Session Information
Date: Friday, November 6, 2020
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Ixekizumab (IXE), a high-affinity monoclonal antibody selectively targeting IL-17A, was superior to adalimumab (ADA) at Week (Wk) 24 for simultaneous achievement of ACR50 and 100% improvement from baseline in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI 100); (primary endpoint) in patients (pts) with active PsA from SPIRIT-H2H. SPIRIT-H2H had 2 major secondary endpoints and achieved both: noninferiority of IXE to ADA for ACR50 and superiority of IXE to ADA for PASI 100, at Wk 24.The aim was to determine how concomitant conventional synthetic (cs) DMARD use affects safety and efficacy of IXE and ADA in prespecified subgroups defined by biologic monotherapy, concomitant MTX use, and concomitant csDMARD use through Wk 52 in SPIRIT-H2H.
Methods: SPIRIT-H2H was a 52-wk, multicenter, randomized, open-label, assessor-blinded, parallel-group study evaluating the efficacy and safety of IXE vs ADA in adults with PsA and naïve to biologic DMARDs. Pts were required to have active PsA fulfilling Classification for Psoriatic Arthritis (CASPAR) criteria and ≥3/68 tender and ≥3/66 swollen joints, ≥3% plaque psoriasis (PsO) body surface area (BSA) involvement, no prior treatment with biologic DMARDs, and with prior inadequate response to ≥1 csDMARD (but not necessarily current treatment with csDMARDs). Randomization (1:1) was stratified by concomitant use of csDMARD and the presence/absence of moderate-to-severe PsO (baseline: BSA≥10% + PASI≥12, + static Physician’s Global Assessment≥3). Pts (N=566) received IXE/ADA through 52 wks according to the labelled dose dependent on presence/absence of moderate-to-severe PsO. In this prespecified subgroup analysis by presence/absence of csDMARDs, efficacy outcomes through Wk 52 were compared between IXE and ADA using logistic regression models and Fisher’s exact tests. Missing data were imputed using non-responder imputation.
Results: At baseline, 167/283 IXE- and 169/283 ADA-treated pts had concomitant MTX use. Of these, 9.0% (15/167) and 7.1% (12/169) treated with IXE and ADA, respectively, were taking an additional csDMARD (sulfasalazine, cyclosporine, or leflunomide). A significantly greater proportion of pts on IXE vs ADA achieved the primary endpoint or PASI 100 when used as monotherapy or in combination with csDMARD (Figs. 1A and 1C). At Wk 52, the proportion of pts achieving ACR50 was not statistically different between IXE and ADA, regardless of monotherapy or concomitant csDMARD use (Fig. 1B). A significantly higher proportion of pts achieved minimal disease activity (MDA) on IXE compared to ADA in the monotherapy subgroup (49% vs 33%), while the response rates were similar in both combination subgroups (Fig. 1D). These data support consistent ACR50, PASI 100, and MDA response for IXE across all 3 subgroups. There were no significant differences in safety data across the 3 subgroups for either IXE or ADA (Fig. 2).
Conclusion: As with prior studies, consistent efficacy across multiple PsA disease-specific endpoints was observed with IXE in SPIRIT-H2H, regardless of whether IXE was taken as monotherapy or in combination with MTX or another csDMARD. Both agents were well tolerated, with no unexpected safety signals.
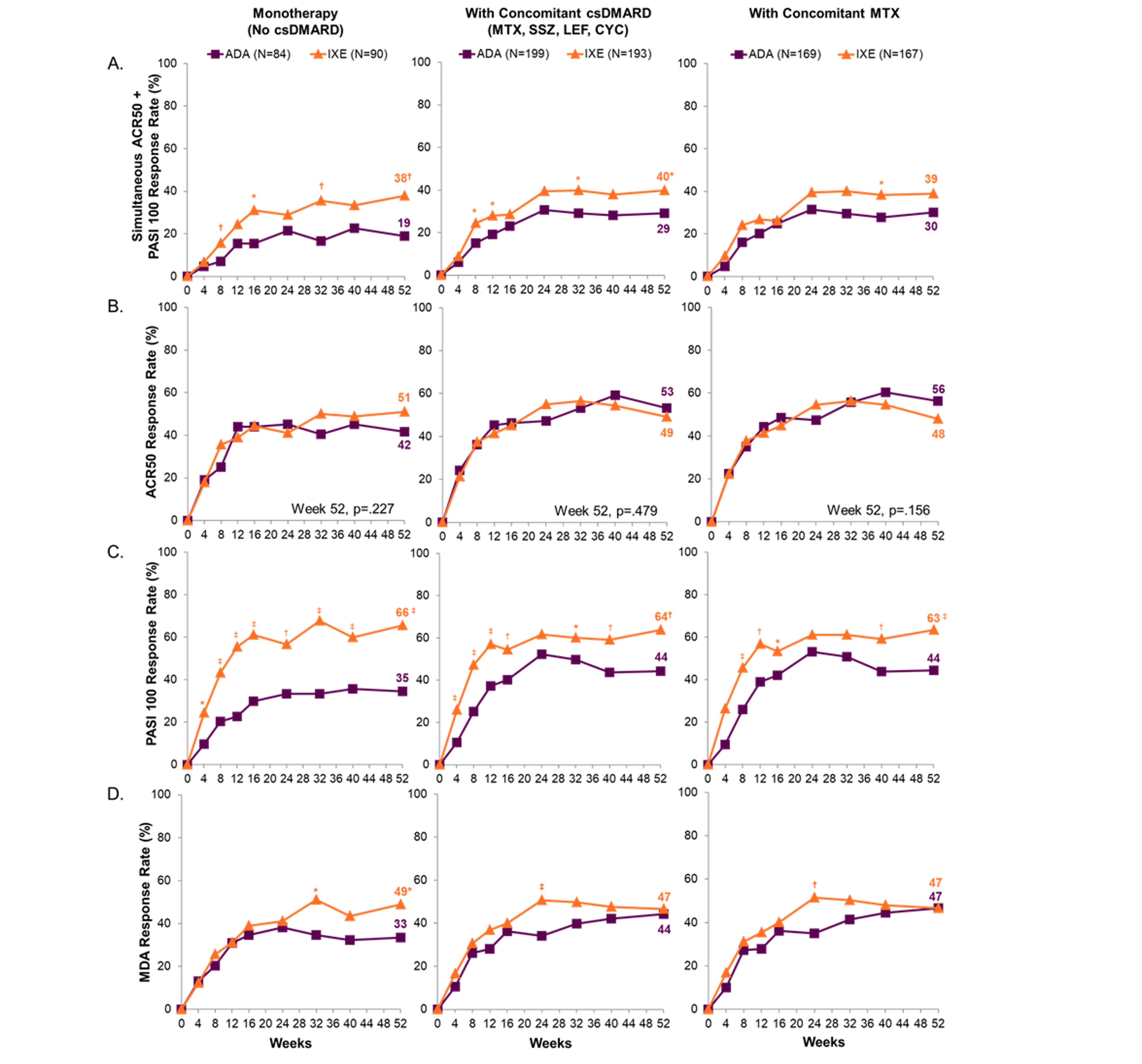 Figure 1. Proportion patients through 52 weeks with simultaneous achievement of ACR50 + PASI 100, ACR50, PASI 100, and MDA-18 Entheseal Points. Nine patients with active PsO and BSA≥3% were assessed as PASI=0 at baseline, a medical inconsistency that was resolved using medical judgement. These patients were considered PASI 100 responders if PASI=0 and BSA=0 at post baseline visit. *p≤.05 vs. ADA; †p < .01 vs. ADA; ‡p≤.001 vs. ADA. ACR=American College of Rheumatology; ADA=adalimumab; BSA=body surface area; csDMARD=conventional synthetic disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs; CYC=cyclophoshamide; Ixe=ixekizumab; LEF=leflunomide; MDA=minimal disease activity PASI=Psoriasis Area and Severity Index; PsO=psoriasis; MTX=methotrexate; SSZ=sulfasalazine.
Figure 1. Proportion patients through 52 weeks with simultaneous achievement of ACR50 + PASI 100, ACR50, PASI 100, and MDA-18 Entheseal Points. Nine patients with active PsO and BSA≥3% were assessed as PASI=0 at baseline, a medical inconsistency that was resolved using medical judgement. These patients were considered PASI 100 responders if PASI=0 and BSA=0 at post baseline visit. *p≤.05 vs. ADA; †p < .01 vs. ADA; ‡p≤.001 vs. ADA. ACR=American College of Rheumatology; ADA=adalimumab; BSA=body surface area; csDMARD=conventional synthetic disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs; CYC=cyclophoshamide; Ixe=ixekizumab; LEF=leflunomide; MDA=minimal disease activity PASI=Psoriasis Area and Severity Index; PsO=psoriasis; MTX=methotrexate; SSZ=sulfasalazine.
 Figure 2. Safety data for patients through 52 weeks. Two events of IBD were reported in the ixekizumab treatment arm but only 1 case met the adjudication criteria of confirmed inflammatory bowel disease. ADA=adalimumab; csDMARD=conventional synthetic disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs; IBD=inflammatory bowel disease; Ixe=Ixekizumab; MTX=methotrexate; TEAE=treatment emergent adverse event.
Figure 2. Safety data for patients through 52 weeks. Two events of IBD were reported in the ixekizumab treatment arm but only 1 case met the adjudication criteria of confirmed inflammatory bowel disease. ADA=adalimumab; csDMARD=conventional synthetic disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs; IBD=inflammatory bowel disease; Ixe=Ixekizumab; MTX=methotrexate; TEAE=treatment emergent adverse event.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Smolen J, Sebba A, Ruderman E, Gellett A, Sapin C, Sprabery A, Liu-Leage S, Pillai S, Reis P, Nash P. Efficacy and Safety of Ixekizumab versus Adalimumab with and Without Concomitant Conventional Synthetic Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARD) in Biologic DMARD-Naïve Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis: 52-Week Results [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-ixekizumab-versus-adalimumab-with-and-without-concomitant-conventional-synthetic-disease-modifying-antirheumatic-drugs-dmard-in-biologic-dmard-naive-patients-with-psoriatic-ar/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-ixekizumab-versus-adalimumab-with-and-without-concomitant-conventional-synthetic-disease-modifying-antirheumatic-drugs-dmard-in-biologic-dmard-naive-patients-with-psoriatic-ar/
