-50 and ZOE-70 studies were phase 3, observer-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trials conducted in 18 countries. Adults ≥50 YOA (ZOE-50) and ≥70 YOA (ZOE-70) received 2 intramuscular doses of RZV or placebo 2 months apart. This post-hoc analysis was performed on the pooled ZOE 50/70 population to evaluate VE overall and by age strata, and safety in participants that had at least 1 pIMD at enrollment. Participants with pre-existing pIMDs were identified by querying the global medical history of the participants included in the total vaccinated cohort (TVC) with a customized MedDRA query for pIMDs.2 VE was estimated in the modified TVC, which excluded participants who did not receive the second RZV dose or who had a confirmed HZ episode within 1 month after the second dose. Safety was evaluated in the TVC, which included all participants who received at least 1 RZV dose or placebo. Here, we present serious adverse events (SAEs) and SAEs with fatal outcome reported up to 1 year post-last vaccination.
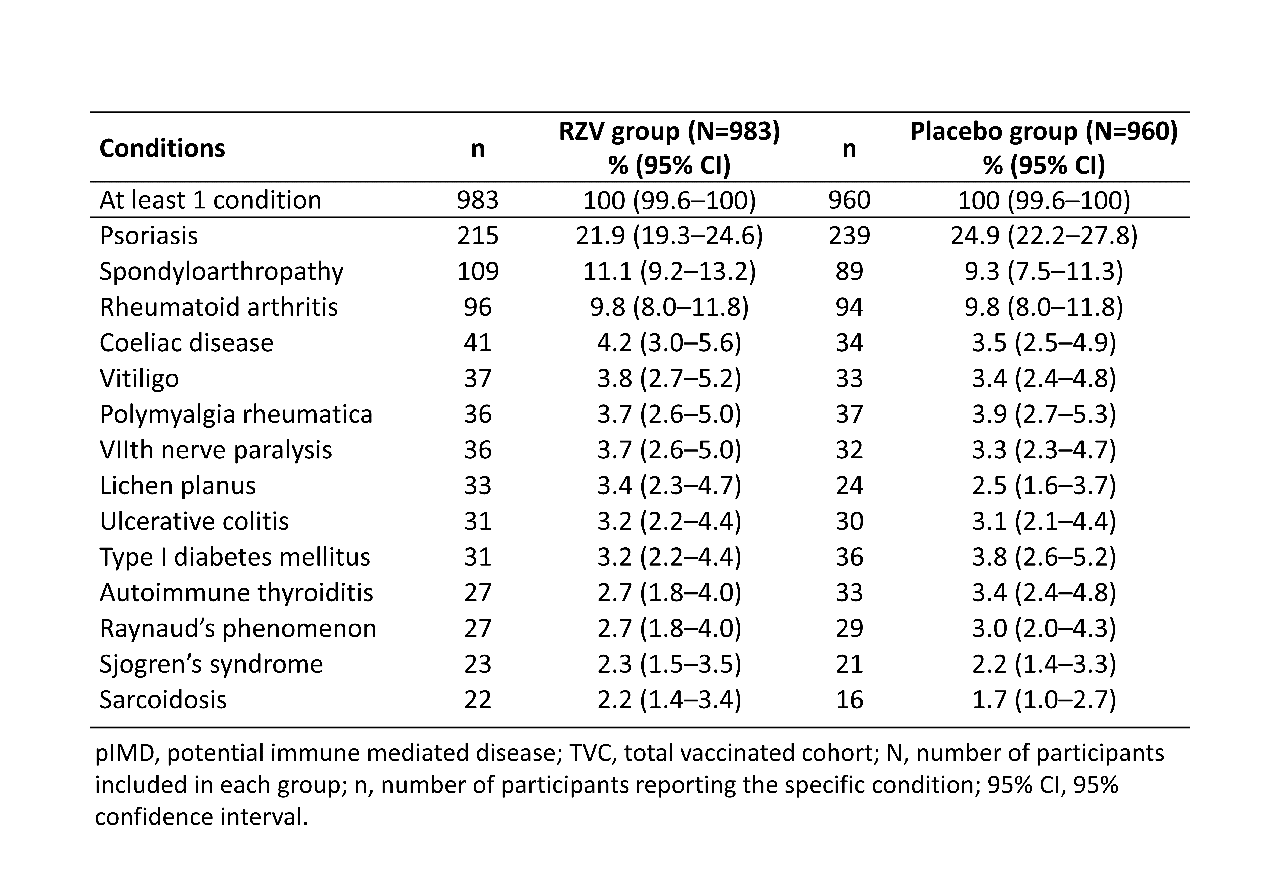
Results: The pooled TVC included 14,645 RZV and 14,660 placebo recipients. Of TVC, 983 (RZV) and 960 (placebo) participants had pre-existing pIMDs, the majority of these (59.9%, RZV; 60.8%, placebo) were females. Table 1 summarizes the most frequent pIMDs in both groups at study enrollment. VE for participants ≥50 YOA with at least 1 pIMD at enrollment was 90.5% (95% confidence intervals: 73.5–97.5%) for the modified TVC (Table 2). High VE against HZ was maintained in all age groups: 50–59 YOA (92.8%), 60–69 YOA (100%), 70–79 YOA (84.4%) and ≥80 YOA (86.2%) (Table 2). SAEs were reported by 144 (14.6%) RZV and 112 (11.7%) placebo recipients and SAEs with fatal outcome were reported for 12 (1.2%) RZV and 9 (0.9%) placebo recipients with pre-existing pIMDs at enrollment (Table 3).
Conclusion: This analysis demonstrated that RZV efficacy in adults ≥50 YOA is not impacted by the presence of pre-existing pIMDs at enrollment. There were no differences in the proportion of reported SAEs or fatal SAEs between RZV and placebo recipients with pre-existing pIMDs.
Funding: GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals SA
Medical writing/editorial support were provided by Maria Maior and Divya Kesters (Modis c/o GSK).
1López-Fauqued et al., Vaccine, 2019
2Tavares Da Silva et al., Vaccine, 2013
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Dagnew A, Rausch D, Hervé C, Zahaf T, Schuind A. Efficacy and Safety of the Adjuvanted Recombinant Zoster Vaccine in Adults with Pre-existing Potential Immune Mediated Diseases: A Pooled Post-hoc Analysis on Two Parallel Randomized Trials [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-the-adjuvanted-recombinant-zoster-vaccine-in-adults-with-pre-existing-potential-immune-mediated-diseases-a-pooled-post-hoc-analysis-on-two-parallel-randomized-trials/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-the-adjuvanted-recombinant-zoster-vaccine-in-adults-with-pre-existing-potential-immune-mediated-diseases-a-pooled-post-hoc-analysis-on-two-parallel-randomized-trials/