Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2016
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy - Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Sarilumab is a human mAb blocking the IL-6Rα. Efficacy of sarilumab + MTX was demonstrated in patients with RA and inadequate response to MTX (MOBILITY; NCT01061736).1 Sarilumab + conventional synthetic DMARDs demonstrated efficacy in patients with RA and inadequate response or intolerance to TNF inhibitors (TARGET; NCT01709578).2 Efficacy and safety of sarilumab across prespecified subpopulations were assessed in a pooled analysis of patients from MOBILITY and TARGET.
Methods: Adult patients from MOBILITY and TARGET were included in this analysis (N=1743). Incidence of ACR20 response at week 24, change from baseline in HAQ–Disability Index (HAQ-DI) at week 12, and change from baseline in DAS28-CRP at week 24 were evaluated for placebo (n=579), sarilumab 150 mg every 2 weeks (q2w) (n=581), and sarilumab 200 mg q2w (n=583) in prespecified subpopulations. Post hoc analysis of clinical disease activity index (CDAI) at week 24 was performed. Treatment-by-subgroup interactions were assessed by a logistic regression model (ACR20: week 24) or mixed-effect model for repeated measures (HAQ-DI: week 12; DAS28-CRP, CDAI: week 24).
Results: Superiority of both sarilumab doses vs placebo was observed across all subgroups except baseline RF status, anti-CCP autoantibody status, and weight (Table; Figure). A smaller treatment effect for sarilumab 150 mg q2w was observed in RF and anti-CCP seronegative patients and those weighing ≥100 kg for ACR20 and DAS28-CRP (Table). Treatment-emergent AEs and serious AEs were more frequent with sarilumab vs placebo. Infections, neutropenia, injection site reactions, and increased transaminases were among the most common TEAEs and occurred more frequently with sarilumab. As previously reported in the individual trials, no serious infections were associated with neutrophil reductions.
Conclusion: Superiority of sarilumab vs placebo, measured by ACR20 response and changes in HAQ-DI, DAS28-CRP, and CDAI, was generally consistent across patient subgroups. The magnitude of the treatment effect was smaller, particularly for sarilumab 150 mg q2w, in patients with baseline seronegativity for RF or anti-CCP autoantibody or with baseline weight ≥100 kg, although there were few patients in these subgroups.
References: 1. Genovese et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67:1424-1437.
2. Fleischmann et al. Presented at: ACR; November 7-11, 2015; San Francisco, CA.
| Table. Incidence of ACR20 Response at Week 24, LS Mean Change From Baseline in HAQ-DI at Week 12, LS Mean Change From Baseline in DAS28-CRP at Week 24, and LS Mean Change From Baseline in CDAI at Week 24 in MOBILITY and TARGET Subgroups: Treatment-by-Subgroup Interactions | ||||
|
P value (interaction) |
||||
| Subgroup |
ACR20 at week 24a |
LS mean change from baseline in HAQ-DI at week 12b |
LS mean change from baseline in DAS28-CRP at week 24b,c |
LS mean change from baseline in CDAI at week 24b |
| Baseline demographics |
|
|
|
|
| Sex (male, female) |
0.699 |
0.190 |
0.768 |
0.348 |
| Race (white vs all other races) |
0.531 |
0.770 |
0.772 |
0.506 |
| Ethnicity (Hispanic vs non-Hispanic) |
0.300 |
0.322 |
0.907 |
0.870 |
| Region (regions 1, 2, 3)d,e |
0.297 |
0.308 |
0.308 |
0.247 |
| Age group (<65, ≥65 y) |
0.269 |
0.982 |
0.687 |
0.800 |
| Baseline weight (<60, ≥60 to <100, ≥100 kg) |
0.013 |
0.189 |
0.006 |
0.199 |
| BMI (<25, ≥25 to <30, ≥30 kg/m2) |
0.081 |
0.463 |
0.002 |
0.051 |
| Number of prior DMARDs (none, 1, ≥2) |
0.941 |
0.946 |
0.435 |
0.225 |
| Smoking history (yes, no) |
0.592 |
0.320 |
0.076 |
0.205 |
| Baseline disease characteristics |
|
|||
| Rheumatoid factor (positive, negative) |
0.006 |
0.001 |
0.011 |
0.360 |
| Anti-CCP autoantibody (positive, negative) |
0.001 |
0.010 |
0.001 |
0.0002 |
| Baseline CRP (≤15, >15 mg/L)c |
0.644 |
0.317 |
0.142 |
0.373 |
| Baseline DAS28-CRP (≤5.1, >5.1)c |
0.379 |
0.379 |
0.096 |
0.074 |
| Duration of RA (≤3, >3 to ≤10, >10 y) |
0.495 |
0.814 |
0.506 |
0.387 |
| CDAI, clinical disease activity index; HAQ-DI, HAQ–Disability Index; LS, least squares; MMRM, mixed-effect model for repeated measures. aLogistic regression model with terms of treatment, region, subgroup, treatment-by-subgroup, and study indicator. bMMRM assuming an unstructured covariance structure with covariate baseline and terms of treatment, region, subgroup, treatment-by-subgroup, visit, treatment-by-visit, treatment-by-visit-by-subgroup, study indicator, and study indicator-by-visit. cCRP was measured via high-sensitivity assay. dRegion 1: Austria, Australia, Belgium, Canada, Czech Republic, Finland, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Israel, Italy, New Zealand, Norway, Portugal, Spain, Switzerland, USA. Region 2: Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Guatemala, Mexico, Peru. Region 3: Belarus, Estonia, Hong Kong, India, Lithuania, Malaysia, Philippines, Poland, Romania, Russia, Slovakia, South Africa, South Korea, Taiwan, Thailand, Turkey, Ukraine. eFor ACR20 at week 24, a logistic regression model with terms of treatment, region, treatment-by-region, and study indicator was used. For LS mean change from baseline in HAQ-DI at week 12 and DAS28-CRP and CDAI at week 24, MMRM model with terms of treatment, region, treatment-by-region, visit, treatment-by-visit, treatment-by-visit-by-region, study indicator, and study indicator-by-visit was used. | ||||
Figure. Odds ratio for ACR20 response for sarilumab vs placebo at week 24 by subgroup. 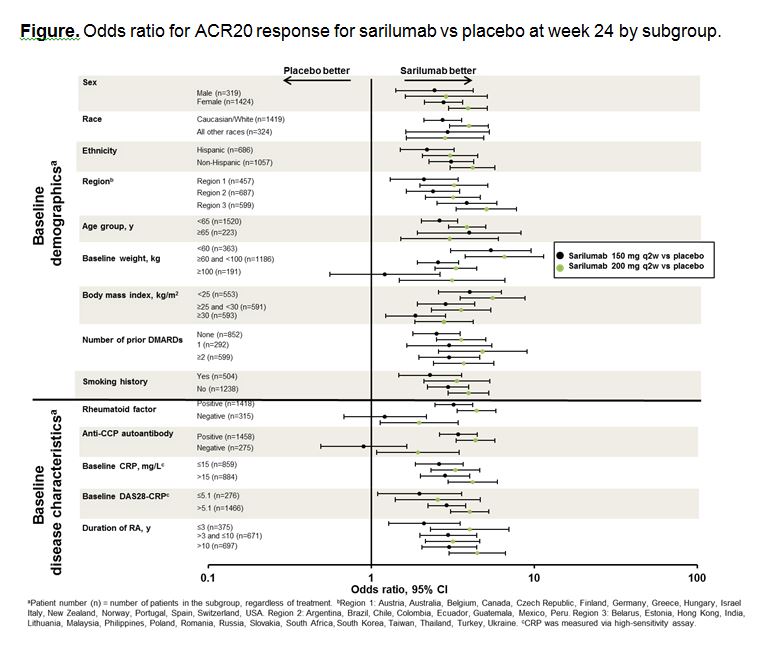
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Genovese MC, Fleischmann R, Mangan E, van Adelsberg J, Iglesias-Rodriguez M, Dukovic D, Fan C, Huizinga TW. Efficacy and Safety of Sarilumab in Subgroups of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis from 2 Phase 3 Studies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-sarilumab-in-subgroups-of-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-from-2-phase-3-studies/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-sarilumab-in-subgroups-of-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-from-2-phase-3-studies/
