Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Title: Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Giant Cell Arteritis (GCA) is a large- and medium-sized vessel vasculitis affecting patients >50 years-old. High-doses of glucocorticoids (GCs) should be initiated promptly to induce remission in active GCA. Adjunctive therapy with methotrexate (MTX) was tested in four randomized-controlled trials but only one met its primary endpoint. Our aim was to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of MTX in clinical practice, using data from a cohort of Portuguese patients with GCA.
Methods: Bicentric observational study using data from the Rheumatic Diseases Portuguese Register (Reuma.pt). We included patients with biopsy- or ultrasound-proven GCA treated with GCs with/without MTX. Clinical features of patients treated with GCs alone or GCs+MTX were compared using exact Fisher and Mann-Whitney U tests, as adequate. Association between continuous variables was assessed with Spearman’s correlation coefficient. For patients on the GCs alone group, an index date, correspondent to the median time to MTX start in the GCs+MTX group, was established for comparison of disease activity and total GCs dose at 6- and 12-months. Active disease was defined according to the presence of GCA-related symptoms and/or increased inflammatory markers. Relapse rate was defined as the number of events per patient-years (p-y) of follow-up, and relapse rates with or without exposure to MTX were compared using mid p-value test.
Results: We included 130 patients, with a median age at diagnosis of 74.9 years (IQR 11.8), 66.9% female. Sixty-six (50.8%) patients received MTX with a median time to start of 174 days (IQR 314), a median starting dose of 10 mg/week (range 5-15) and a median maximum dose of 15 mg (range 5-25). Characteristics of patients in the two treatment groups are summarized in Table 1. Inflammatory markers and proportion of patients with active disease at 6- and 12-months were not reduced in patients receiving MTX. Patients on the GCs+MTX group had a significantly higher median GC dose at index date and total GC cumulative dose, but a longer time to start MTX positively correlated with total GC cumulative dose (r=0.32, p=0.01). Relapses occurred in 28 patients, in a median of 13.5 (IQR 43.0) months from diagnosis: relapse rate in patients exposed to MTX was 2.75/100 p-y vs. 6.72/100 p-y in patients not exposed to MTX, with a rate ratio reduction of 0.41 (95%CI: 0.17-0.91). In subgroup analysis, comparing patients with or without relapses, neither demographic, baseline disease features or cumulative GC dose were different between groups. Twenty-one patients (31.8%) stopped MTX: 2 due to disease remission and 19 due to adverse events (AEs) – 10 mild, 7 moderate, and 2 severe AEs (pneumonitis and Kaposi sarcoma).
Conclusion: Treatment with MTX in GCA was associated with a reduced relapse rate during follow-up. Cumulative GC dose was higher in patients in the GCs+MTX group. In subgroup analysis, GC dose was not different in patients with or without relapses. The proportion of severe AEs was similar to previous studies. This is not a randomized study: the results may have been affected by confounding by indication, co-medication and other sources of bias. They suggest, however, that MTX provides a safe and effective contribution to prevent relapse in GCA.
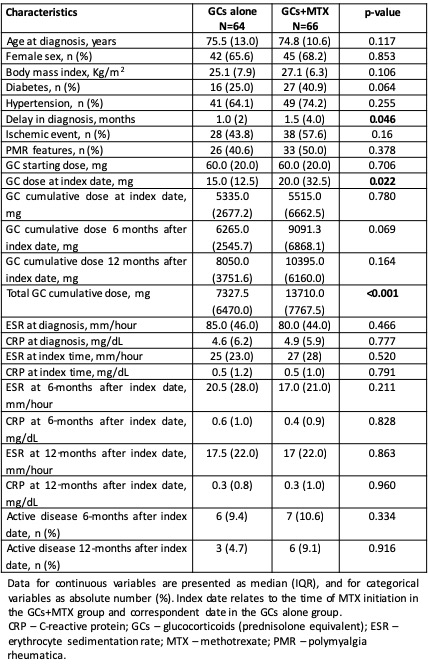 Table 1 – Characteristics of the patients with GCA treated with GCs alone compared with patients treated with GCs+MTX
Table 1 – Characteristics of the patients with GCA treated with GCs alone compared with patients treated with GCs+MTX
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Barreira S, Cruz-Machado A, Dourado E, Martinho J, Raimundo D, Brites L, Assunção H, Teixeira V, Khmelinskii N, Macieira C, da Silva J, Fonseca J, Ponte C. Efficacy and Safety of Methotrexate in Giant Cell Arteritis: Results from a Bicentric Portuguese Cohort Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-methotrexate-in-giant-cell-arteritis-results-from-a-bicentric-portuguese-cohort-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-methotrexate-in-giant-cell-arteritis-results-from-a-bicentric-portuguese-cohort-study/
