Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose : A period of 4 weeks (w) has been recommended for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients as the interval between tocilizumab (TCZ, 8mg/kg) infusions. However, A previous study has shown that the interval between successive TCZ infusions can be extended from 4 weeks to 6 weeks in more than 60% of patients suffering from RA who had previously shown good responses to TCZ infused at intervals of 4 weeks along with a constant low disease activity (LDA) for more than 2 years (1). Herein, we aimed to investigate the efficacy and safety of extending the interval from 4w to 6w.
Methods : The intervals between TCZ (8mg/kg) infusions were increased from 4 weeks to 6 weeks in patients responding favorably for more than 2 years. A retrospective observational study was conducted by enrolling patients in whom the intervals of TCZ infusions could be extended from 4w to 6w with an LDA for more than 2 years. We compared the efficacy and side effects of TCZ infusions at intervals of 4w and 6w in the same patients. We also examined serum levels of IL-6 and trough TCZ during the course of the study.
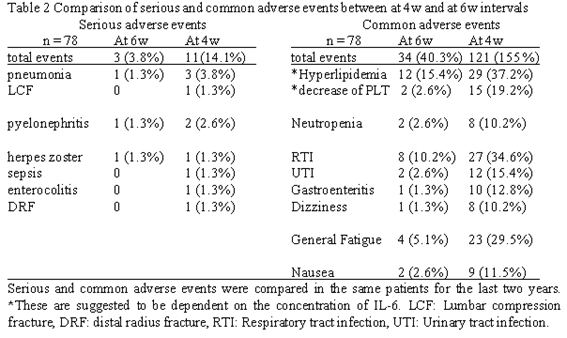
Results : A total of 125 patients were enrolled in this study, of which 78 patients showed a good response to TCZ infused at intervals of 6w. After extending the infusion intervals, the efficacy of the treatment was maintained, and the side effects decreased significantly. Parameters reflecting the disease activity such as serum CRP levels and DAS28-CRP scores were considerably low when the infusion interval was 4 weeks whereas they were slightly elevated when infusion interval was increased to 6 weeks, although within the LDA limit. During the course of the study, 11 patients who were administered TCZ at intervals of 4 weeks showed serious adverse events, whereas only 3 patients who were administered TCZ at intervals of 6 weeks showed similar adverse events. Common adverse events such as general fatigue, nausea, and dizziness were frequently observed in patients administered TCZ at intervals of 4 weeks. These common adverse events significantly decreased after the infusion interval was extended to 6 weeks. In addition, the levels of total cholesterol and triglyceride were returned to normal, and the serum trough levels of TCZ became undetectable.
Conclusion : We proved that intervals between TCZ infusions can be extended from 4w to 6w in more than 50% of RA patients along with a decrease in the side effects, thus suggesting the need to change the infusion intervals in suitable patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Uda H, Saiki O. Efficacy and Safety of Extending Tocilizumab Infusion Intervals from 4 Weeks to 6 Weeks in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-extending-tocilizumab-infusion-intervals-from-4-weeks-to-6-weeks-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-extending-tocilizumab-infusion-intervals-from-4-weeks-to-6-weeks-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/