Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 1:00PM-2:30PM
Background/Purpose: Sonelokimab is a novel humanized Nanobody designed to inhibit IL-17A and IL-17F and penetrate clinically relevant sites of inflammation. The 24-week Phase 2 ARGO trial in patients with active PsA met its primary endpoint at Week (W) 12 with sonelokimab 120 mg and 60 mg (Q4W from W8 with induction doses at Weeks 0, 2, 4, and 6) achieving significantly higher rates of ACR50 vs. placebo (McInnes et al, EULAR 2024). Given the chronicity of PsA and the need to demonstrate robust responses over time, we now present the W24 results at conclusion of study treatment.
Methods: ARGO is a global, randomized, prospective, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (NCT05640245). Eligible patients were ≥18 years old with active PsA (SJC66 ≥3, TJC68 ≥3), and had active psoriasis or a dermatologist-confirmed diagnosis of psoriasis. Patients were randomized 1:1:1:1:1 to sonelokimab 120 mg, sonelokimab 60 mg, sonelokimab 60 mg with no induction (NI), placebo, or adalimumab 40 mg Q2W (reference arm, not powered for statistical comparison). Randomization was stratified by sex and prior biologic use. The primary endpoint was ACR50 response and key secondary endpoints were ACR20 and PASI 90 (all vs. placebo at W12). The primary analysis was NRI, ITT (PASI in patients with ≥3% BSA at baseline; 69%). Patients with SJC and TJC improvement < 20% were reassigned treatment at W12, with last observation (W12 response) carried forward at subsequent visits. Patients receiving placebo switched to sonelokimab 120 mg NI at W12.
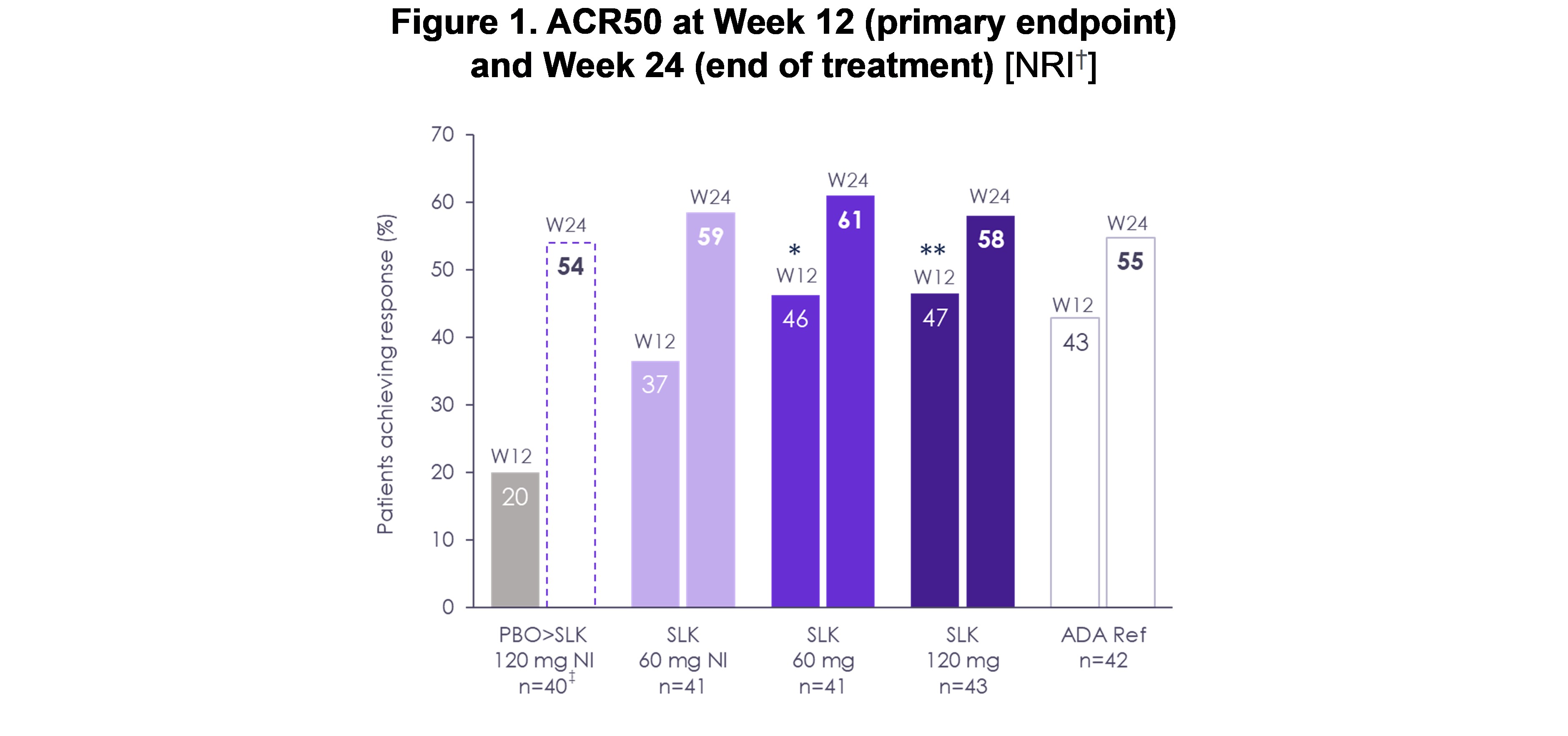
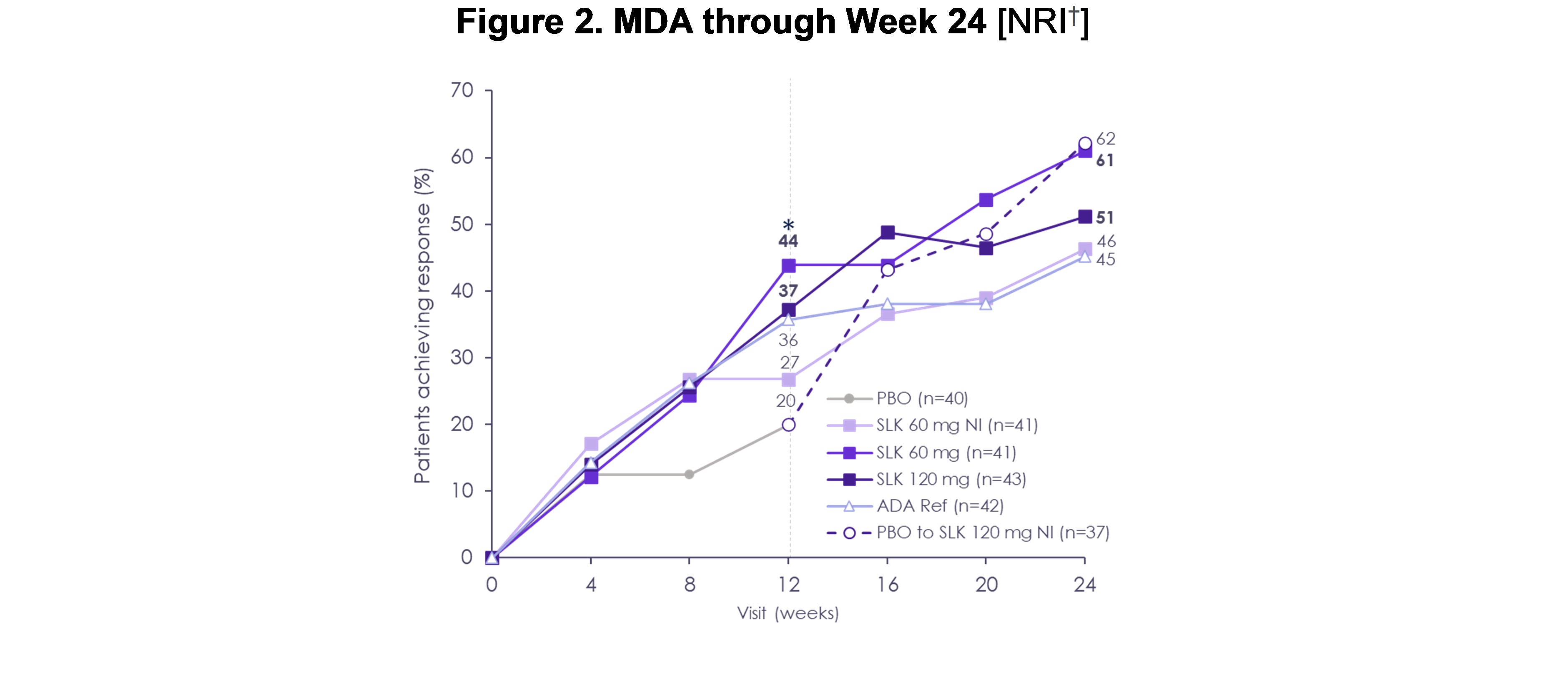
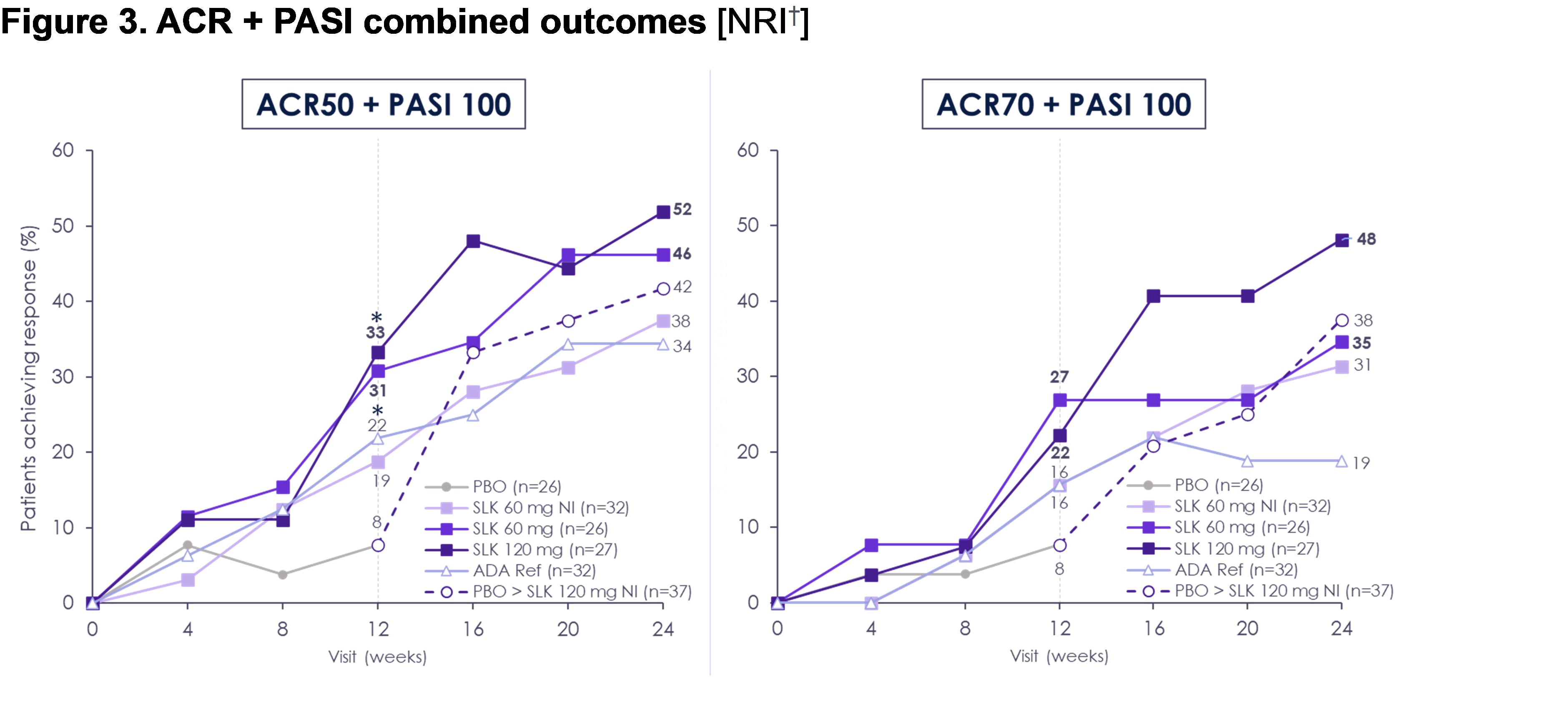
Results: ACR50 response rates improved from W12 to W24 in patients receiving sonelokimab (60 mg: W24, 61% from W12, 46%; 120 mg: W24, 58% from W12, 47%; Figure 1). By W24, ACR50 response with sonelokimab 60 mg NI was similar to other sonelokimab dose regimens (W24, 59% from W12, 37%). ACR20 and PASI 90 responses with sonelokimab were sustained or improved through W24. Positive change subsequent to W12 was noted for higher hurdle endpoints including ACR70 (60 mg: W24, 39% from W12, 29%; 120 mg: W24, 42% from W12, 26%; 60 mg NI: W24, 39% from W12, 24%) and multidomain endpoints, namely MDA (Figure 2). Similarly, the clinically relevant combined outcomes of ACR50 + PASI 100 (60 mg: 46%; 120 mg: 52%; 60 mg NI: 38%) or ACR70 + PASI 100 (60 mg: 35%; 120 mg: 48%; 60 mg NI: 31%) at W24 demonstrated simultaneous achievement of endpoints across disease domains (Figure 3). Patients switching from placebo showed levels of response after 12 weeks of sonelokimab 120 mg NI (ACR20/50/70, 73/54/43%; PASI 90, 83%; MDA, 62%) similar to or exceeding patients assigned to sonelokimab 120 mg at baseline. Finally, patient-reported outcomes, including PsAID-12, continued to improve with all sonelokimab doses through W24. Sonelokimab was well tolerated with no unexpected safety findings; there were no cases of IBD or MACE, and four (2.4%) mild or moderate cases of oral candidiasis.
Conclusion: 24-week data from the ARGO Phase 2 trial in patients with active PsA demonstrate that the high levels of multidomain clinical responses achieved at W12 with the Nanobody sonelokimab are further improved upon continued treatment. There were no unexpected safety findings. These robust data support advancement of sonelokimab to Phase 3 trials.
†LOCF was used for visits after W12 for participants who switched treatment. NRI was used for participants who continued randomized treatment at W12.
‡n number represents participants originally randomized to the PBO arm; n=37 for participants who switched treatment at W12.
ADA Ref, adalimumab reference; LOCF, last observation carried forward; NI, no induction; NRI, non-responder imputation; PBO, placebo; SLK, sonelokimab; W, Week.
†LOCF was used for visits after W12 for participants who switched treatment. NRI was used for participants who continued randomized treatment at W12.
ADA Ref, adalimumab reference; LOCF, last observation carried forward; NI, no induction; NRI, non-responder imputation; PBO, placebo; SLK, sonelokimab; W, Week.
†LOCF was used for visits after W12 for participants who switched treatment. NRI was used for participants who continued randomized treatment at W12.
ADA Ref, adalimumab reference; LOCF, last observation carried forward; NI, no induction; NRI, non-responder imputation; PBO, placebo; SLK, sonelokimab; W, week.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
McInnes I, Coates L, Mease P, Ogdie A, Kavanaugh A, Eder L, Schett G, Kivitz A, Brennan N, Godwood A, Cullen E, Reich K, Ritchlin C, Merola J. Efficacy and Safety of Sonelokimab, a Novel IL-17A- and IL-17F-Inhibiting Nanobody, in Patients with Active PsA: 24-Week Results from a Global, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase 2 Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-sonelokimab-a-novel-il-17a-and-il-17f-inhibiting-nanobody-in-patients-with-active-psa-24-week-results-from-a-global-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-phase-2-tri/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-sonelokimab-a-novel-il-17a-and-il-17f-inhibiting-nanobody-in-patients-with-active-psa-24-week-results-from-a-global-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-phase-2-tri/